1. Background
In complex distributed systems (especially large microservice architectures), the following pain points are commonly encountered:
-
Differentiated Logic Bloat: As business diversification develops (multi-tenant, multi-region, multi-scenario), the same interface needs to support a large number of differentiated implementations.
-
Severe Hard-Coding Coupling: Traditional
<span>if-else</span>or strategy patterns lead to logic branch explosion, bloated code, difficult maintenance, and poor scalability. -
Low Reusability of Capabilities: Common cross-cutting logic (such as logging, risk control, validation) is difficult to elegantly embed into different main business processes.
-
Missing Dynamic Routing: There is a lack of mechanisms to automatically select implementations based on runtime context (such as business scenarios, multi-tenancy, etc.).
Limitations of Traditional SPI:
-
Can only load all implementations and cannot dynamically select based on request context.
-
Does not support nested combinations and capability enhancements of implementation classes.
-
Lacks unified orchestration and lifecycle management.
The Goal of This SPI Framework: To provide a set of dynamic routing and capability combination framework based on business identity, achieving decoupling of business logic, flexible orchestration, and efficient reuse.
2. Core Capabilities
-
Business Identity Definition and Recognition:
-
Supports defining and extracting a unique identifier for the business scenario at the request entry point,
<span>Identity</span>(e.g.,<span>tenantId + region + productType + userIdType</span>). -
<span>Identity</span>is the core basis for routing decisions.
SPI Interface and Implementation Declaration:
-
Provides a standard way to define business interfaces (
<span>SpiInterface</span>). -
Implementation classes (
<span>SpiImpl</span>) are declared via annotations and associated with their supported<span>Identity</span>patterns (supporting exact matches).
Dynamic Routing Engine:
-
Core function: routes to the corresponding
<span>SpiImpl</span>instance in real-time and accurately based on the<span>Identity</span>carried by the request. -
Supports priority, default implementation, and matching rule configuration (which can be dynamically updated).
Vertical Capabilities:
-
Represents the core business logic backbone, which is the main implementation for solving specific business scenarios (
<span>SpiImpl</span>). -
Each
<span>SpiImpl</span>encapsulates a complete vertical business solution for a specific<span>Identity</span>. -
Example:
<span>PaymentService</span>interface’s<span>AlipayCnPaymentImpl</span>(Alipay domestic payment),<span>CreditCardUsPaymentImpl</span>(credit card payment in the US).
Horizontal Capabilities:
-
Product represents reusable, cross-cutting capabilities orthogonal to core business.
-
Example: Marketing campaigns, discount strategies, risk control checks, monitoring points, etc.
Flexible Orchestration of Capabilities:
-
Reusability: Horizontal capabilities are developed once and reused in multiple places.
-
Decoupling: Separates core business logic from cross-cutting logic, resulting in clearer code.
-
Flexibility: Different
<span>Identity</span>can dynamically configure different combinations of horizontal capabilities for the same<span>SpiImpl</span>. -
Maintainability: Adding/modifying cross-cutting logic only requires adjusting orchestration configuration without affecting core business code.
-
Core Innovations: The framework allows for the orchestration of a vertical capability (
<span>SpiImpl</span>) with zero or more horizontal capabilities as needed. -
Orchestration Definition: Specifies which
<span>SpiImpl</span>should automatically apply which<span>Product</span>and their execution order (priority) through JSON configuration. -
Effect: On the basis of core business logic (
<span>SpiImpl</span>), transparently overlay enhancement functions (<span>Product</span>), forming the final execution chain. -
Advantages:
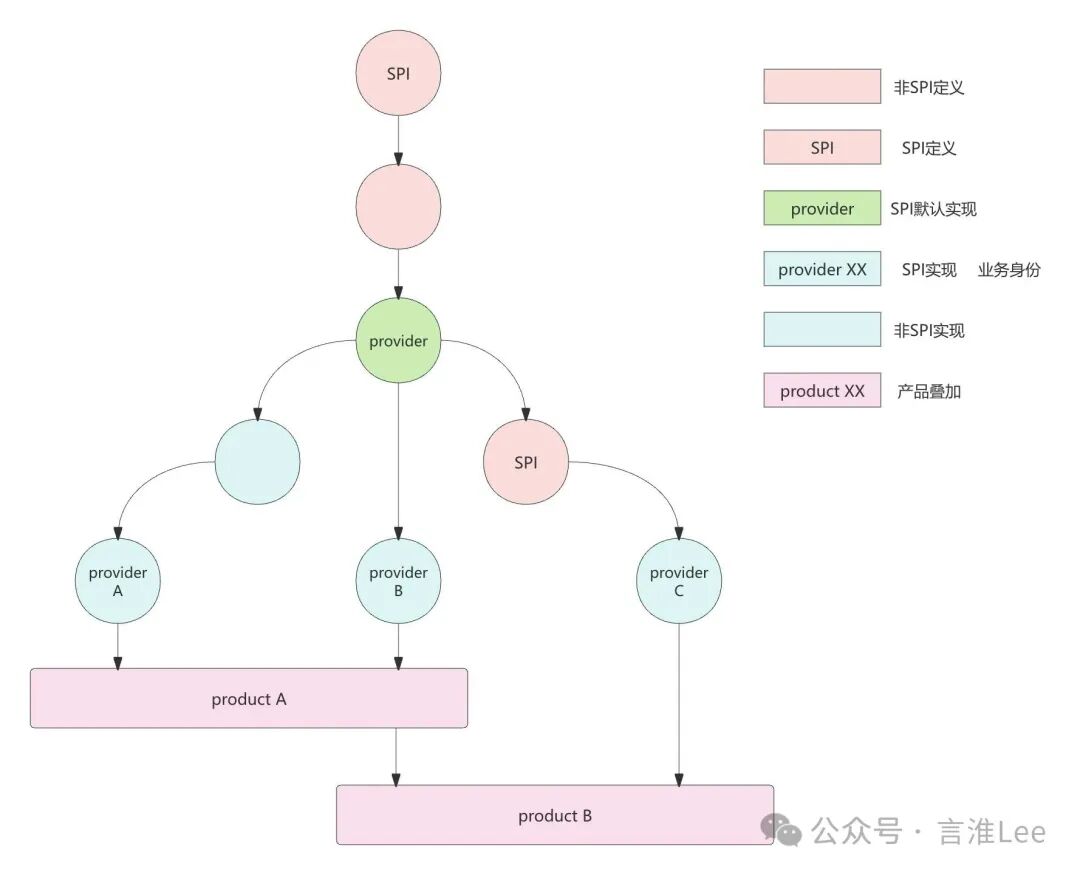
-
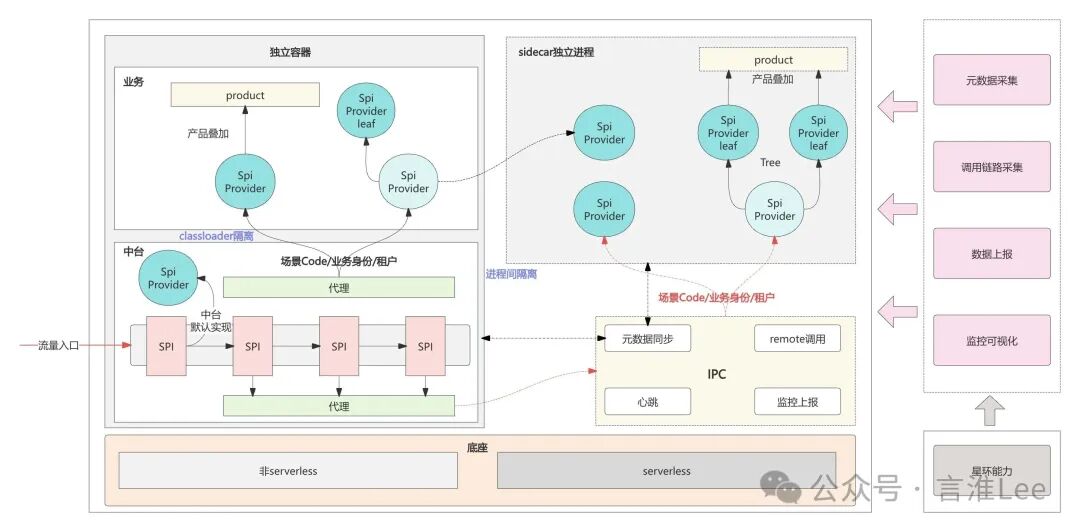
Core Modules:
-
Business Identity (
<span>Identity</span>): Context object carrying the business scenario identifier. -
SPI Registry: Manages
<span>SpiInterface</span>,<span>SpiImpl</span>and their mapping relationships with<span>Identity</span>rules. -
Routing Strategy Engine: Finds the best matching
<span>SpiImpl</span>based on<span>Identity</span>and routing strategies (exact, priority). -
Capability Repository: Registers and manages all available horizontal capability implementations.
-
Orchestration Configuration: Stores and manages the binding relationships and execution order (JSON) of
<span>SpiImpl</span>and<span>product</span>chains. -
Orchestration Execution Engine: Responsible for constructing and executing the
<span>SpiImpl</span>+<span>product</span>chain. Uses the chain of responsibility pattern. -
Context (
<span>BizSession</span>): A unified context object for passing requests, responses, and intermediate data in the execution chain. -
Key Processes:
-
Execute core
<span>SpiImpl.execute(ctx)</span>method (vertical capability). -
Execute all
<span>Product.execute(ctx)</span>methods (horizontal enhancements).
-
Request Access: The framework interceptor/entry parses the request and generates
<span>Identity</span>. -
Routing Decision: The routing engine finds the matching
<span>SpiImpl</span>based on<span>Identity</span>. -
Capability Chain Construction: The orchestration engine finds the
<span>SpiImpl</span>associated<span>product</span>chain and its order based on configuration. -
Chained Execution:
-
Result Return: The final result is returned to the caller.
4. Typical Scenarios Addressed
-
Multi-Tenant SaaS Platform:
-
<span>Identity</span>=<span>tenantId</span> -
Define
<span>BillingService</span>,<span>AuthService</span>, and other SPI interfaces. -
Implement specific
<span>SpiImpl</span>for each tenant (e.g.,<span>TenantABillingImpl</span>). -
Common capabilities such as
<span>DataIsolationProduct</span>(data isolation) are orchestrated as horizontal capabilities to the tenant’s<span>SpiImpl</span>.
-
Scenario: Different tenants (
<span>tenantId</span>) require different billing strategies, permission models, etc. -
Solution:
Global Business Adaptation:
-
<span>Identity</span>=<span>region + language + currency</span> -
Define
<span>PaymentService</span>,<span>ComplianceService</span>, and<span>NotificationService</span>SPI interfaces. -
Implement
<span>EuPaymentImpl</span>(supports SEPA/credit card),<span>UsPaymentImpl</span>(supports ACH/credit card),<span>CnPaymentImpl</span>(supports Alipay/WeChat). -
Horizontal capabilities
<span>LocalizationProduct</span>(localization translation),<span>CurrencyConvertProduct</span>(currency conversion),<span>LegalComplianceProduct</span>(compliance checks) are orchestrated to payment implementations by region.
-
Scenario: The same business must comply with different regulations, payment methods, and languages in different regions (
<span>region</span>). -
Solution:
Differentiated Marketing Strategies:
-
<span>Identity</span>=<span>userLevel + channel</span> -
Define
<span>DiscountStrategyService</span>,<span>PointsService</span>SPI interfaces. -
Implement
<span>VipDiscountStrategy</span>,<span>AppChannelPointsImpl</span>, etc. -
Horizontal capabilities
<span>AntiCheatProduct</span>(anti-cheat),<span>PromoBudgetProduct</span>(budget control),<span>RealTimeAnalysisProduct</span>(real-time effect analysis) are orchestrated to strategy implementations.
-
Scenario: Provide different discount calculations and points distribution rules for different user levels (
<span>userLevel</span>) or channels (<span>channel</span>). -
Solution:
Summary: This SPI framework effectively addresses the core pain points of differentiated logic management, public capability reuse, and flexible expansion in complex business systems through <span>business identity</span> driven <span>dynamic routing</span> and <span>vertical capabilities</span> + <span>horizontal capabilities</span> free orchestration, significantly enhancing the system’s maintainability, scalability, and development efficiency.
Github Address:https://github.com/leeco-cloud/spi.git