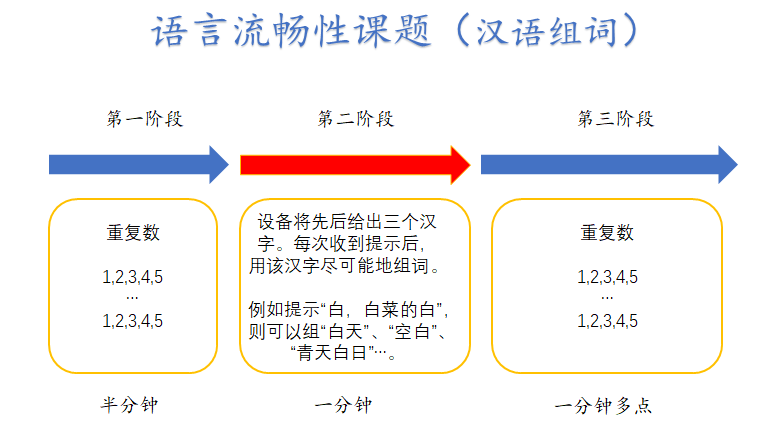
Neuroimaging tools identifying specific frontal lobe dysfunctions related to mental disorders assist doctors in improving assessment, prognosis, and treatment progress of diseases. Functional near-infrared brain imaging (fNIRS) combined with the verbal fluency test (VFT) has become a cheap and convenient way to understand mental disorders. The NirSmart, a portable near-infrared brain imaging device independently developed by Huichuang, is the world’s first and the only near-infrared brain functional imaging system approved by the NMPA medical device certification, featuring built-in VFT, Go/No-go, and other paradigms to meet basic clinical examination needs. Currently, there are still controversies regarding the specificity and uniqueness of fNIRS measurements for different diseases and the reliability of application methods. To clarify the clinical application of the fNIRS-VFT paradigm and enhance its practical application in psychiatric research, we conducted a systematic review of fNIRS studies exploring mental disorders using VFT.
Research Summary
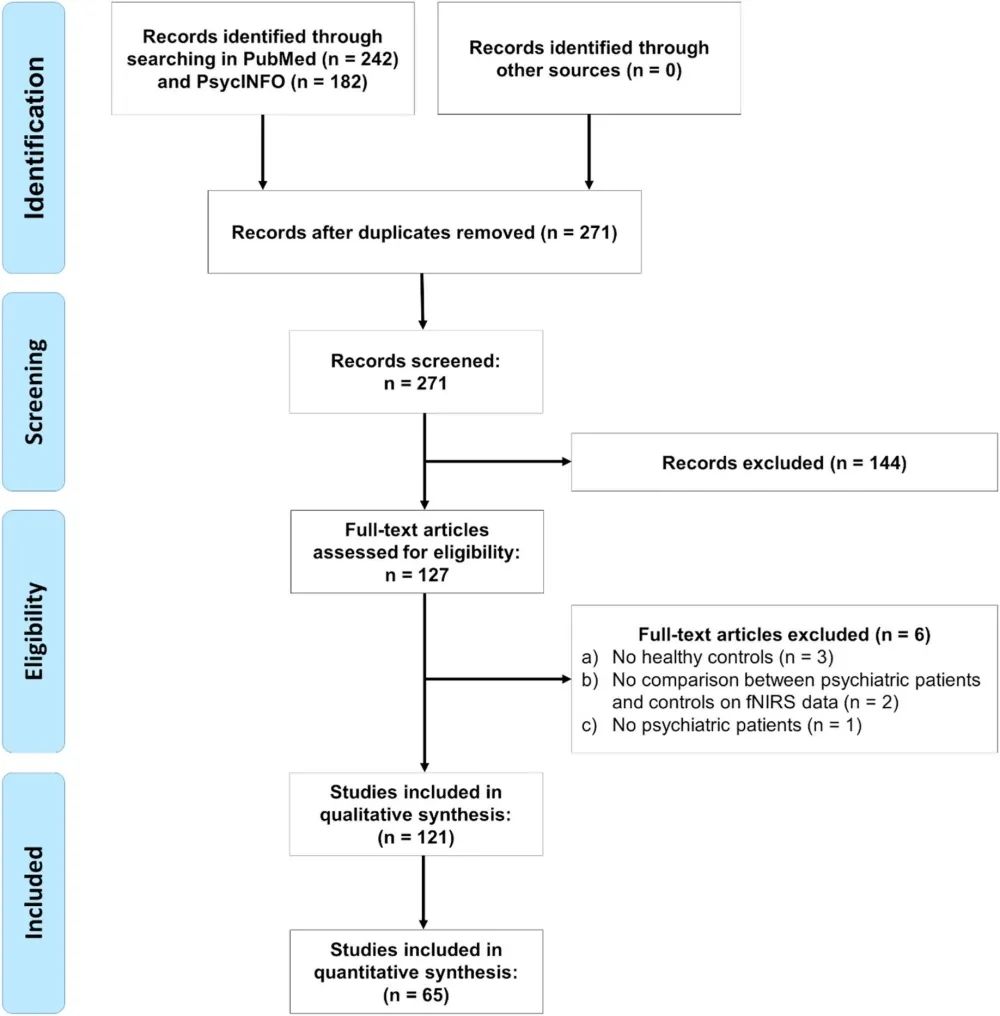
Literature searches were conducted using PubMed and PsycINFO. Overall, compared to healthy control groups, 82% and 49% of the 121 studies included reported a significant decrease in changes of oxygenated hemoglobin concentration (HbO) during VFT in patients with psychosis, resulting in a significantly reduced number of words produced. For most mental disorders, changes in HbO are more sensitive than changes in deoxygenated hemoglobin concentration and VFT performance in detecting psychopathology. Additionally, a meta-analysis based on the proportion of channels showing significant differences in HbO changes between patients and control groups and the effect size of intergroup differences consistently indicated low activation in the frontal-temporal regions for major depression and schizophrenia, but the topological distribution was disordered.
Research Conclusion
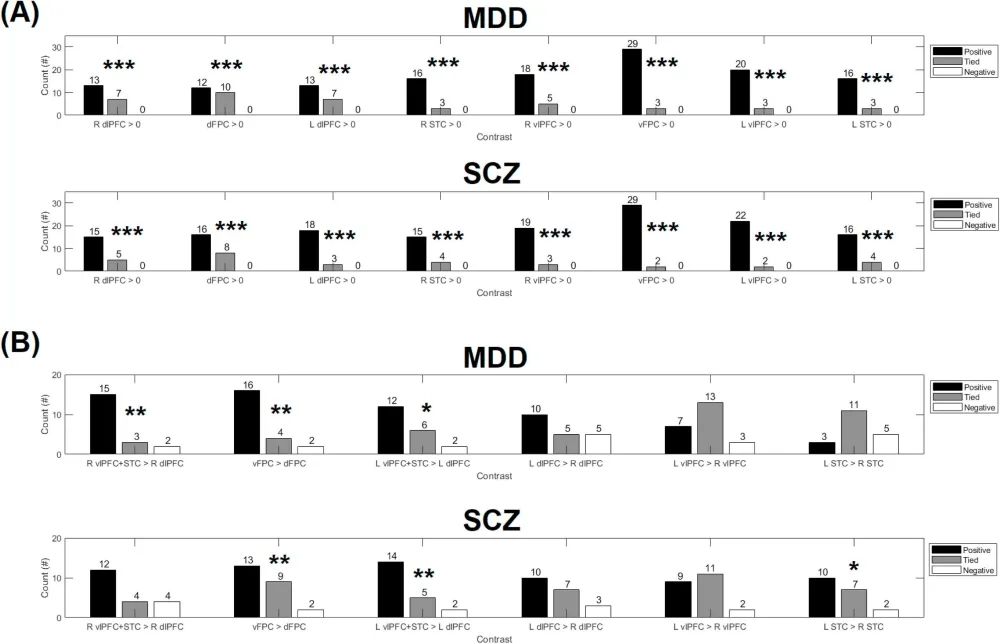
▲ In the verbal fluency test, the proportion of channels or channel clusters with significantly reduced oxygenated hemoglobin concentration compared to healthy control groups increased in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) and schizophrenia (SCZ). Asterisks indicate significance levels of (a) one-sample sign test (proportion ≠ 0) and (b) paired sample sign test (proportion of one area ≠ proportion of another area).
01
Most fNIRS studies using VFT found significant reductions in HbO in some frontal and temporal regions during VFT performance in various mental disorders (i.e., low activation). Compared to control groups, patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease exhibited reduced activation in the parietal lobe or decreased activation in the left frontal lobe during VFT. Low activation may indicate a manifestation of neurofunctional impairment or pathological changes in neurovascular coupling. When VFT performance is poor, low activation may also be associated with task disengagement, lack of motivation, or both.
02
In contrast, findings of reduced HbR in psychosis patients are relatively few. This difference may indicate increased sensitivity of HbO in detecting brain activity or selective disruption of neurovascular coupling due to psychopathology. Interestingly, slightly less than half of the studies reported that patients’ VFT performance was affected, with a few reporting poorer performance without changes in brain activation.These findings suggest that for most mental disorders, fNIRS measurements, especially increased HbO, are more sensitive in detecting psychopathology in the context of VFT than task performance variables, supporting the unique value of fNIRS.
03
The study conducted meta-analysis separately for major depressive disorder (MDD) and schizophrenia (SCZ), both characterized by frontal lobe pathology. Although both common disorders showed increased reductions in HbO in the frontal-temporal regions during VFT performance, they exhibited partially different low activation patterns. Specifically, while MDD and SCZ patients had higher degrees of low activation in the lower frontal regions than in the upper prefrontal regions, only SCZ patients showed a higher degree of low activation in the left temporal cortex compared to the right homologous area. This lateralized effect is specific to the temporal cortex, which may indicate functional differences between the temporal cortex and the lateral prefrontal cortex, as well as vocabulary semantic processing deficits supported by the left anterior temporal lobe in SCZ. In contrast, no similar lateralized effect was observed in patients with major depressive disorder. Four VFT studies compared MDD and SCZ but found no significant differences in HbO increases between any single channel or cluster between the two groups.Therefore, when using fNIRS and VFT, lateralization of low activation (i.e., differences in low activation levels between the two hemispheres) may be more discriminative in distinguishing major depressive disorder from schizophrenia than low activation levels in a specific region. This may be necessary for individualized treatment.
04
In conclusion, this study provides supporting evidence that the combined use of fNIRS and VFT has a unique and valuable role in psychiatry. It also evaluates different possibilities that may explain the fNIRS results from previous studies involving patients with psychosis. The review is an important first step in quantitatively synthesizing the results of studies involving the use of VFT as fNIRS to detect mental disorders. The findings encourage the expanded application of the fNIRS-VFT paradigm to improve the identification, differentiation, and management of mental disorders and highlight the importance of taking rigorous measures to enhance the strength and clarity of evidence derived from fNIRS methods.
Recommendations
First, unitless measures (e.g., effect sizes) should be used to minimize potential confounding effects of different brain structures between patients with psychosis and healthy controls. Second, motion correction methods, especially wavelet filtering, should be applied to improve signal quality. Third, HbR data should be reported whenever possible, as this data provides important information on the basis of HbO changes. Fourth, the lateralization of activation and the impact of retrieval effort and conversion demands on cortical activation should be examined to further understand the neural mechanisms behind VFT performance in mental disorders. Given the region-specific low activation lateralization in SCZ patients, the functional differences between the temporal cortex and the lateral prefrontal cortex should also be considered. Finally, we recommend that future studies adequately report effect sizes, preferably in tables, to facilitate more refined quantification in the future.
About Huichuang
Huichuang Near-Infrared is a leading enterprise focusing on the research and application of near-infrared brain functional imaging technology, having developed the world’s first NMPA registered product NirScan with over 100 channels for near-infrared brain functional imaging, achieving full-brain synchronous detection and excellent image quality even in difficult-to-detect brain regions such as the parietal and occipital lobes. In addition to the mobile floor-standing product NirScan, Huichuang Near-Infrared has also launched the portable product NirSmart, which is the world’s first portable near-infrared brain imaging device to obtain NMPA medical device certification. Based on the technical foundation of the mobile floor-standing product, the portable product NirSmart condenses large equipment to about the size of an iPAD, making it portable and lightweight while still retaining high sensitivity and high-channel performance. At the same time, the portable product NirSmart is particularly suitable for mobile applications such as walking through wireless connections.

References:
[1] Yeung M K , Lin J. Probing depression, schizophrenia, and other psychiatric disorders using fNIRS and the verbal fluency test: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 2021, 140:416-435.
END

Scan to Follow
Get More Exciting Content
