The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed cybersecurity guidelines for IoT device manufacturers, providing directions and guidance for the secure manufacturing of IoT products.
As part of the IoT cybersecurity program, NIST recently released two documents aimed at providing cybersecurity guidelines and best practices for IoT device manufacturers. These guidelines are part of the “Strengthening Federal Cybersecurity of Networks and Critical Infrastructure” executive order that NIST began implementing in 2017. NIST offers a series of recommendations in these documents that IoT device manufacturers should consider to improve the security of their IoT devices.
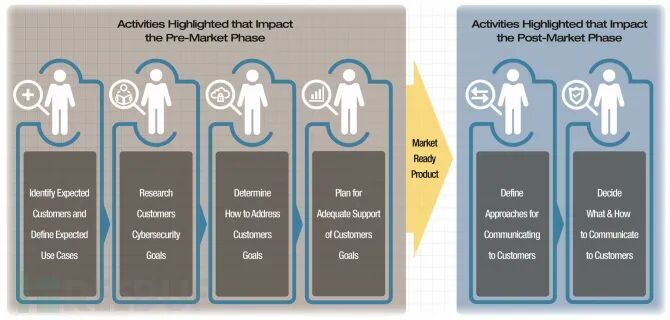
The first document is NISTIR 8259, which provides a detailed roadmap for IoT device manufacturers to address cybersecurity issues encountered during the development of IoT products. The document recommends preparation in six areas, four of which focus on identifying risks and implementing appropriate security controls before the product is launched; the other two areas address how to meet customer cybersecurity needs after the device is on the market. These measures emphasize identifying customers and their cybersecurity needs, as well as how to handle cybersecurity issues once the device is released.
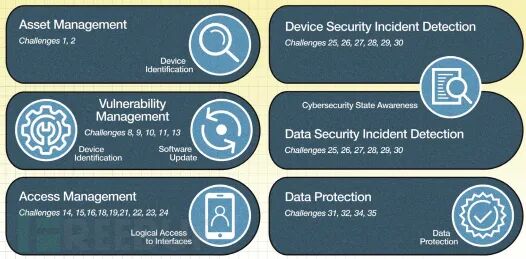
The second document, NISTIR 8259A, establishes core essential requirements to meet common cybersecurity control needs. These are as follows:
Device Identification: The ability to logically and physically identify individual devices.
Device Configuration: The ability to change the software configuration of IoT devices, with such changes only being made by authorized entities.
Data Protection: Data from IoT devices must be protected during storage and transmission to prevent unauthorized access or modification.
Access Interface: Only authorized entities can logically access the interface.
Software Updates: Software updates for IoT devices can be provided by authorized entities.
Security Status Awareness: IoT devices can report their security status to authorized entities.
As mentioned earlier, the security of IoT devices is increasingly being standardized through joint efforts at the federal and state levels. NIST indicates that it is actively updating NISTIR 8259 and 8259A to enable federal agencies to use more secure IoT devices.
While there are currently no legal requirements to implement the security controls outlined in these two documents, they may serve as an important reference when determining the reasonableness of IoT device security. Manufacturers of IoT devices, especially those targeting government markets, should proactively meet NIST’s standard requirements and consider these two documents in the actual design and manufacturing of new IoT devices.
Source Reference
Lexology
Recommended Highlights




