Recently, I’ve been discussing addition and subtraction with regrouping within 20 in our activity group. We have progressed from understanding numbers within 100, practicing making ten, basic methods of regrouping, to the second round of learning numbers within 10, and now we’ve reached more strategies for calculations within 20.
In the past couple of days, we happened to talk about games involving addition and subtraction within 20. Besides various calculation battles played with playing cards and calculation board games, there is another unique type of game that can help children practice calculations, and most children will enjoy it, which is—the Code Game.
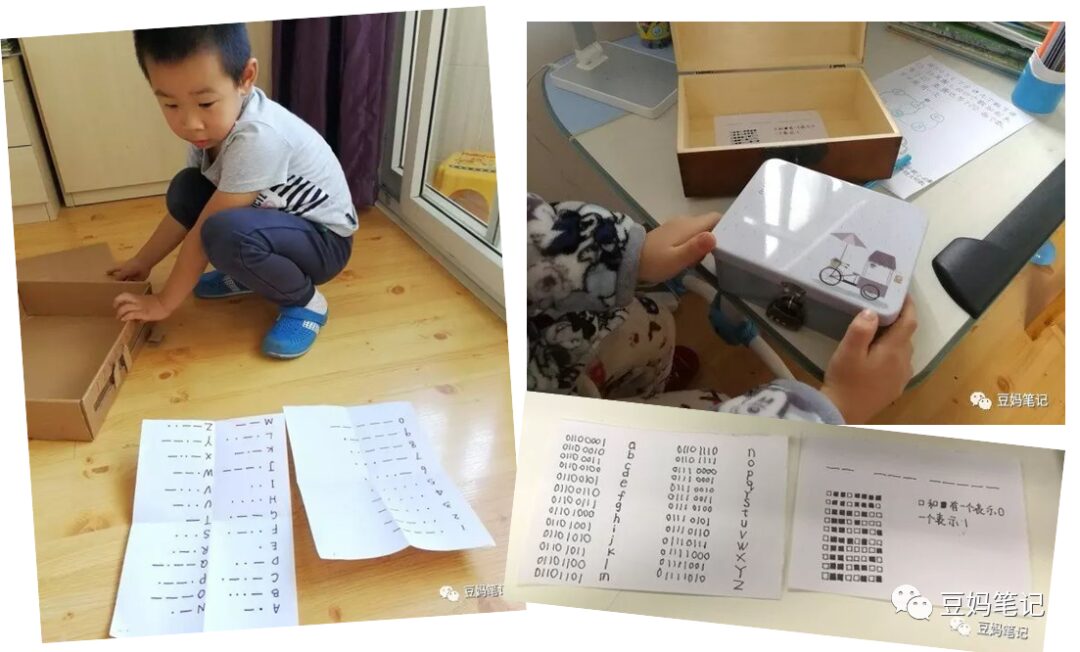
(Dou Dou played the code game a lot when he was younger)
The fun of this type of game that uses mathematical calculations for encryption and decryption lies in the fact that once they successfully decode, they reveal a piece of originally unknown information, and the children’s curiosity about the encrypted information will make them not mind doing more calculations, and they might even find such calculations very meaningful.
I would like to share this fun and interesting game that can make kids enjoy practicing calculations.
1
Preparation for the Code Game: Codebook + Encryption Rules
The code game involves us and the children passing information using encryption methods. We encrypt the information, the children decode it, or vice versa. We can convey a piece of information individually or use it as part of a treasure hunt challenge.
Before playing this game, we need to prepare two things: a codebook and encryption rules.
1. Codebook
First, we need to prepare a codebook, which is essentially a basic reference book that converts one type of information into another.
For example, converting English letters into numbers. In the table below, e is converted to the number 5, while 19 corresponds to the letter s.
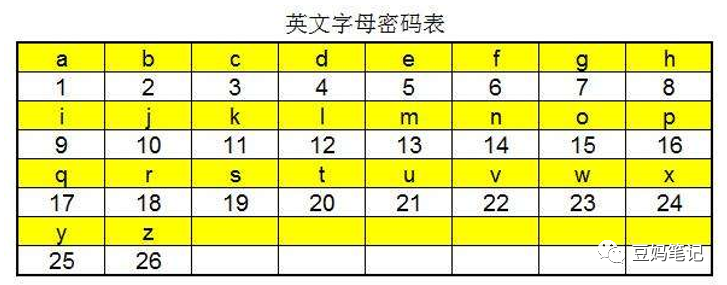
Another example is converting pinyin into numbers.
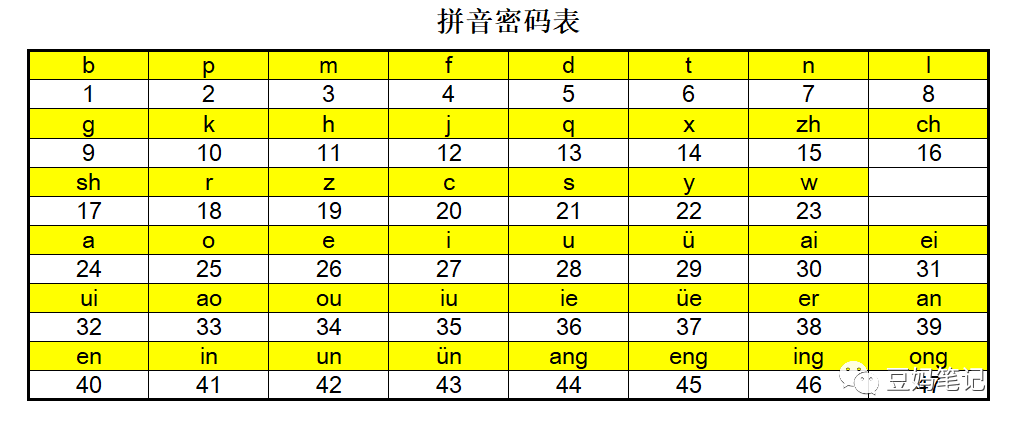
Yet another example is Morse code, which converts letters, numbers, and punctuation into radio signals.

The type of codebook we prepare can actually reflect some of our thoughts; we can prepare a codebook for the content we want to help the children familiarize themselves with.
2. Encryption Rules
Once we have the codebook, we also need a set of encryption rules.
The simplest encryption rule is direct substitution.
For example, using the codebook that converts English letters into numbers. If we receive a string of numbers: 14 9 3 5, we can refer to the code table to translate this string of numbers into the meaning of ‘nice’.
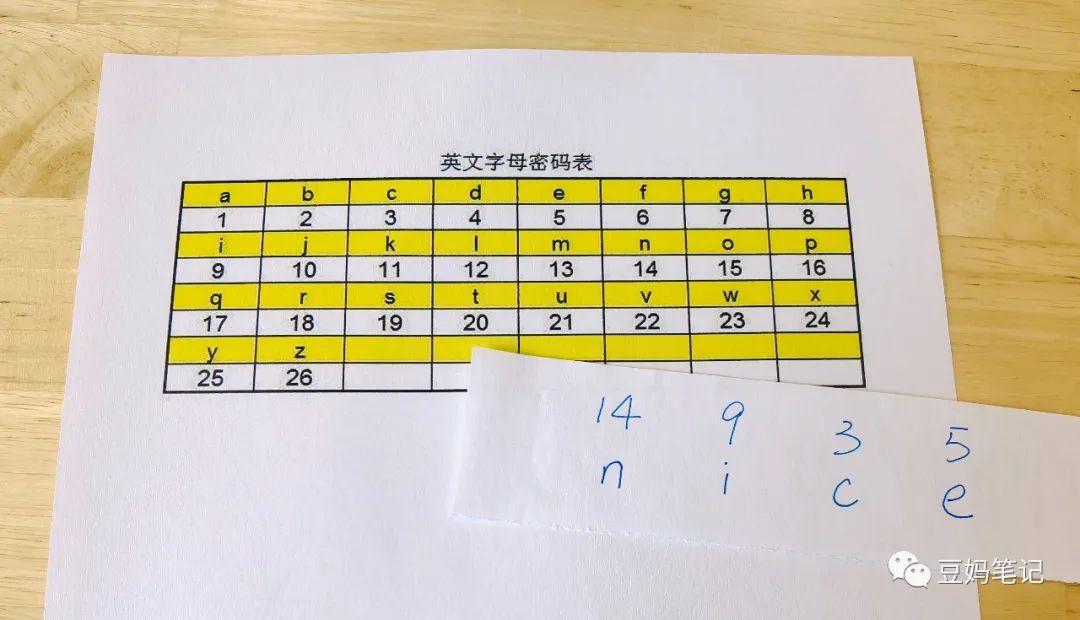
Here comes the key point~~
If our encryption rule is not a simple substitution but is designed to be a bit more complex by incorporating addition and subtraction calculations, then the children will naturally need to use calculations when decoding.
Let me give a clearer example.
For instance, we agree on a number 13 with the children and tell them that the ciphertext consists of letters whose numbers in the codebook are all increased by 13.
We wrote a ciphertext paper for the children: (13) 27 22 16 18. The number in parentheses, 13, indicates that the numbers corresponding to the letters in the codebook have all been increased by 13.
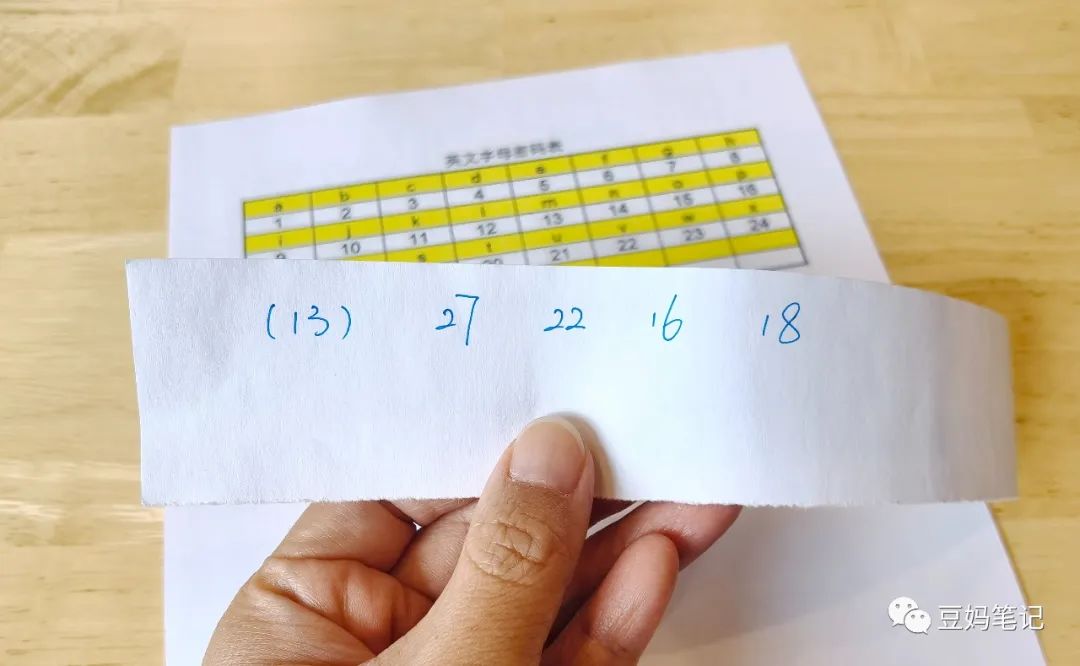
Knowing this encryption rule, to decode, the children will need to use the inverse calculation to subtract 13 from each number in the ciphertext, and then refer to the codebook.
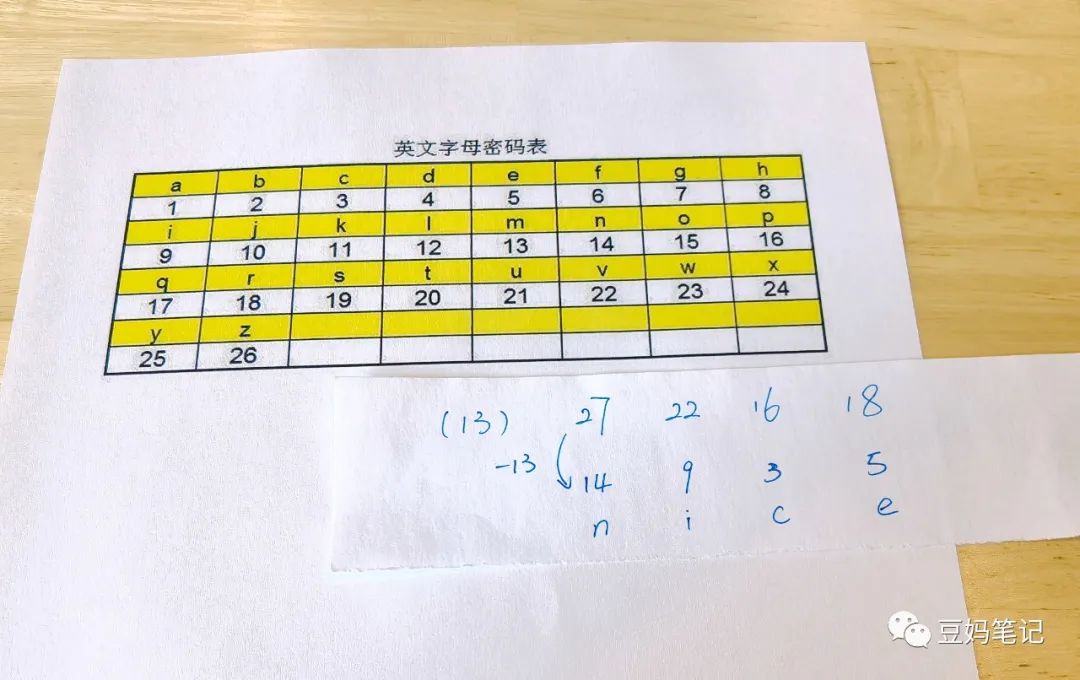
Having written this, I believe everyone can see thatto help children practice calculations, we can fully utilize the ‘encryption rules’.
2
From Kindergarten to Primary School
Different Stages Can Play This Game
If we delve deeper into the encryption rules, we will find that they can actually be divided into two parts: one is the encryption algorithm, such as adding or subtracting a certain number from the basic numbers in the codebook; the other part describes the characteristics of the algorithm, which has a more technical name called the key. In the previous example, 13 is the key.
Therefore, when using the code game to help children practice calculations, we can approach it from two aspects.One is to keep the algorithm unchanged while only changing the key, for example, changing 13 to 17, then the children will switch from writing many -13 calculations to writing many -17 calculations.
Kindergarten Middle Class: Substitution Without Calculation
For children in the middle class of kindergarten, we can start playing the code game with them.
When playing for the first time, we first need to explain to the children what a code is and why we use codes, and then start with the simplest level of “substitution without calculation”. This is beneficial for children’s substitution thinking.
When Dou Dou was in kindergarten, I started playing the code game with him from simple substitution.

-
Morse code, which can be played as long as one knows the numbers 0-9, can also connect pinyin, literacy, and natural phonics review; this game is definitely a must-try!
-
Last Christmas, Santa Claus played a treasure hunt with Dou Dou.
-
I turned my house into a treasure hunt + escape room game venue; a 5-year-old kid spent 50 minutes solving puzzles and finally succeeded; it was so exciting!
Kindergarten Senior Class, First Grade: Incorporating Addition and Subtraction Calculations
At this stage, children are learning addition and subtraction within 20 and 100. Understanding the principles of calculations is essential, and appropriate practice is also indispensable. The code game is a very interesting practice.
In addition to the earlier example of moving a certain position based on the basic reference table (adding a number), there is another, slightly more complex algorithm, which is adding two adjacent numbers, with the first number adding 0.
Thus, if the received ciphertext is 14 23 12 8, the decoding process will involve the inverse operation:

We will find that the decoding process not only has the children practicing calculations, but also effectively training their reverse thinking abilities.
Second and Third Grades: Incorporating Multiplication and Division, Four Basic Operations
The encryption algorithm can be addition and subtraction, and of course, it can also be multiplication and division, or even a mix of the four basic operations. Therefore, this encryption and decryption game can continue to be played in the second and third grades.
For example, if we agree that this time the algorithm is to first multiply the corresponding numbers in the codebook by a number, and then add another number.
The ciphertext is (3,5) 47 32 14 20. The first number in the parentheses, 3, indicates to multiply by 3 first, and the second number, 5, indicates that the resulting number should then be added to 5.
Knowing this encryption rule, when restoring the information, the child will need to perform the opposite calculations for this group of numbers:
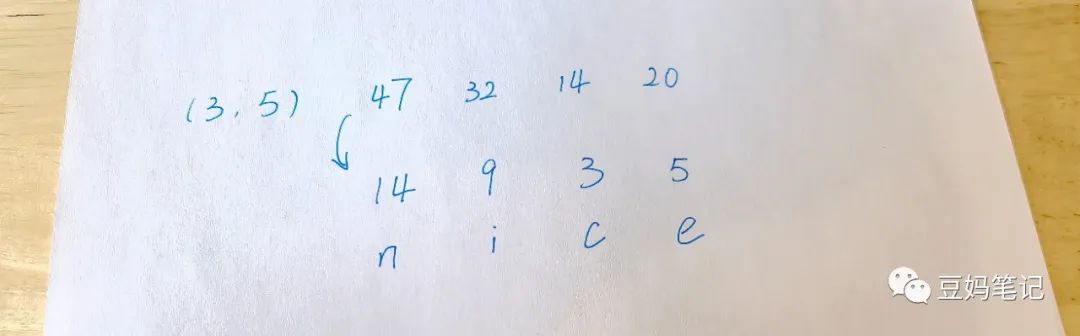
Come on, let’s play one.
Using the English letter code table, with the same encryption rules as before, first multiply by a number, then add a number. The ciphertext is as follows:
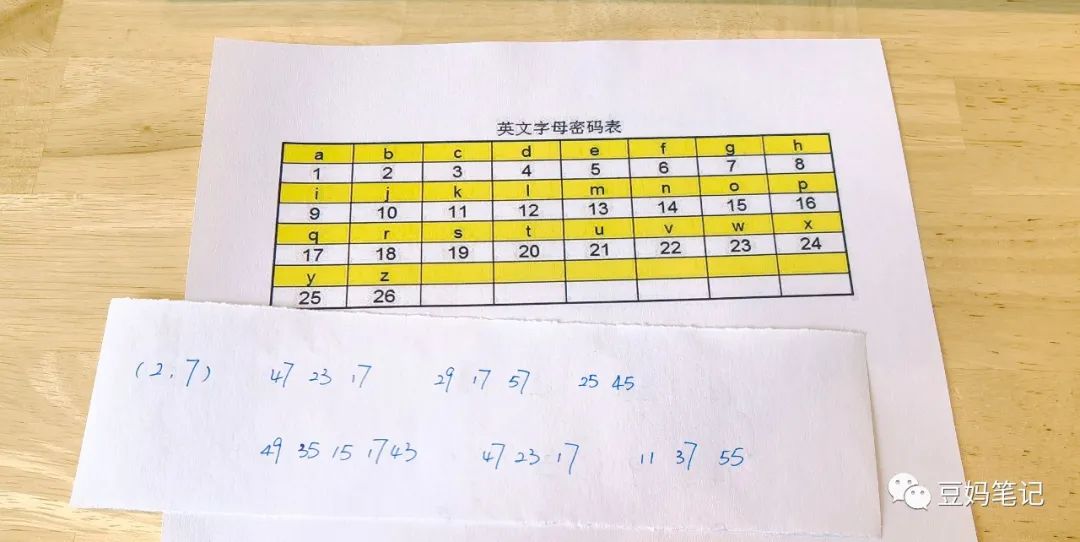
Does everyone know what I want to say? ^_^
The encryption and decryption game has always been closely related to mathematics. In higher grades, as children’s mathematical knowledge becomes richer, they can also use frequency analysis, factorization, modular arithmetic, and more to play code games.
I will continue to share more in future articles.

For more games to help children practice calculations, please see:
-
Addition and subtraction within 10: Card Games | Dice Games
-
Addition and subtraction within 100: Card Games | Dominoes | Polyhedral Dice -
Multiplication and division: Prime Number Chess -
Four Basic Operations: 24 Point Game -
Fractions: Fraction Formula
—— Follow me for more exciting content ——