In a LoRaWAN network, there are many parameters such as node type, transmission rate, ADR, channel mask, etc. Today, we will discuss how to modify these parameters to suit your needs.
1. Parameter Definition
The parameters related to LoRaWAN are defined in a structure within the SDK, which allows us to understand which parameters can be set and their corresponding value ranges.
/*! * LoRaMAC MIB-RequestConfirm structure */typedef struct eMibRequestConfirm{ /*! * MIB-Request type */ Mib_t Type; /*! * MLME-RequestConfirm parameters */ MibParam_t Param;}MibRequestConfirm_t;The members of this structure are themselves enumerations and unions. The Mib_t enumeration describes the parameters that can be set, as follows:
typedef enum eMib{ MIB_DEVICE_CLASS, // Node class type, which can be Class A, Class B, or Class C MIB_NETWORK_ACTIVATION, // Activation method, either OTAA or ABP MIB_DEV_EUI,// DEVEUI, 8 bytes, related to OTAA network access, also commonly used to identify devices MIB_JOIN_EUI, // JOINEUI, also called APPEUI, 8 bytes, related to OTAA network access MIB_ADR, // Whether to enable ADR, used for platform adjustment of rate and transmission power to save energy MIB_NET_ID, // Node network ID MIB_DEV_ADDR, // Node short address MIB_GEN_APP_KEY,// Encryption key, 16 bytes, related to OTAA network access MIB_PUBLIC_NETWORK, // Whether it is a public network MIB_REPEATER_SUPPORT,// Whether it supports repeaters MIB_CHANNELS, MIB_RX2_CHANNEL,// Receive window 2 MIB_RX2_DEFAULT_CHANNEL,// Rate for receive window 2 MIB_RXC_CHANNEL,// Receive window in Class C mode MIB_RXC_DEFAULT_CHANNEL, MIB_CHANNELS_MASK, // Channel mask MIB_CHANNELS_DEFAULT_MASK,// Default channel mask MIB_CHANNELS_NB_TRANS,// Number of retransmissions MIB_MAX_RX_WINDOW_DURATION, MIB_RECEIVE_DELAY_1, // Time for opening receive window 1 MIB_RECEIVE_DELAY_2, // Time for opening receive window 2 MIB_JOIN_ACCEPT_DELAY_1, // Time for opening receive window 1 for join response MIB_JOIN_ACCEPT_DELAY_2, // Time for opening receive window 2 for join response MIB_CHANNELS_DEFAULT_DATARATE,// Default rate MIB_CHANNELS_DATARATE,// Rate MIB_CHANNELS_TX_POWER,// Transmission power MIB_CHANNELS_DEFAULT_TX_POWER,// Default transmission power MIB_SYSTEM_MAX_RX_ERROR,// MIB_MIN_RX_SYMBOLS, MIB_ANTENNA_GAIN,// Antenna gain MIB_DEFAULT_ANTENNA_GAIN,// Default antenna gain // Many parameters, only a portion is shown}Mib_t;MibParam_t is a union corresponding to the value ranges of the above parameters, as follows:
typedef union uMibParam{ DeviceClass_t Class; ActivationType_t NetworkActivation; uint8_t* DevEui; uint8_t* JoinEui; bool AdrEnable; uint32_t NetID; uint32_t DevAddr; uint8_t* GenAppKey; bool EnablePublicNetwork; bool EnableRepeaterSupport; uint16_t* ChannelsMask; uint16_t* ChannelsDefaultMask; uint8_t ChannelsNbTrans; uint32_t MaxRxWindow; uint32_t ReceiveDelay1; uint32_t ReceiveDelay2; uint32_t JoinAcceptDelay1; uint32_t JoinAcceptDelay2; int8_t ChannelsDefaultDatarate; int8_t ChannelsDatarate; int8_t ChannelsDefaultTxPower; int8_t ChannelsTxPower; McChannelParams_t MulticastChannel; uint32_t SystemMaxRxError; uint8_t MinRxSymbols; float AntennaGain; float DefaultAntennaGain; // Many parameters, only a portion is shown}MibParam_t;2. Setting Parameters
Let’s take the following parameters as examples:
uint8_t JoinEui[]={0x3C,0x9B,0x5F,0x76,0xE3,0x81,0x47,0xB1 };uint8_t DevEui[]={0x00,0x01,0x01,0x0C,0xFF,0x00,0x00,0xE5};uint8_t AppKey[]={0xc4,0x66,0x6e,0x42,0x54,0xc0,0x58,0x73,0x2c,0xf7,0xbc,0xe6,0x36,0x0d,0x07,0x27};void UserConfig(void){ MibRequestConfirm_t mibReq; mibReq.Type = MIB_JOIN_EUI; mibReq.Param.JoinEui = JoinEui; LoRaMacMibSetRequestConfirm( &mibReq ); mibReq.Type = MIB_DEV_EUI; mibReq.Param.DevEui = DevEui; LoRaMacMibSetRequestConfirm( &mibReq ); mibReq.Type = MIB_GEN_APP_KEY; mibReq.Param.GenAppKey = AppKey; LoRaMacMibSetRequestConfirm( &mibReq ); mibReq.Type = MIB_DEVICE_CLASS; mibReq.Param.GenAppKey = CLASS_A; LoRaMacMibSetRequestConfirm( &mibReq ); mibReq.Type = MIB_ADR; mibReq.Param.GenAppKey = false; LoRaMacMibSetRequestConfirm( &mibReq ); mibReq.Type = MIB_CHANNELS_DATARATE; mibReq.Param.GenAppKey = DR_0; //DR_0 is defined in Region.h, here DR_0 corresponds to SF12, DR_1 corresponds to SF11, and so on LoRaMacMibSetRequestConfirm( &mibReq ); // ………… // Other parameters can be set similarly}In the above function, the custom function void UserConfig(void) sets the parameters. The method is straightforward: first, specify the parameter to be set, then assign the corresponding variable.
Next, let’s look at the function LoRaMacMibSetRequestConfirm( MibRequestConfirm_t* mibSet ) as follows:
LoRaMacStatus_t LoRaMacMibSetRequestConfirm( MibRequestConfirm_t* mibSet ){ LoRaMacStatus_t status = LORAMAC_STATUS_OK; ChanMaskSetParams_t chanMaskSet; VerifyParams_t verify; if( mibSet == NULL ) { return LORAMAC_STATUS_PARAMETER_INVALID; } if( ( MacCtx.MacState & LORAMAC_TX_RUNNING ) == LORAMAC_TX_RUNNING ) { return LORAMAC_STATUS_BUSY; } switch( mibSet->Type ) { case MIB_DEVICE_CLASS: { status = SwitchClass( mibSet->Param.Class ); break; } case MIB_NETWORK_ACTIVATION: { if( mibSet->Param.NetworkActivation != ACTIVATION_TYPE_OTAA ) { MacCtx.NvmCtx->NetworkActivation = mibSet->Param.NetworkActivation; } else { // Do not allow to set ACTIVATION_TYPE_OTAA since the MAC will set it automatically after a successful join process. status = LORAMAC_STATUS_PARAMETER_INVALID; } break; } case MIB_DEV_EUI: { if( SecureElementSetDevEui( mibSet->Param.DevEui ) != SECURE_ELEMENT_SUCCESS ) { status = LORAMAC_STATUS_PARAMETER_INVALID; } break; } case MIB_JOIN_EUI: { if( SecureElementSetJoinEui( mibSet->Param.JoinEui ) != SECURE_ELEMENT_SUCCESS ) { status = LORAMAC_STATUS_PARAMETER_INVALID; } break; } case MIB_ADR: { MacCtx.NvmCtx->AdrCtrlOn = mibSet->Param.AdrEnable; break; }…………}As can be seen, after the parameters are passed to this function, a switch statement is used to determine which parameter it is. Some parameters also undergo validity checks. For example, the MIB_JOIN_EUI parameter requires checking the return value; if it is not LORAMAC_STATUS_OK, then the parameter’s validity needs to be verified. The MIB_NETWORK_ACTIVATION parameter is directly assigned to MacCtx.NvmCtx->NetworkActivation, and this value is ultimately passed to the sx127x registers. The JoinEui, DevEui, and AppKey are purely protocol stack elements and are not related to sx127x.
3. Parameter Validity
Regarding the value ranges of parameters, they vary across frequency bands. Refer to the document lorawan_regional_parameters_v1.0.3reva_0.pdf. Taking CN470 as an example:
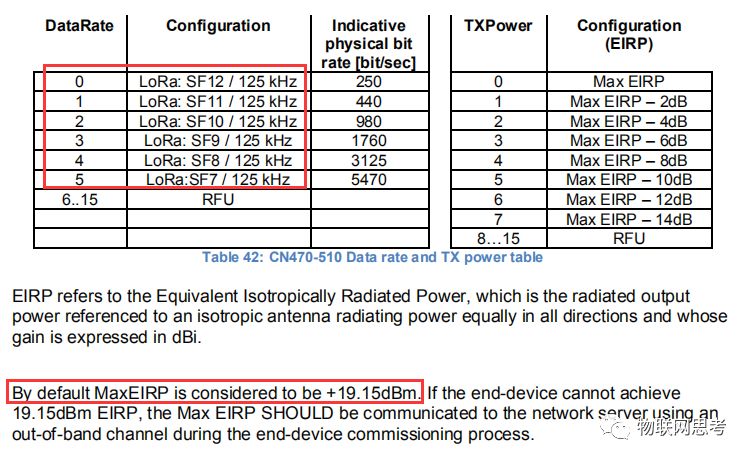
As can be seen, CN470 supports DR_0 to DR_5; the maximum transmission power is 17dBm, while the document states 19.15dBm, and the default antenna gain is -2.15dBm.
Other parameter ranges can be set by referring to the document, and the methods for setting other frequency bands are similar.
——————END——————
Recommended Reading:
LoRa Node Development – Detailed Code Explanation on Modifying Transmission and Reception Channels (Frequencies)
LoRa Node Development – Detailed Code Explanation on Sending and Receiving Data in LoRaWAN
LoRa Node Development – Detailed Code Explanation on LoRaWAN Node Network Access
LoRa Node Development – Overall Design Concept of SDK
LoRaNode Development – Building a Keil Project
LoRaNode Development – Introduction to SDK
Original content is not easy to create, please indicate the source when reprinting. Sharing and forwarding is the greatest support for the author.

[Long press to identify and follow for more exciting IoT content to share with you]