🏖️ Zblock Compressed Slab Memory Allocator Expected to Land in Linux 6.16 Kernel
With only one month left until the merge window for Linux 6.16 opens, the new Zblock allocator has been incorporated into Andrew Morton’s “MM” memory management code tree, and is highly likely to appear in the next kernel merge cycle.The design goal of Zblock is to achieve dense packing of objects of various sizes while maintaining a low internal fragmentation rate. Tests indicate that Zblock can provide a compression ratio that is “significantly higher” than that of solutions like Z3fold and Zbud. In terms of average performance and worst-case execution time, Zblock also outperforms Zsmalloc.Documentation indicates that tests on the Raspberry Pi 5 show that Zblock’s bogo ops/s performance is approximately 5-10% higher than that of Zsmalloc. Previously, Z3fold and Zbud were removed from the mainline kernel as they were marked as deprecated.Now, Zblock is poised to join the fray and compete with Zsmalloc. Vitaly Wool wrote in the Zblock patch notes in mm.git: “Zblock is a dedicated allocator for storing compressed pages. Each block stores an integer number of objects of the same size, and these blocks consist of several physical pages (2 to the power of n, i.e., 1/2/4/8 pages). Zblock allows for dense packing of objects of different sizes, thereby achieving a lower internal fragmentation rate.The allocator also prioritizes filling partially filled blocks over creating new blocks, which can provide a compression ratio comparable to zmalloc in most cases. In terms of average performance and worst-case execution time, Zblock generally outperforms Zsmalloc, thereby improving the overall system response time and real-time characteristics.Currently, Zblock does not support high-end memory and page migration features. Test results (zstd compressor, 8-core Ryzen 9 virtual machine, compiling bzImage):
| Metric | Zblock | Zsmalloc |
|---|---|---|
| Real Time | 6 minutes 52.621 seconds | 7 minutes 4.355 seconds |
| User Time | 33 minutes 41.771 seconds | 34 minutes 37.538 seconds |
| System Time | 6 minutes 28.825 seconds | 6 minutes 22.086 seconds |
| Zswap Usage | 162,328 KB | 175,704 KB |
| Zswapped Amount | 754,468 KB | 778,692 KB |
| Zswpin Count | 93,851 | 101,243 |
| Zswpout Count | 542,481 | 448,217 |
| Zswpwb Count | 935 | 640 |
If all goes well, Zblock will be released as a new memory management feature with Linux version 6.16.
🤤 GNOME Mutter Adds Relative Mode Support for Tablet Knobs in Wayland
The Mutter window manager for GNOME 49 has recently merged a new feature exclusive to Wayland—support for relative mode of tablet knobs. With the latest libinput and libwacom drivers, drawing tablets equipped with such knobs (like the Huion Inspiroy Dial Q620M) can now perform relative displacement operations in GNOME Wayland sessions.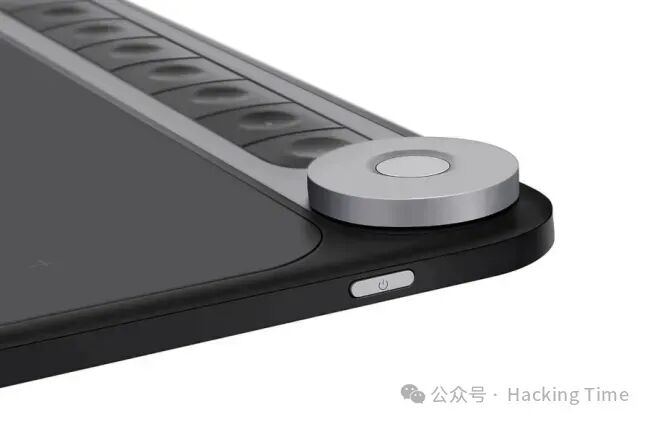 Red Hat input device expert Peter Hutterer has been continuously developing this feature over the past year. After completing support for the Wayland protocol and adapting libinput/libwacom, the code for GNOME Mutter has been merged into the main branch, but only for the Wayland code path (excluding X11 support). The accompanying GNOME Shell knob support modifications are still under code review.The Wayland tablet-v2 protocol extension describes the design intent for relative knobs as follows:
Red Hat input device expert Peter Hutterer has been continuously developing this feature over the past year. After completing support for the Wayland protocol and adapting libinput/libwacom, the code for GNOME Mutter has been merged into the main branch, but only for the Wayland code path (excluding X11 support). The accompanying GNOME Shell knob support modifications are still under code review.The Wayland tablet-v2 protocol extension describes the design intent for relative knobs as follows:
“Some tablets are equipped with rotary controls (such as the Huion Inspiroy Dial 2), and the incremental information they provide is essentially equivalent to a mouse wheel. These controls should be exposed in the same way as touch rings/touch strips, with event handling following the wl_pointer.axis_v120 specification.”
Relevant users can find more details in today’s merged Mutter code submission, and this feature will officially debut with GNOME 49, scheduled for release in September this year.
🚃 KDE Developers Actively Prepare Wayland Improvements for Plasma 6.4
As April comes to a close, KDE developers continue to develop new features for the Plasma 6.4 desktop environment, with many gathering this week in Graz, Austria for in-depth development and planning discussions.KDE developer Nate Graham released the latest weekly report, summarizing the key highlights of important changes in KDE Plasma this week:
-
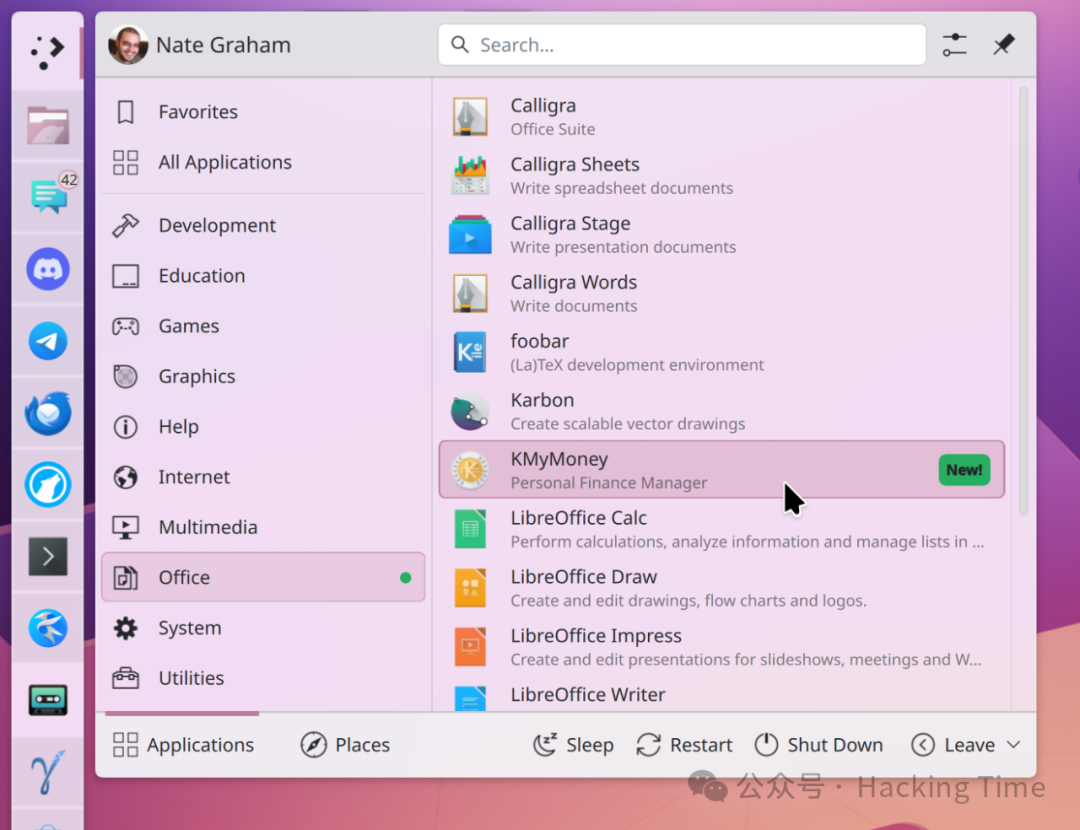
In the upcoming Plasma 6.4, newly installed applications will receive visual highlighting in the Kickoff launcher.
-
New Wayland relative mode support for stylus pens on drawing tablets.
-
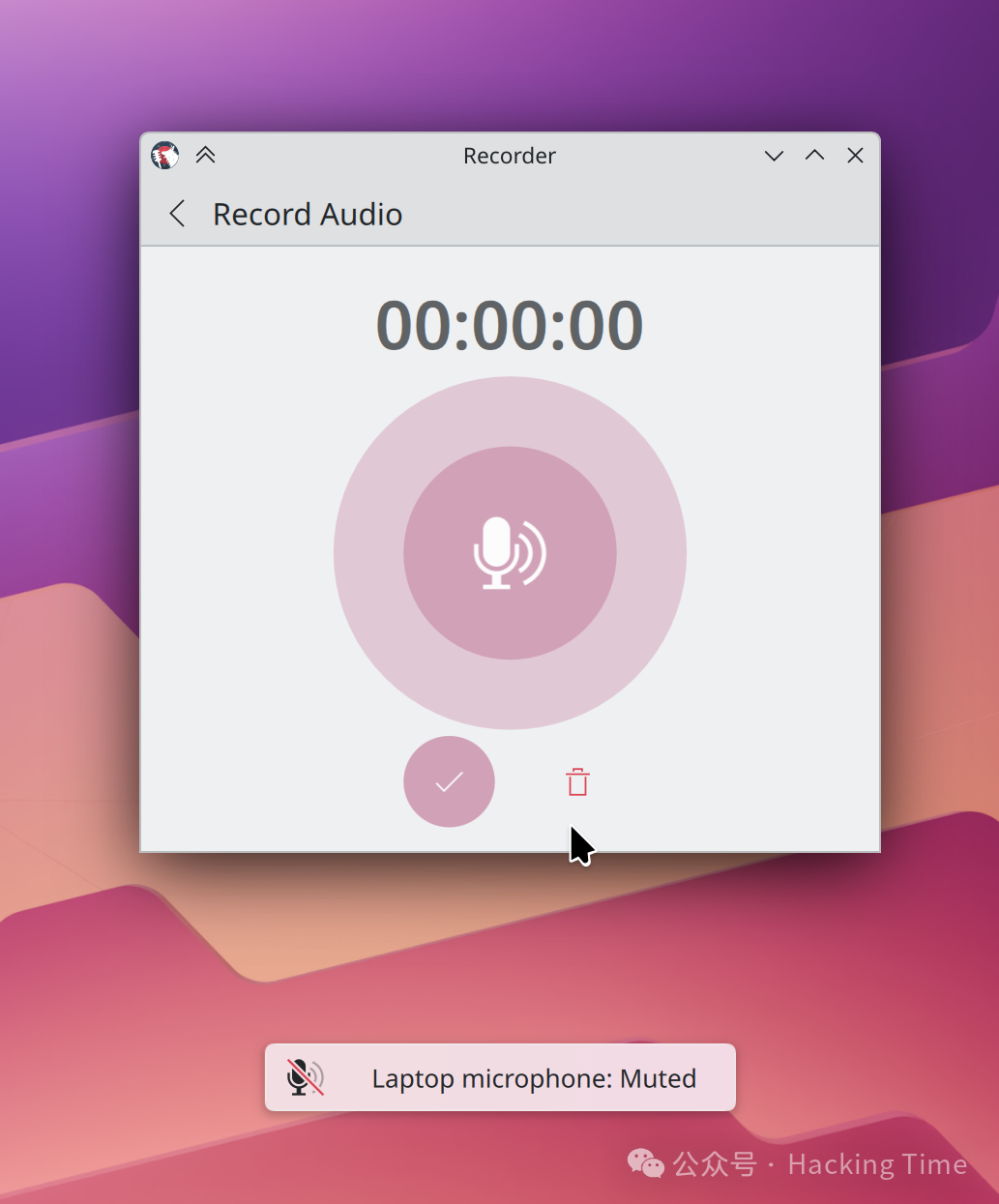
Plasma 6.4 introduces screen notifications for microphone mute status (when applications attempt to access it).
-
A dedicated configuration page for “Animation Effects” has been added to System Settings (Plasma 6.4 version).
-
Plasma 6.3.5 maintenance version will fix a KWin crash issue when laptops are disconnected from certain docks.
-
Also fixing a scheduling issue that causes KWin to continuously trigger redraws when the screen dims (Plasma 6.3.5).
-
Accessibility feature for controlling pointer movement with the numeric keypad is now supported in Wayland environments.
-
KWin in Plasma 6.4 will adopt the stable version of the Wayland ext-data-control protocol.
-
KMenuEdit now supports configuring applications to “always use the dedicated graphics card” (hardware support required).
For more details on this week’s updates, see the KDE Plasma weekly news.