Large Campus Networking Solutions: VLAN Division and Bandwidth Calculation Example (with Configuration Template)
Abstract: The efficient operation of large campus networks relies on scientific VLAN planning and precise bandwidth calculations. This article provides a step-by-step guide using a real case study of a campus with 5000 people, teaching you how to avoid broadcast storms, optimize resource allocation, and offering a directly applicable configuration template.
1. Why Does Your Campus Network Always Have Problems? 90% of Operations and Maintenance Have Fallen into These Pits
A smart manufacturing campus once paid a heavy price due to network planning errors:
- Production Network Sudden Outage: IP conflicts between cameras and AGV carts caused the MES system to crash for 3 hours, resulting in a direct loss of 800,000 yuan.
- Conference Room Live Streaming Lag: During a video conference with 200 participants, unisolated broadcast traffic filled the core switch.
- Security Audit Not Up to Standard: The R&D area and visitor area were interconnected, posing a risk of data leakage.
Three Fatal Flaws of Traditional Networking:
- Excessively large broadcast domains causing ARP storms.
- Mixed business traffic leading to QoS failure.
- Ambiguous security boundaries increasing the attack surface.
2. Four-Step VLAN Planning Method (with IP Address Template)
Case Background:
- Campus Size: Office Area 3000 people + Production Area 1500 people + Visitor Area 500 people.
- Business Systems: ERP/OA (20Mbps), Video Surveillance (50Mbps), IoT Terminals (10Mbps).
Step 1: Business Logic Isolation
| VLAN ID | Functional Area | IP Segment | Typical Devices | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Core Office Area | 192.168.10.0/24 | PC/Printer | ★★★★ |
| 20 | Smart Manufacturing Workshop | 172.16.20.0/24 | PLC/Industrial Camera | ★★★★★ |
| 30 | Video Dedicated Network | 10.30.30.0/24 | NVR/Cameras | ★★★☆ |
| 40 | Visitor Wireless | 192.168.40.0/24 | Mobile Phones/Tablets | ★☆ |
| 50 | IoT Management Platform | 172.18.50.0/24 | Environmental Sensors | ★★★☆ |
Pitfall Guide:
- The production network segment must enablePrivate VLAN to prevent device intercommunication.
- It is recommended to enableIGMP Snooping on the video VLAN to suppress multicast traffic.
Step 2: Bandwidth Calculation Formula
Golden Rule: Total Bandwidth = ∑(Number of Terminals × Single Device Demand) × Concurrency Factor + Redundancy.
Example Calculation:
-
Office Area (300 Terminals):
- General Office: 300×2Mbps×70% = 420Mbps.
- Video Conference: 50×8Mbps×90% = 360Mbps.
Production Area (100 Devices):
- PLC Communication: 100×5Mbps×100% = 500Mbps.
- Quality Inspection Cameras: 20×20Mbps×80% = 320Mbps.
Core Link Redundancy:
- (420+360+500+320)×150% = 2400Mbps
- Select2×10G Aggregated Links to meet the demand.
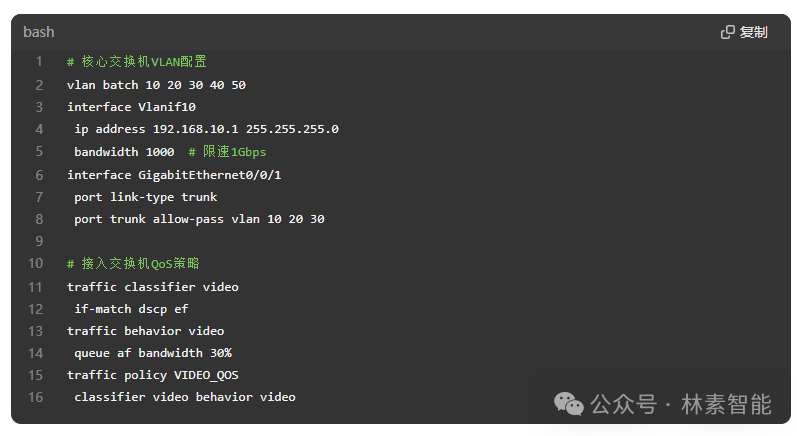
Step 3: Typical Configuration Example (Huawei Switch)
3. Essential Tools for Operations and Maintenance
- Cacti Traffic Monitoring Template: Real-time tracking of VLAN utilization.
- Subnet Calculator: Quickly generate non-conflicting IP planning.
- Broadcast Storm Suppression Script: Automatically block abnormal MAC flooding.
Expert Recommendations:
- Conduct aNetwork Health Assessment every quarter.
- Deploy key VLANs withNetFlow to analyze abnormal traffic.
- UseSDN Controllers to implement automated policy distribution.
