Click the blue text above to follow us



1. Essential Conditions for Network Troubleshooting

1. Familiarity with the OSI Seven-Layer Model and TCP/IP Protocol Stack
2. Understanding Basic Network Devices and Their Corresponding OSI Layers
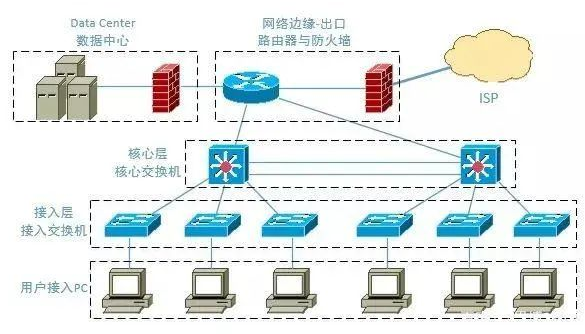
3. Understanding the Basic Architecture of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Networks
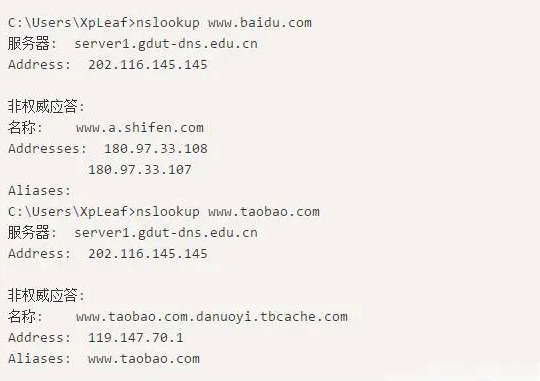
4. Knowing Common Network Troubleshooting Commands
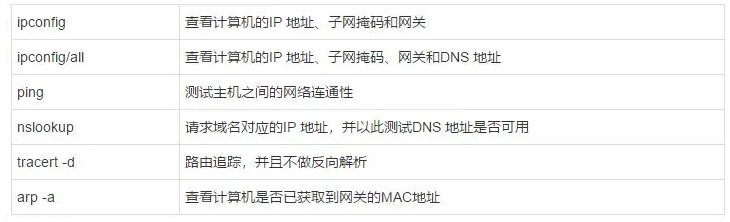
5. Clearly Understanding an Important Principle of Network Troubleshooting


II. Basic Ideas of Network Troubleshooting



III. Detailed Steps for Network Troubleshooting

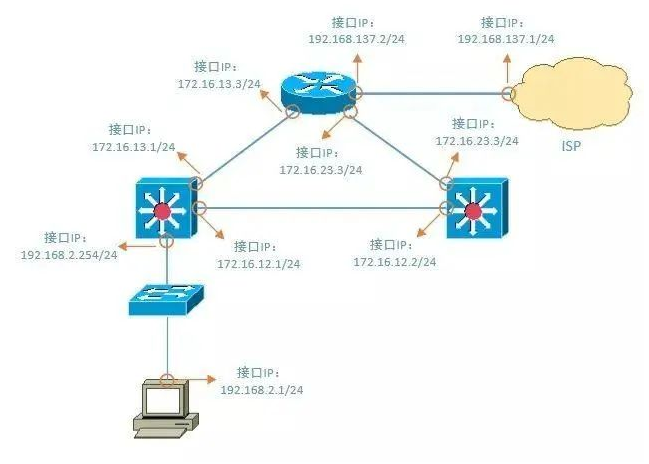
1. Check if there are issues with the physical link
2. Check if there are issues with the local IP address, routing, and DNS settings
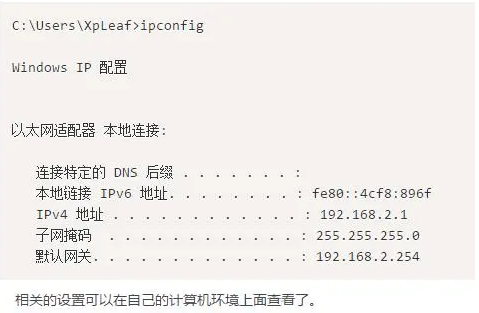
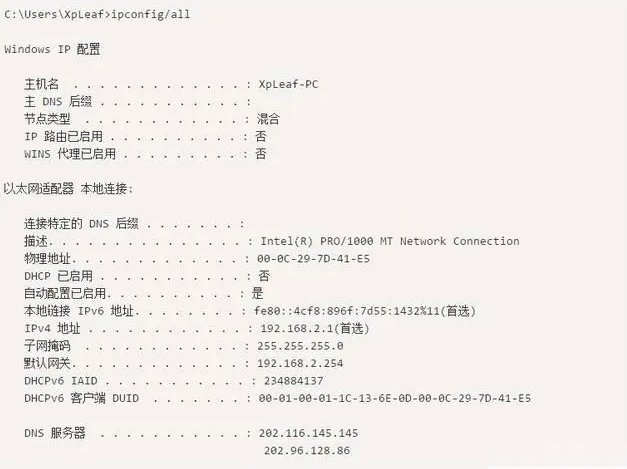
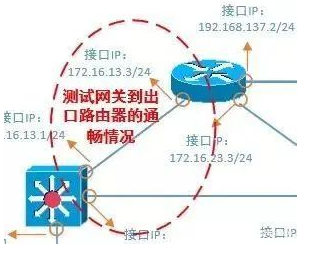
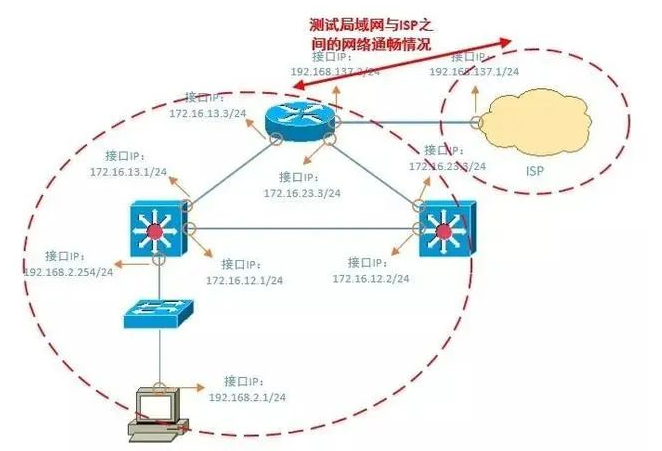
3. Test the connectivity of the gateway or router. Test the gateway first, then the router, testing step by step.
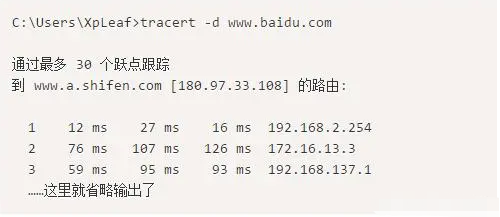
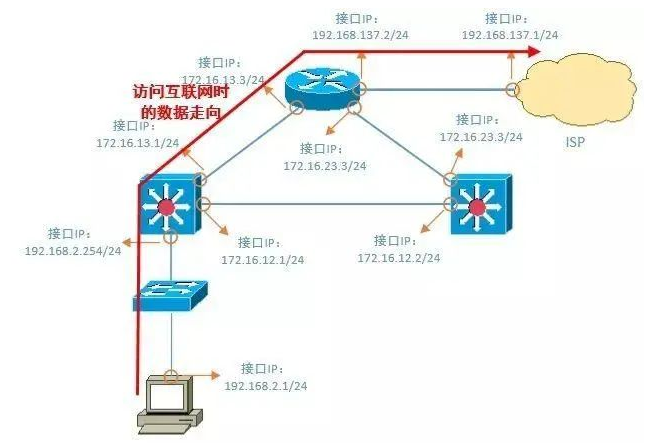
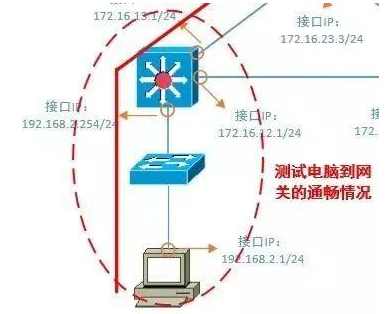
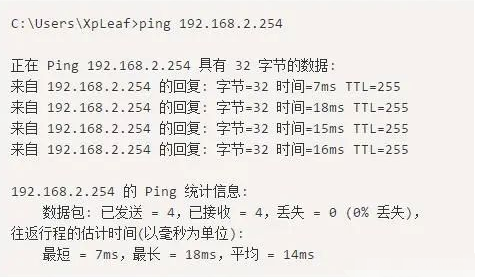
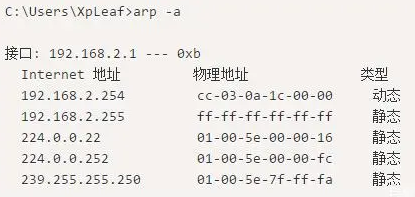

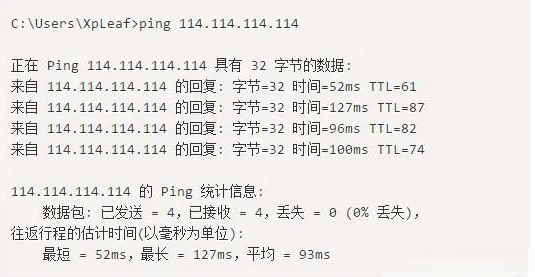
4. Test the connectivity of pinging a public IP address
5. Test the connectivity of DNS; you can directly ping the website address