Official systemctl manual: https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemctl.html#Official systemd manual: https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd.html#enabled: Indicates that this daemon will be executed at boot;
disabled: Indicates that this daemon will not be executed at boot;
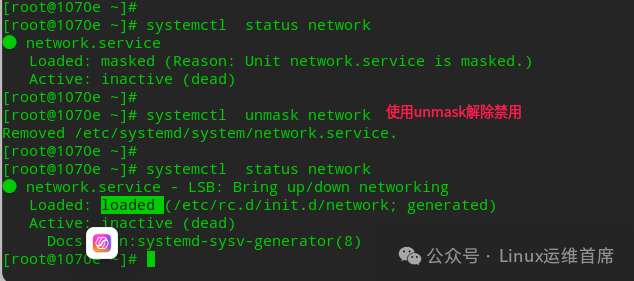
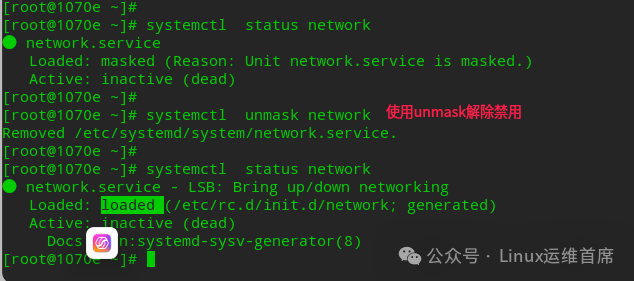
mask: Indicates that this daemon cannot be started under any circumstances, as it has been forcibly disabled (not deleted). It can be reverted to its original state using the systemctl unmask command; see the official explanation:This is a stronger version of disable
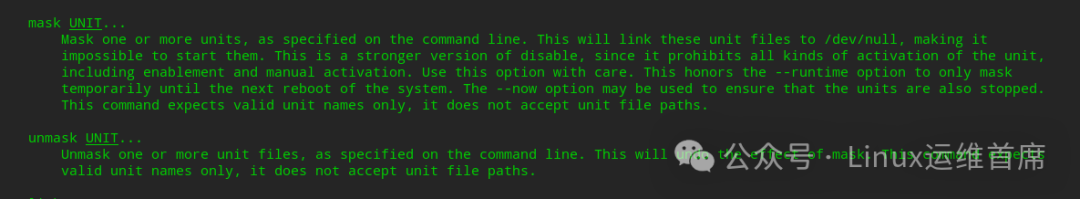
3. Why Use the Mask Parameter?
In domestic Linux server systems and CentOS 7.x, there are two network management services: one is the network service (which is inactive by default), and the other is the NetworkManager service.
Since the NetworkManager service is powerful and convenient to manage, domestic Linux server systems generally use NetworkManager for network management. However, due to unfamiliarity with domestic Linux systems, many continue to use the old network management service, which can lead to conflicts in network service management, causing unnecessary trouble for users.
4. To completely resolve the issue, it is necessary to disable the network service through other means and ensure that users cannot start the network service using the start or restart commands. Below is a verification example using the Tongxin V20 -1070e.
The verification steps are as follows:systemctl status network // Check the status of the network service.systemctl mask network // Disable the network service.systemctl status network // Check the status of the network service.systemctl start network // Attempt to start the network service, which will fail.systemctl restart network // Attempt to restart the network service, which will also fail.systemctl status network // Check the status of the network service.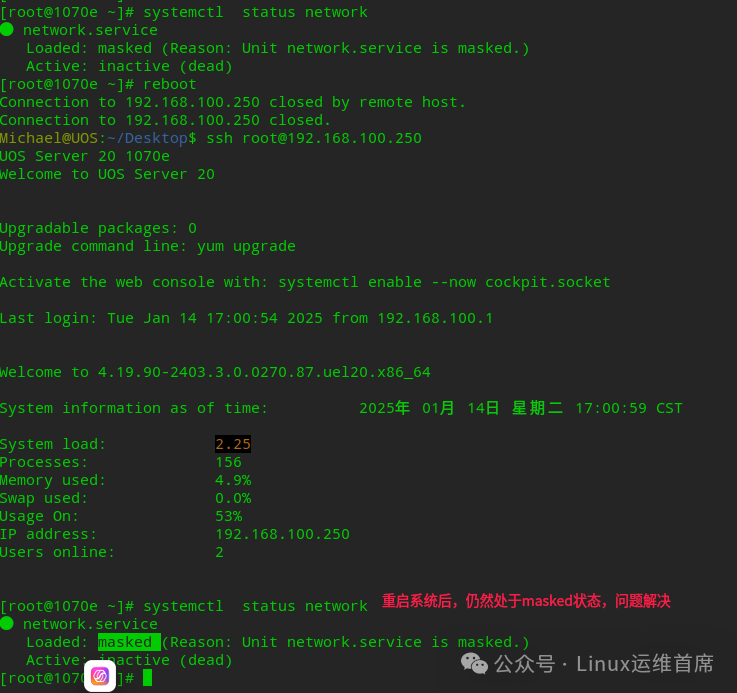
5. After disabling with mask, verify whether it remains in masked state after rebooting the server.