Today’s Sharing
【Introduction】Smart buildings provide viable insights for improving management and comfort, aiming to reduce costs, enhance user comfort, automate energy management, monitor assets, and meet sustainability standards. LoRaWAN offers advantages such as easy deployment, indoor coverage, and low power consumption, providing smart building solutions for new construction and renovation projects.

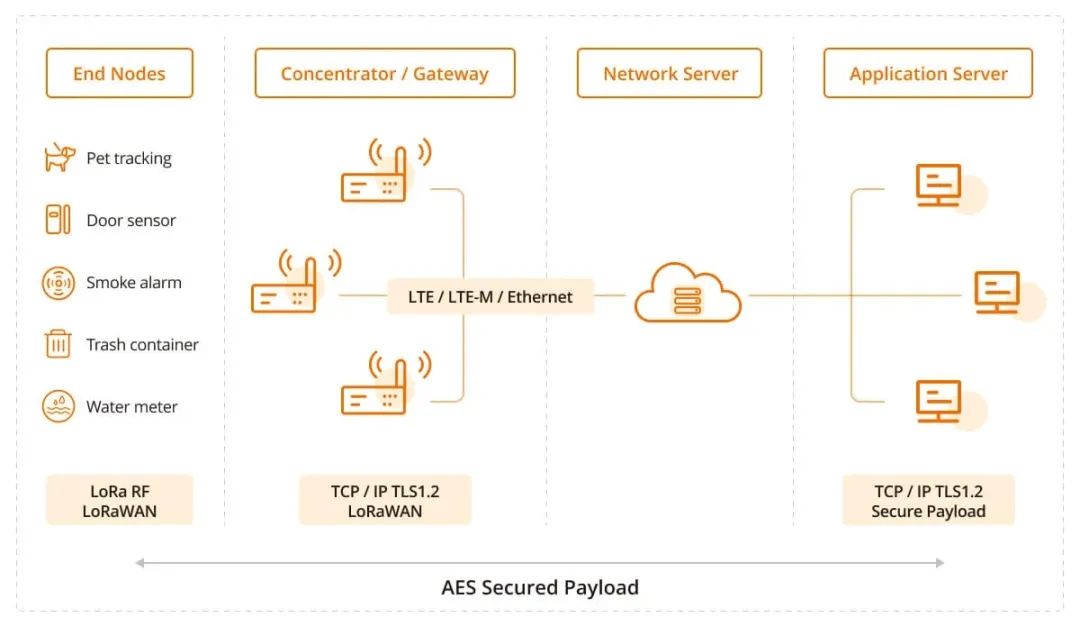
What Are Smart Buildings Using IoT?
How Does LoRaWAN Enable Smart Building Solutions?
Examples of LoRaWAN-Based Smart Building Use Cases
Smart Residential Utility Metering
Indoor Air and Environmental Quality Sensors
Gas Leak Prevention
Real-Time Fire Detection
Building Security
Fault Prediction
Space Optimization
LoRaWAN Smart Building IoT Solutions
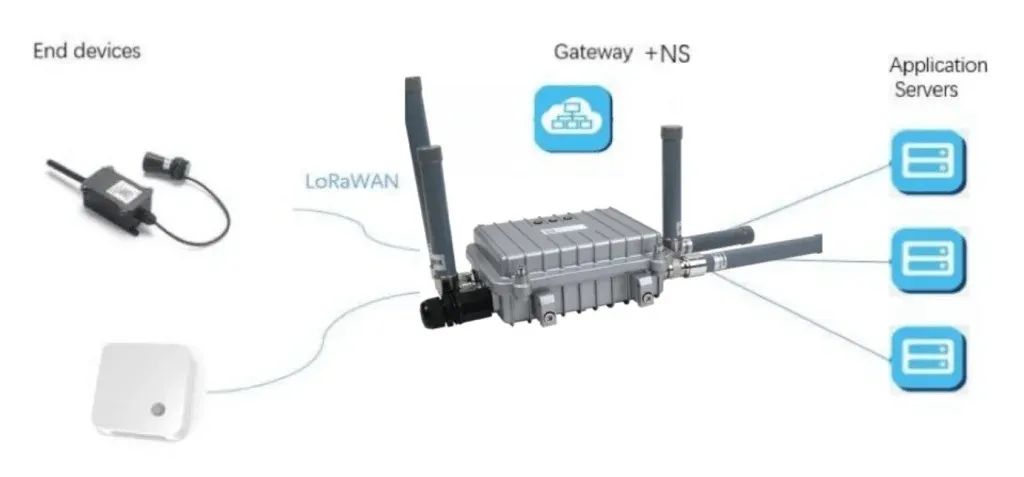
How to Deploy LoRaWAN into BMS Systems?
LoRaWAN-Based BACnet/BACS (Building Automation and Control Systems)
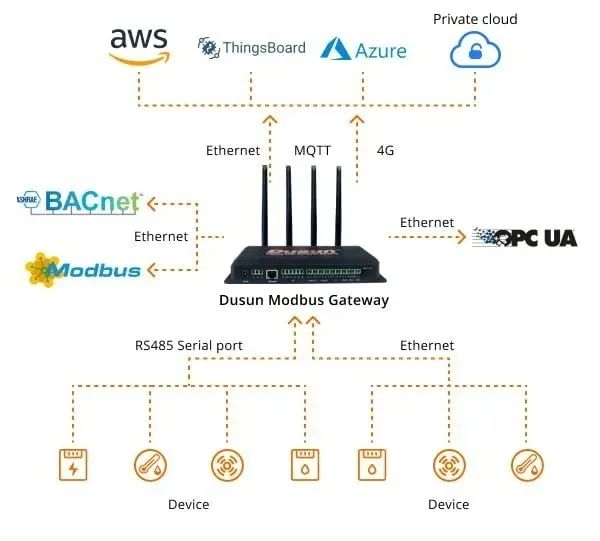
Complementary Networks and BMS Integration
-
Assessment and Planning: Assess the current BMS to identify areas that can benefit from LoRaWAN integration. -
LoRaWAN Network Setup: Strategically deploy LoRaWAN gateways to establish dedicated complementary networks. Install LoRaWAN-supported sensors and devices in areas of interest to collect relevant data. -
Data Transformation and Integration: Develop dedicated servers or software layers to convert LoRaWAN data into formats compatible with BMS (e.g., BACnet). Integrate the decoded data into your BMS, allowing communication between LoRaWAN devices and BMS. -
Data Analysis and Visualization: Utilize integrated data in the BMS to perform advanced analytics and gain insights into building performance. -
Testing and Optimization: Thoroughly test the integration to ensure data accuracy, reliable communication, and correct functionality. Optimize system settings for optimal performance and responsiveness.
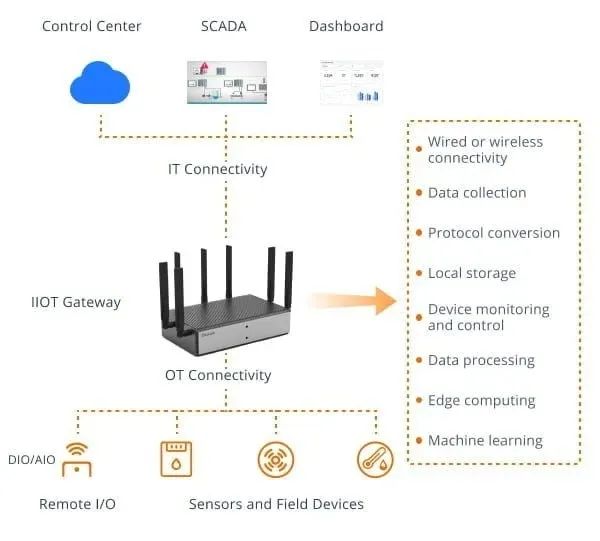
Cloud Integration
-
Select a suitable cloud platform or service provider that meets the organization’s requirements and BMS functionalities. -
Configure IoT devices, sensors, and gateways to securely transmit data to the cloud platform using protocols such as MQTT or HTTP. -
Set up cloud-based storage to securely store incoming BMS data. Organize and structure the data for easy retrieval and analysis. -
Utilize cloud-based analytics tools to process and analyze the collected data. Generate insights, trends, and reports to optimize building performance, energy usage, and maintenance. -
Enable remote access to the BMS via the cloud platform, allowing authorized users to monitor and control building systems from anywhere. Implement user authentication and access control to ensure security. -
Configure automatic alerts and notifications based on predefined thresholds or anomalies detected in the data. Receive real-time alerts via email, SMS, or push notifications for timely issue resolution.
Common Questions and Answers About LoRaWAN Smart Buildings
What is IoT in Smart Buildings?
Can LoRaWAN be used for the Internet?
What is the difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN?
-Upcoming Events-


What Do Matter and Thread Mean for Your Smart Home?
What Do Matter and Thread Mean for Your Smart Home?
How Will Next-Gen Wi-Fi Change Smart Homes?

What Do Matter and Thread Mean for Your Smart Home?
What Do Matter and Thread Mean for Your Smart Home?
The Key to Decarbonizing the Global Building Industry: Efficiency, Electrification, and Equity

What Do Matter and Thread Mean for Your Smart Home?
What Do Matter and Thread Mean for Your Smart Home?
Smart Home Data Privacy Report | Sharing Insights from Thousands