【Hua Bin Note: The day before yesterday, I answered a question from a netizen about the grading of varicoceles, and today I would like to provide a learning resource for everyone.】
Introduction: Varicocele is defined as the dilation of the pampiniform venous plexus beside the testis, accompanied by venous blood reflux.Although it can be asymptomatic and discovered incidentally, varicocele is a relatively common problem among patients seeking medical attention for infertility issues or complaining of chronic scrotal pain or discomfort.
Color Doppler ultrasound (US) is the preferred imaging modality, but the need for imaging itself is controversial.
The European Society of Urogenital Radiology Scrotal and Penile Imaging Working Group (ESUR-SPIWG) conducted a systematic review of the existing literature and published a guideline and recommendations aimed at standardizing the ultrasound imaging of varicoceles. They provided 20 evidence-based recommendations for everyone to learn from:
ESUR-SPIWG Recommendations for Ultrasound Evaluation of Varicoceles
| # | Recommendation | Evidence Level | Recommendation Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gray-scale and Doppler ultrasound modalities can provide the parameters needed for assessing the classification of varicoceles. However, there is no recognized classification system. | 3 | C |
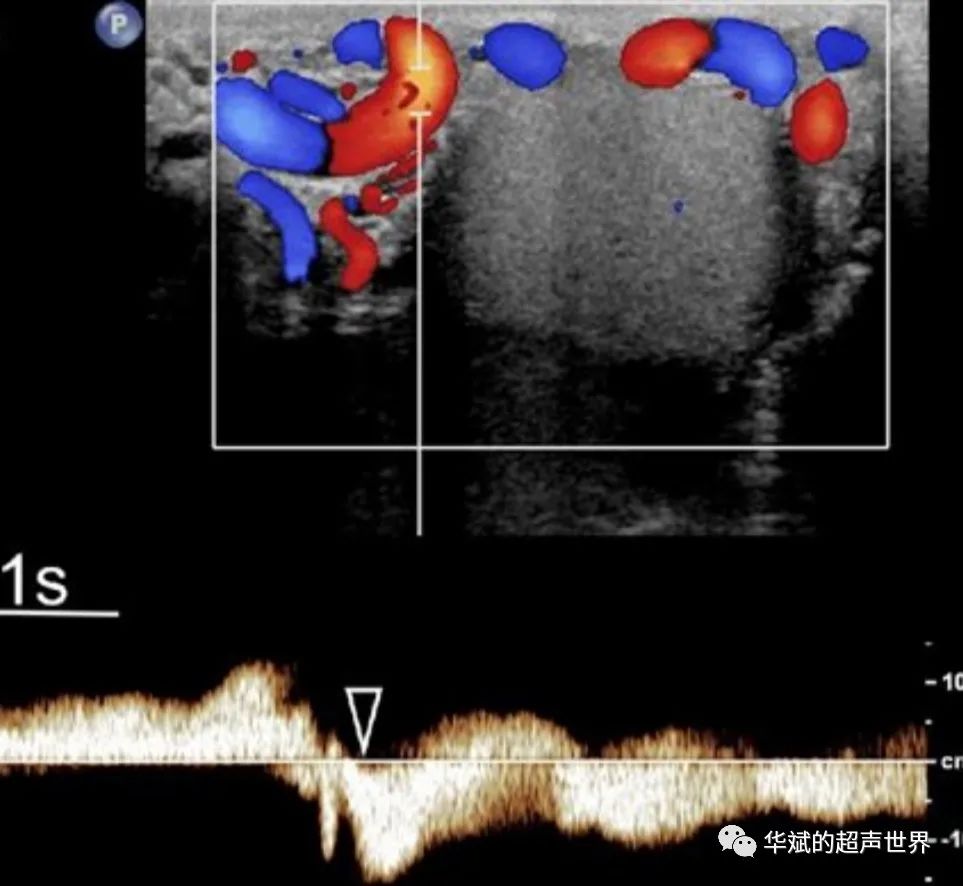
| 2 | Given the wide variability in the measurement methods of venous diameter in varicocele assessment, it is crucial to record the patient’s position, whether the measurement was taken at rest or during the Valsalva maneuver, and the position of the vein relative to the spermatic cord or testis. | 1 | A |
| 3 | It is recommended to measure the maximum vein while the patient is in an upright position and during the Valsalva maneuver, regardless of its location. | 5 | D |
| 4 | When measured during the upright position and Valsalva maneuver, a maximum venous diameter of 3 mm or greater can be considered diagnostic for varicocele. | 2 | B |
| 5 | The testicular volume should be measured in all cases, as it is related to testicular function in infertile patients and those with varicocele. | 1 | A |
| 6 | Precise measurements of the three diameters of the testis are required to estimate testicular volume. The Lambert formula (V= L × W × H × 0.71) is recommended. The mathematical formula used for volume calculation should be reported. | 2 | B |
| 7 | The ultrasound examination for varicocele requires a standardized protocol. Bilateral gray-scale and color Doppler examinations should be performed while the patient is supine and standing, along with spectral Doppler analysis during spontaneous respiration and the Valsalva maneuver. | 2 | B |
| 8 | The most important part of Doppler ultrasound studies is to demonstrate and assess the reflux in patients evaluated for varicocele. | 3 | C |
| 9 | Color Doppler assessment should be supplemented by spectral Doppler analysis. The duration of reflux flow is a fundamental parameter that needs to be measured (evidence level 3, recommendation grade C). The measurement of peak reflux velocity is optional and not required. | 5 | D |
| 10 | Reflux duration of the testicular vein exceeding 2 seconds during standing and the Valsalva maneuver should be considered abnormal. | 4 | C |
| 11 | There is insufficient data to recommend using peak reflux velocity measurement as a factor in determining the need for varicocele repair. | 5 | C |
| 12 | When issuing reports for patients with varicocele, the examination technique should be described. | 1 | A |
| 13 | Grading varicocele according to the Sarteschi classification may assist clinical practice. For standardization purposes, it is recommended to report all US parameters used in the evaluation of the patient. | 5 | D |
| 14 | Assessment of intratesticular blood flow in varicocele patients is an active area of research and may provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of testicular parenchymal injury. However, this assessment cannot currently be recommended for clinical use. | 3 | C |
| 15 | Bilateral color Doppler ultrasound should be performed in patients with left-sided varicocele, as it often shows subclinical right-sided varicocele. | 3 | B |
| 16 | In patients with isolated clinical right-sided varicocele, ultrasound may extend to the abdomen to look for pathology in the abdomen and retroperitoneum, as well as congenital vascular anomalies. | 5 | D |
| 17 | For patients with subclinical varicocele on imaging, it is recommended to follow up all adolescents and young adults who have not undergone surgical repair and have normal semen analysis and testicular volume. | 3 | C |
| 18 | Post-repair ultrasound can be used to determine early postoperative complications. | 3 | C |
| 19 | Semen analysis is the basis for follow-up after varicocele repair. Existing data do not support our routine use. | 1 | A |
| 20 | If semen analysis remains unsatisfactory, color Doppler ultrasound can be used post-varicocele repair to assess testicular volume and identify signs of persistent or recurrent disease. | 2 | B |
Source: Ultrasound evaluation of varicoceles: guidelines and recommendations of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology Scrotal and Penile Imaging Working Group (ESUR-SPIWG) for detection, classification, and grading