@Getting Started with Embedded Linux Using Buildroot – Part 6
-
Configuring QT5 for Embedded Linux in QT Creator -
Adding SAMA5D2 QT5 Configuration in QTCreator -
Simple QT5 Code Demo -
Adding Copilot Plugin in VSCode -
Using Copilot to Generate Reference Source Code -
Using Open Source QT Project as a Template -
Configuring SAMA5D2 Platform -
Demo of Running Effects – Linux PC -
Demo of Running Effects – Running on SAMA5D2 -
Next Episode Preview
This series will create my first runnable Embedded Linux system based on the Buildroot repository provided by Microchip.
This time, I will introduce how to configure the cross-compilation tools and QT5 code library generated by buildroot in QT Creator, and then explain the configuration of the QT5 project to enable cross-compilation and running on the target board.
Configuring QT5 for Embedded Linux in QT Creator
Adding SAMA5D2 QT5 Configuration in QTCreator
<span>Open the installed QT Creator, then select Tools->Options from the main interface:</span>
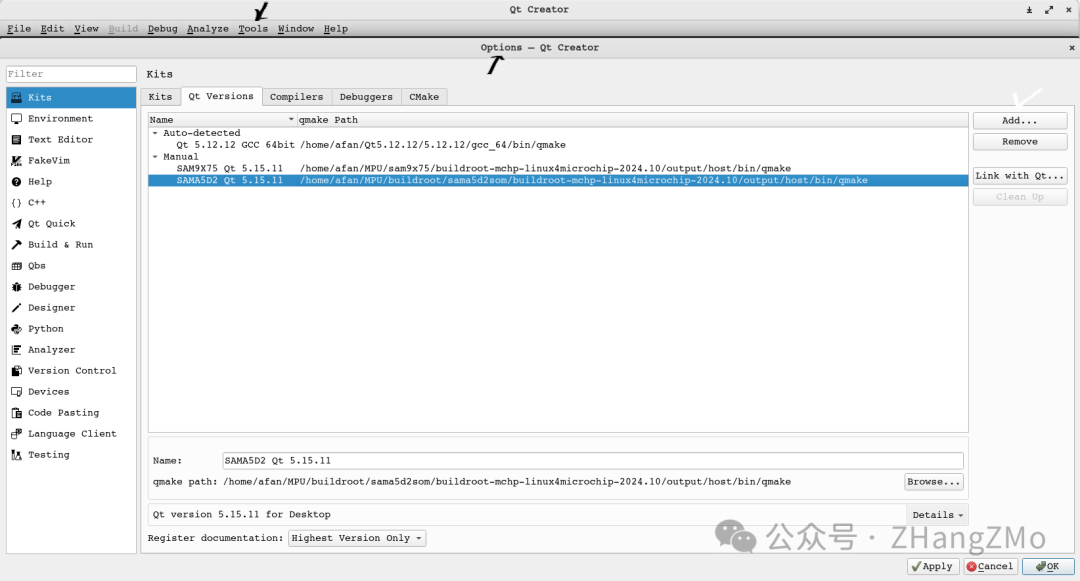
QT Versions Configuration
/home/XXX/MPU/buildroot/sama5d2som/buildroot-mchp-linux4microchip-2024.10/output/host/bin/qmake
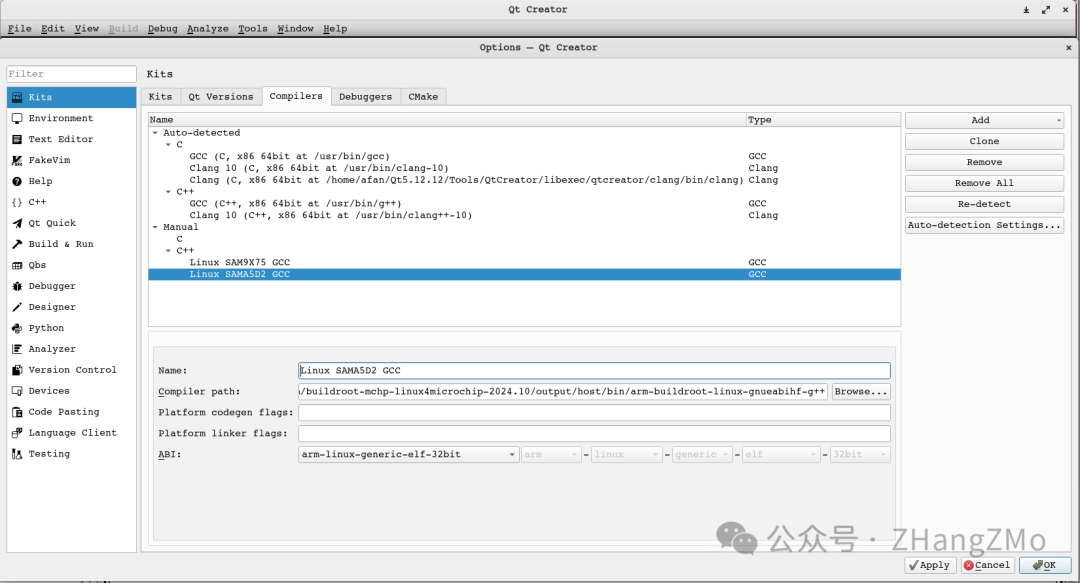
Compiler
/home/XXX/MPU/buildroot/sama5d2som/buildroot-mchp-linux4microchip-2024.10/output/host/bin/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-g++
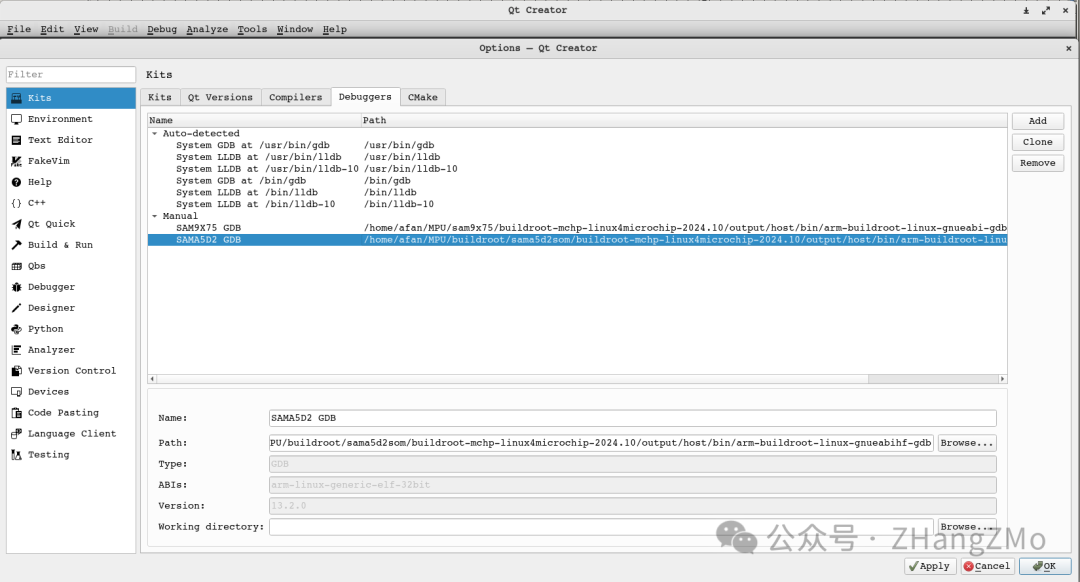
Debuggers
/home/XXX/MPU/buildroot/sama5d2som/buildroot-mchp-linux4microchip-2024.10/output/host/bin/arm-buildroot-linux-gnueabihf-gdb
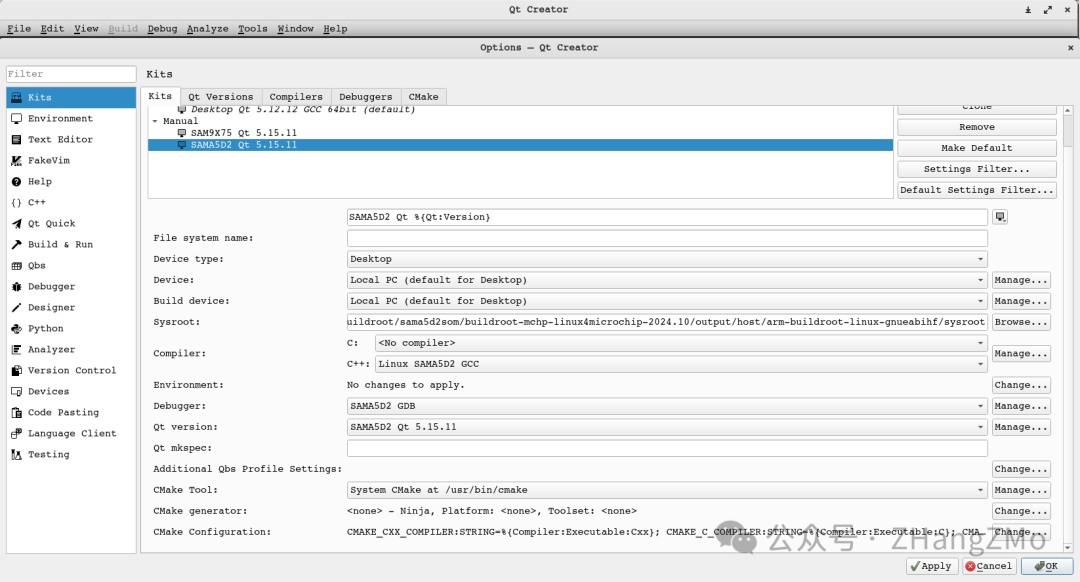
Adding Target Platform SAMA5D2 QT5 Configuration Options
Simple QT5 Code Demo
Adding Copilot Plugin in VSCode
<span>You can add the Copilot plugin in the VSCode marketplace:</span>

Using Copilot to Generate Reference Source Code
For example, use such input information to tell Copilot to help generate demonstration code.
Generate a QT code, the QT version is QT5.8 or higher, need to create a circular interface with a resolution of 800×480, create a clock dial in the center of the graphical interface, the clock dial includes a second hand, a minute hand, and an hour hand, all of which need to rotate according to the change of time. The resolution of the clock interface is 480×480. At the same time, display the current system clock in the upper right corner of the main interface.

<span>Copilot's functionality is powerful enough to allow you to input other requirements in the prompt and generate corresponding code to add to your own project.</span>
Using Open Source QT Project as a Template
Recommended learning open source QT project<span>https://github.com/feiyangqingyun</span>
Download this open source project and open the battery project in QT Creator.
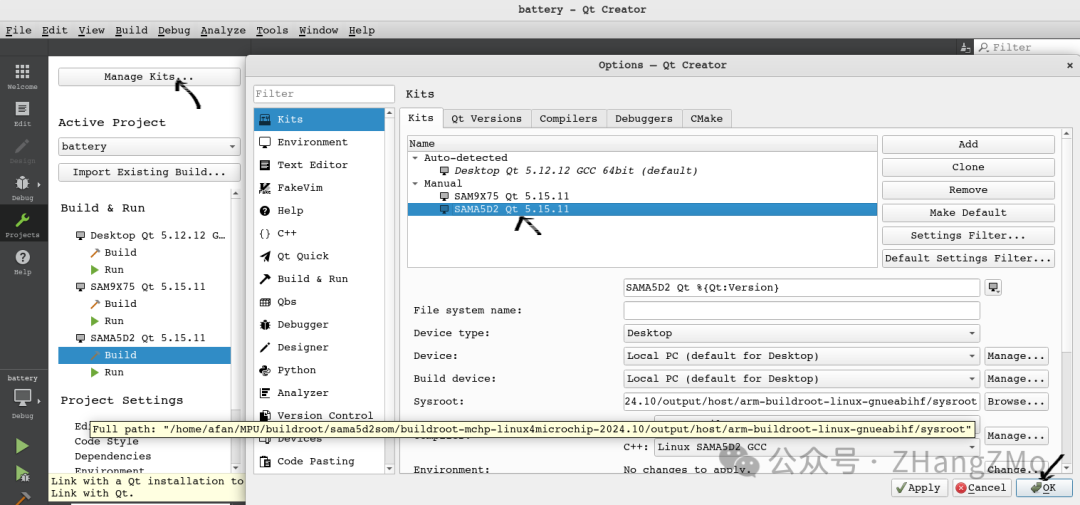
Configuring SAMA5D2 Platform
Add SAMA5D2 configuration under Kits.
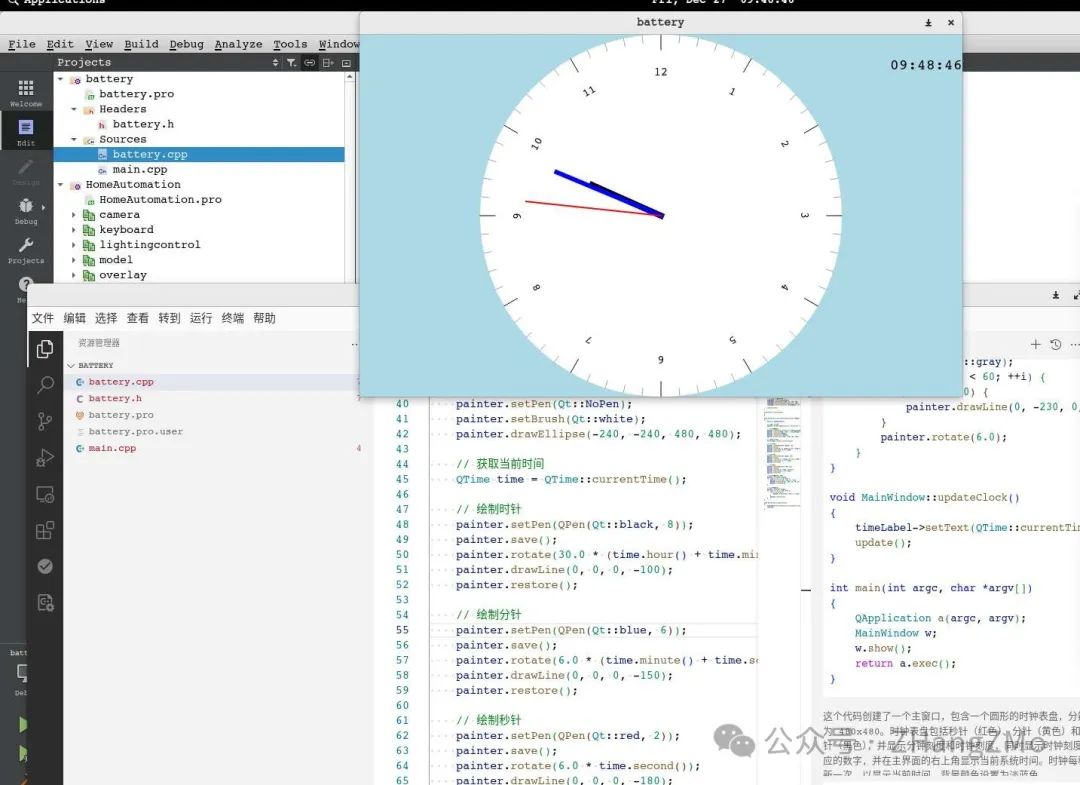
Demo of Running Effects – Linux PC
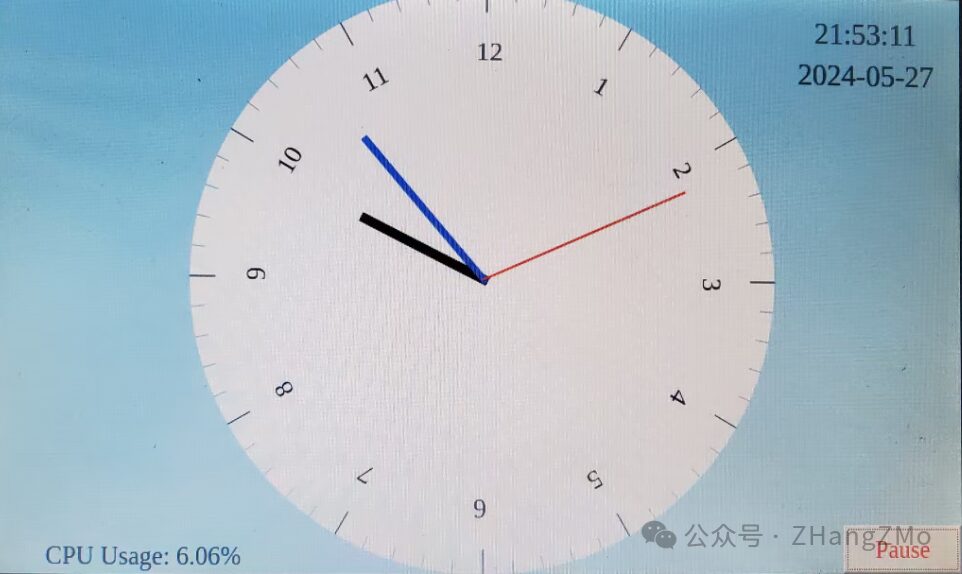
Demo of Running Effects – Running on SAMA5D2
Next Episode Preview
-
Creating a New Linux User Project in Eclipse -
Using GDB for Remote Debugging