(Click the public account above to quickly follow)
Author: Cheng Mo,
www.cnblogs.com/chengmo/archive/2010/10/14/1851434.html
If you have good articles to submit, please click → here for details
The Linux shell has its own set of control statements, including conditional statements (if), loop statements (for, while), and selection statements (case). Below, I will introduce the usage of each statement through examples.
1. Shell Conditional Statements (Usage of if)
The structure of the if statement is [if/then/elif/else/fi]
if condition test statement
then
action
[elif condition
action
else
action
]
fi
If you are not very clear about the condition test statement, you can refer to: Linux shell logical operators and logical expressions detailed explanation.
Shell commands can be separated by semicolons or newline characters. If you want to write multiple commands in one line, you can separate them with ‘;’.
For example:
[chengmo@centos5 ~]$ a=5;if [[ a -gt 4 ]] ;then echo ‘ok’;fi;
ok
Example: (test.sh)
#!/bin/sh
scores=40;
if [[ $scores -gt 90 ]]; then
echo “very good!”;
elif [[ $scores -gt 80 ]]; then
echo “good!”;
elif [[ $scores -gt 60 ]]; then
echo “pass!”;
else
echo “no pass!”;
fi;
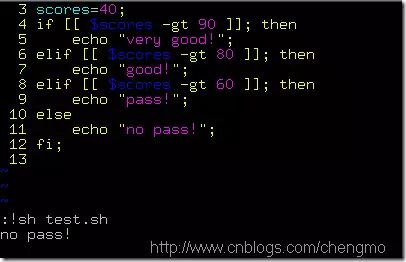
Condition tests include: [[]], [], test, etc. Note that there should be a space between [[]] and the variable.
2. Loop Statements (Usage of for, while, until):
Usage of for loop (for/do/done)
Syntax structure:
1. for … in statement
for variable in seq string
do
action
done
Note: The seq string is separated by space characters, and each time for…in reads, it will sequentially assign the read value to the preceding variable.
Example (testfor.sh):
#!/bin/sh
for i in $(seq 10); do
echo $i;
done;
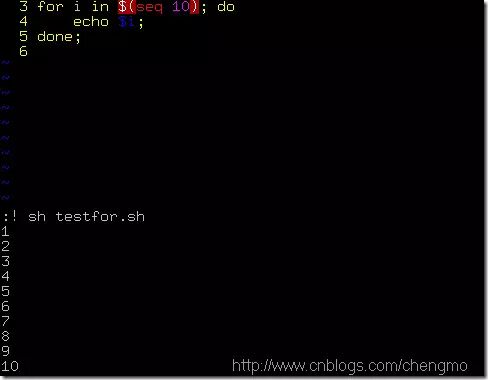
seq 10 generates a space-separated string of 1 2 3 … 10.
2. for((assignment; condition; operation statement))
for((assignment; condition; operation statement))
do
action
done;
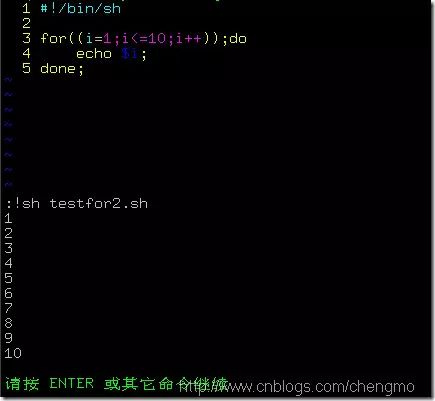
Example (testfor2.sh):
#!/bin/sh
for((i=1;i<=10;i++));do
echo $i;
done;
-
Usage of while loop (while/do/done)
Structure of while statement
while condition statement
do
action
done;
Example 1:
#!/bin/sh
i=10;
while [[ $i -gt 5 ]];do
echo $i;
((i–));
done;
Running result: ========================
sh testwhile1.sh
10
9
8
7
6
Example 2: (Loop reading file content:)
#!/bin/sh
while read line;do
echo $line;
done < /etc/hosts;
Running result: ===================
sh testwhile2.sh
# Do not remove the following line, or various programs
# that require network functionality will fail.
127.0.0.1 centos5 localhost.localdomain localhost
-
Until loop statement
Syntax structure:
until condition
do
action
done
This means: until the condition is met, exit. Otherwise, execute action.
Example (testuntil.sh):
#!/bin/sh
a=10;
until [[ $a -lt 0 ]];do
echo $a;
((a–));
done;
Result:
sh testuntil.sh
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
3. Shell Selection Statements (Usage of case, select)
Usage of case selection statement (case/esac)
Syntax structure
case $arg in
pattern | sample)
# arg in pattern or sample
;;
pattern1)
# arg in pattern1
;;
*)
#default
;;
esac
Note: pattern1 is a regular expression, and the following characters can be used:
* Any substring
? Any character
[abc] One of a, b, or c
[a-n] Any character from a to n
| Multiple choices
Example:
#!/bin/sh
case $1 in
start | begin)
echo “start something”
;;
stop | end)
echo “stop something”
;;
*)
echo “Ignorant”
;;
esac
Running result: ======================
testcase.sh start
start something
-
Usage of select statement (produces menu selection)
Syntax:
select variable name in seq variable
do
action
done
Example:
#!/bin/sh
select ch in “begin” “end” “exit”
do
case $ch in
“begin”)
echo “start something”
;;
“end”)
echo “stop something”
;;
“exit”)
echo “exit”
break;
;;
*)
echo “Ignorant”
;;
esac
done;
Running result:
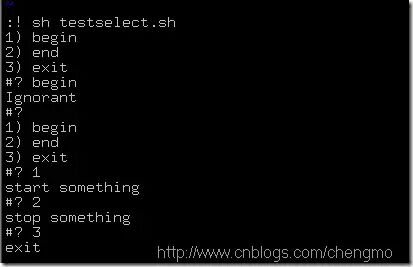
Note: select is a loop selection, generally used with case statements.
The above are the control statements of the shell: condition, loop, and selection. Welcome to discuss and exchange!
Did you gain something from this article? Please share it with more people
Follow ‘Linux Enthusiasts’ to enhance your Linux skills