Sources of DAC Phase Noise
For high-speed DACs, phase noise primarily comes from the following aspects: clock noise, power supply noise, as well as internal noise and interface noise.
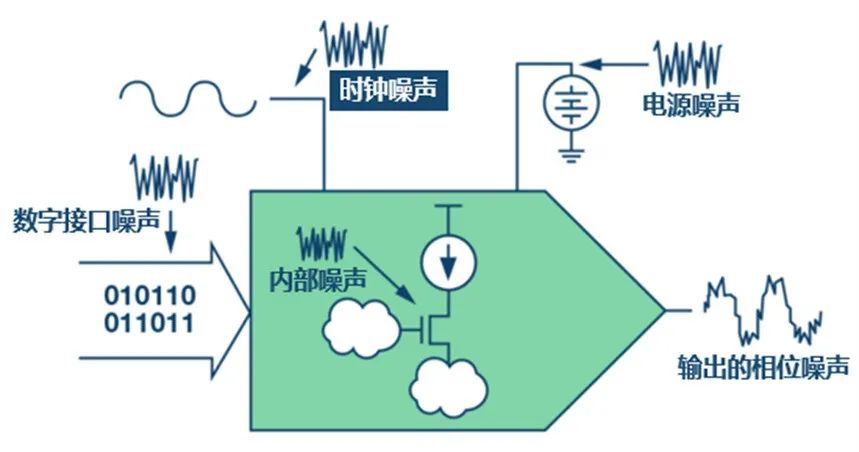
Figure 1: Sources of DAC Phase Noise (Image Source: ADI)
The two most important sources are clock noise and power supply noise. This article will mainly introduce the impact of clock noise on DAC phase noise.
Learn more about ADI’s DAC chip products
Click here
Generation of Clock Phase Noise
The DAC clock is the primary source of phase noise in the DAC. The clock determines when to send the next sample, so any noise in the phase (or timing) will directly affect the output phase noise.
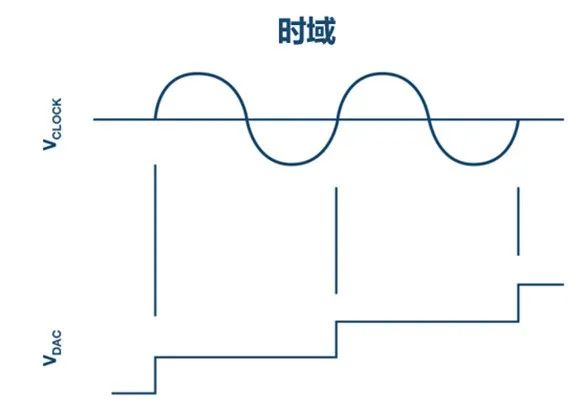
Figure 2: Correlation Between Clock and Phase Noise (Image Source: ADI)
As shown in the figure above, the effect of the clock on phase noise can be viewed as the multiplication of discrete values by a rectangular function defined by the clock timing.
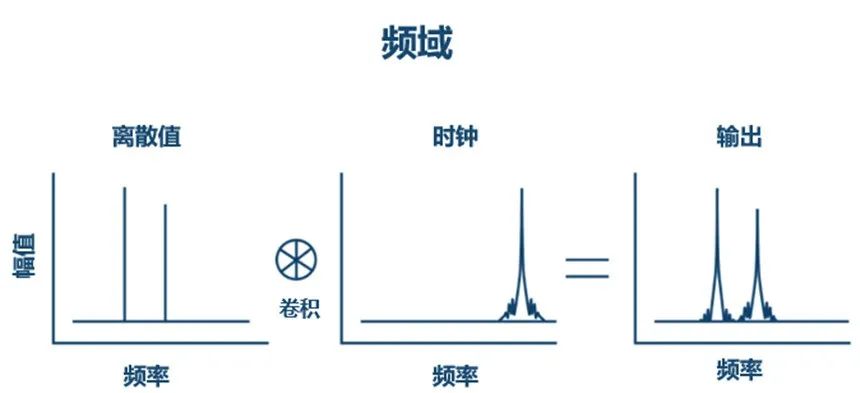
Figure 3: Convolution of Phase Noise (Image Source: ADI)
As shown in the figure above, in the frequency domain, multiplication becomes convolution. As a result, the desired spectrum is corrupted by clock phase noise.
Signal Frequency and Phase Noise
The ratio of signal frequency to clock frequency amplifies or diminishes the noise relative to the carrier; for every halving of the signal frequency, the noise improves by 6 dB. To demonstrate this, the following figure shows the phase noise of a modulated clock signal (precision controlled) with a slight 100kHz phase offset at different frequencies (5GHz, 1GHz, 500MHz) to simulate phase noise and examine the relationship between signal frequency and phase noise.
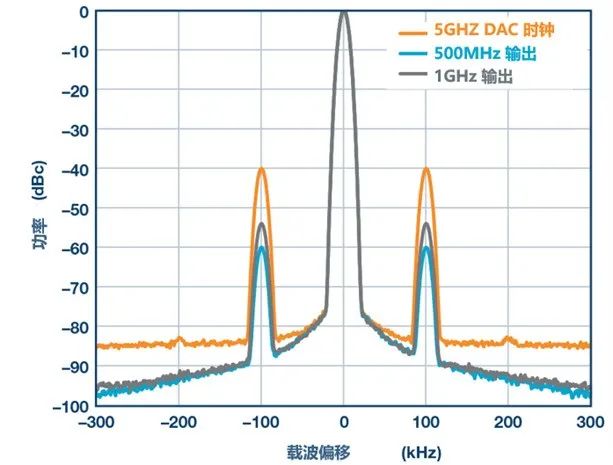
Figure 4: Phase Noise of Clock Output with 100kHz Phase Modulation (Image Source: ADI)
We can observe a 20dB drop from the 5GHz clock to the 500MHz DAC output, and a 6dB increase from the 500MHz output to the 1GHz output.
Reducing DAC Phase Noise
Selecting a high-performance crystal oscillator can achieve significant results in dealing with phase noise.
The Digi-Key Chinese technical forum gathers a wide array of technical resources needed by engineers in the electronics field, including many posts related to crystal oscillator selection and reducing DAC phase noise. For details, please visit——Basic Selection of Electronic Components – Crystal Oscillator.
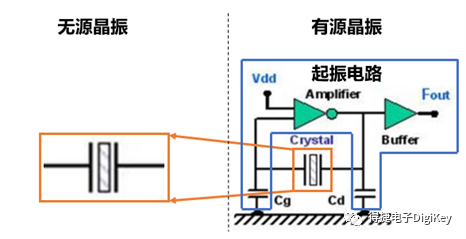
Crystal oscillators can be divided into active crystal oscillators and passive crystal oscillators, the table below compares the two types of oscillators:
|
Passive Crystal Oscillator |
Active Crystal Oscillator |
|
|
Pins |
Generally 2 pins (You may see 4-pin packages of passive crystal oscillators, but usually only 2 of the 4 pins are used) |
Generally 4 pins or more |
|
Can it self-oscillate? |
Cannot oscillate by itself Requires external oscillation circuit |
Can self-oscillate Includes oscillation circuit |
|
Voltage |
Voltage is variable, determined by external circuit |
Generally fixed voltage, good signal quality, relatively stable |
|
Physical Diagram |
Passive Crystal Oscillator
|
Active Crystal Oscillator
|
|
Schematic |
|
A detailed analysis of the characteristics and typical applications of different types of crystal oscillators is provided in the table below:
|
Crystal Oscillator Type |
Characteristics |
Applications |
|
Standard Crystal Oscillator (XO) |
The most basic type is the crystal oscillator |
Widely used |
|
Temperature Compensated Oscillator (TCXO) |
Temperature compensation is performed to stabilize the output frequency |
Suitable for environments with significant temperature variations, dynamic applications. For example, cellular phones, smartphones, etc. |
|
Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCXO) |
The output frequency is controlled by the input voltage |
Commonly found in phase-locked loops, mixers, signal generators, etc. |
|
Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator (OCXO) |
Maintains a constant temperature for the crystal oscillator, thus stabilizing the output frequency |
Commonly used in situations requiring high frequency stability |
If you want to learn how to quickly select low phase noise crystal oscillators through the Digi-Key website, you can refer to the following article——How to Choose Low Phase Noise Crystal Oscillators?
Summary
In summary, understanding the causes of noise allows us to treat the problem effectively. Clock noise has a significant impact on DAC phase noise; thus, selecting a high-precision crystal oscillator may be the simplest and most feasible solution.
Finally, if you like this article, please share and like it! You are also welcome to leave comments for discussion at the end of the article.
For more articles on noise technology, please refer to the following articles:
-
Propagation Path of DAC Power Supply Phase Noise
-
What is Phase Noise?
-
Measuring Power Supply Noise with Probes
-
Reducing Inductive Noise by Optimizing Wire Selection and PCB Layout
-
Eliminating Noise in High-Frequency Switching Applications
[This Month’s Points Lottery Activity is Here]
In 2022, on the last Wednesday of each month
the points mall will launch a limited-time “Points Lottery” activity
DK members can exchange points for “lottery chances”
Participate in the lucky draw
The lottery prizes vary each month, with surprises at any time!
This month’s prize is——
Clip-on Quiet USB Fan

Note
This month’s points lottery time:
From July 27 to August 3
Announcement of lottery results:
August 17


DK members have many benefits
Points can be exchanged for various gifts

If you have any questions, please contact Digi-Key
Digi-Key‘s customer service team

400-920-1199

Service Support > Contact Customer Service > WeChat Customer Service


QQ Online Real-time Consultation | QQ Number: 4009201199

400-882-4440

852-3104-0500



↙
Click on “Read the original text” below for more