Soy protein isolate (SPI) is a major source of high-quality protein, low in cost, and has high nutritional value. The use of polyphenols to improve the functional properties of proteins has become a research hotspot. Blueberry anthocyanins (BANs) are a type of polyphenolic substance with rich biological activity. The interaction between BANs and SPI can enhance the functional activity of SPI, presenting broad application prospects. Research shows that, in addition to external factors such as temperature, pH, and ionic concentration, some physical processing techniques, such as ultrasound, high pressure, and pulsed electric fields, can also affect the interaction between anthocyanins and proteins by altering the structure and function of proteins.High-power pulsed microwave (HPPM), as a new food processing technology, can generate periodic high-frequency pulsed microwaves by applying high-pressure pulses to a magnetron, characterized by low average power, low energy consumption, high efficiency, instantaneous high energy, and intermittent action.
Researchers such as Wu Han, Liu Xiaoli*, and Zhou Jianzhong from the Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences mainly utilize the physical field of HPPM as a means to enhance mass transfer, studying its role in the modification of SPI by BANs. On one hand, they explore the effects of HPPM on the processing characteristics and functional activity of SPI-BANs complexes; on the other hand, they further clarify the application effects of the novel soybean protein ingredient—high-power pulsed microwave-soy protein isolate-anthocyanins (HPPM-SPI-BANs) complex in chiffon cakes, providing a theoretical reference for in-depth exploration of the mechanism of physical field synergistic modification of macromolecular proteins, while offering new ideas for expanding the application scope of HPPM in the food field.


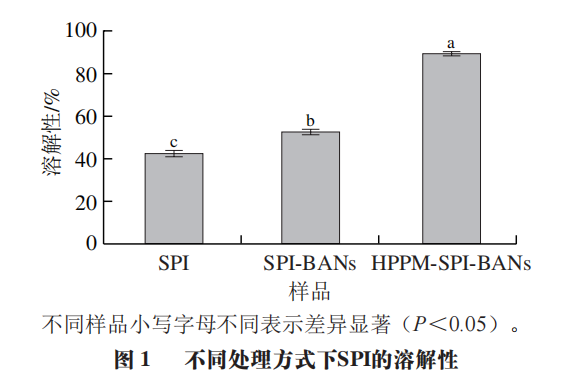
1 Impact of HPPM and Anthocyanins on SPI Solubility
As shown in Figure 1, the solubility of SPI is 42.44%, and compared to the control SPI, the solubility of the SPI-BANs complex significantly increased by 0.39 times (P<0.05), which may be due to the interaction between anthocyanins and soybean protein, causing changes in the protein structure, unfolding of peptide chains, and exposure of hydrophobic groups. Additionally, under HPPM treatment conditions, the solubility of the HPPM-SPI-BANs complex increased by 1.11 times, indicating that physical field treatment may disrupt the secondary structure of proteins, altering β-folding and α-helix, making it easier for water molecules to enter the protein and interact with its molecules, thereby enhancing protein solubility.
2 Effects of HPPM Waves and Anthocyanins on SPI Functional Properties
Effects of HPPM Waves and Anthocyanins on SPI Foaming and Foam Stability
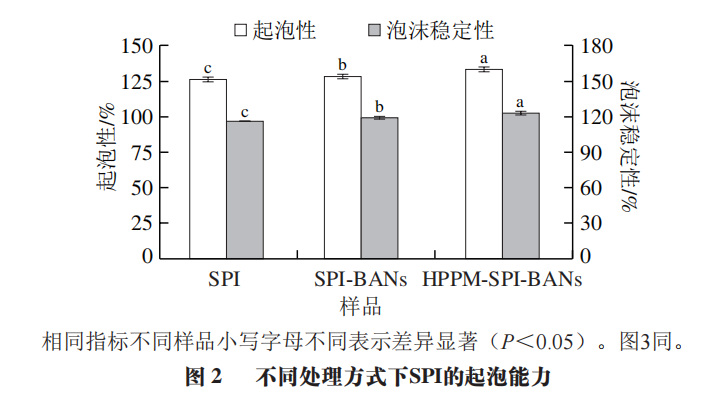
Based on the rapid diffusion and structural unfolding at the air-water interface, the surface tension of the protein decreases, resulting in foaming behavior. However, the spatial conformation and surface charge density can alter the secondary and tertiary structures of SPI, affecting the protein’s foaming function. As shown in Figure 2, the foam stability of the SPI-BANs complex is significantly higher than that of SPI (P<0.05), which may be related to the structural changes of the protein after the interaction with anthocyanins. Furthermore, the foaming ability and foam stability of HPPM-SPI-BANs are significantly higher than those of SPI and SPI-BANs (P<0.05), indicating that high-power pulsed microwave treatment may enhance the flexibility of the protein structure, leading to lower surface tension, allowing the complex to form more elastic bubbles at the air-liquid interface, adsorbing at the gas-water interface, demonstrating that HPPM treatment in synergy with anthocyanins can more effectively improve the foaming function of SPI.
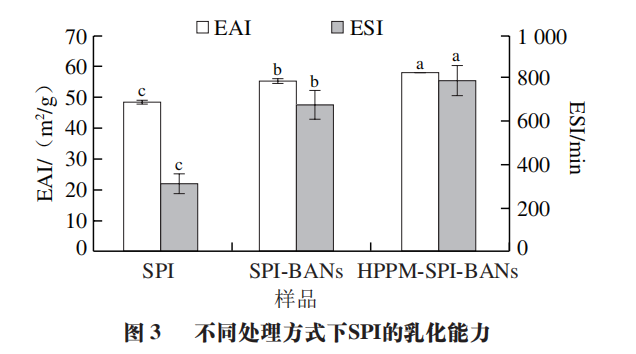
Effects of HPPM Waves and Anthocyanins on SPI Emulsifying and Emulsion Stability
Figure 3 shows the emulsifying and emulsion stability analysis results for SPI, SPI-BANs, and HPPM-SPI-BANs. At the same mass concentration, the EAI and ESI of SPI-BANs are significantly higher than those of SPI (P<0.05), which may be due to the structural changes of the protein after the binding with anthocyanins, increasing spatial repulsion between droplets and altering surface charge. For HPPM-SPI-BANs, its EAI and ESI are significantly higher than those of SPI-BANs, indicating that HPPM treatment can stretch the protein structure, making the chains more flexible, conducive to molecular rearrangement at the interface, while enhancing the intermolecular forces between proteins and anthocyanins, improving the hydrophilicity and emulsifying ability of the protein.
3 Effects of HPPM Waves and Anthocyanins on SPI Antioxidant Activity
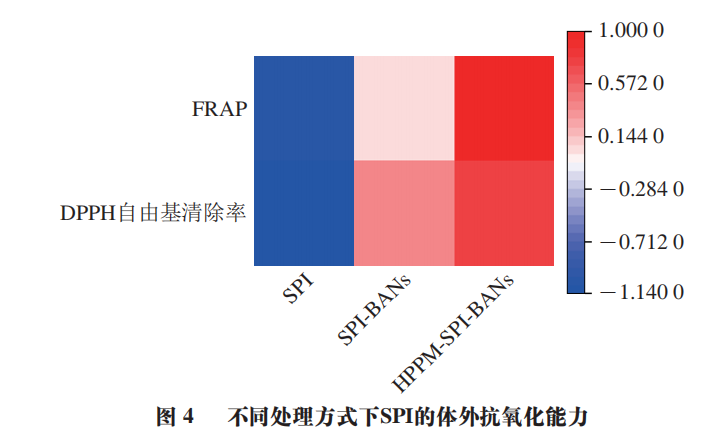 Heat map analysis of the antioxidant capacities of SPI, SPI-BANs, and HPPM-SPI-BANs is shown in Figure 4. The color depth in the heat map indicates the strength of the samples’ antioxidant capacity, with SPI exhibiting almost no antioxidant capacity. In terms of DPPH radical scavenging ability, HPPM-SPI-BANs show significantly higher scavenging ability than SPI and SPI-BANs, with SPI-BANs also significantly higher than SPI (P<0.05). The trend of iron ion reduction ability among the three samples is consistent with that of DPPH radical scavenging ability. Thus, the enhancement of the antioxidant capacity of the complex mainly comes from the action of anthocyanins, which possess strong antioxidant activity and can impart higher functional activity to SPI through interaction with proteins. Furthermore, the antioxidant activity of HPPM-SPI-BANs is significantly higher than that of SPI-BANs, as HPPM and other physical fields can effectively promote the binding of SPI with BANs, increasing the binding rate of anthocyanins in the complex, while exposing more buried reducing groups in the proteins, thereby greatly enhancing the antioxidant activity of the complex. In summary, treating SPI with HPPM in synergy with BANs can more effectively impart functional activity to SPI. The resulting complex HPPM-SPI-BANs can also serve as a novel protein ingredient in the food industry to enhance the antioxidant activity of products.
Heat map analysis of the antioxidant capacities of SPI, SPI-BANs, and HPPM-SPI-BANs is shown in Figure 4. The color depth in the heat map indicates the strength of the samples’ antioxidant capacity, with SPI exhibiting almost no antioxidant capacity. In terms of DPPH radical scavenging ability, HPPM-SPI-BANs show significantly higher scavenging ability than SPI and SPI-BANs, with SPI-BANs also significantly higher than SPI (P<0.05). The trend of iron ion reduction ability among the three samples is consistent with that of DPPH radical scavenging ability. Thus, the enhancement of the antioxidant capacity of the complex mainly comes from the action of anthocyanins, which possess strong antioxidant activity and can impart higher functional activity to SPI through interaction with proteins. Furthermore, the antioxidant activity of HPPM-SPI-BANs is significantly higher than that of SPI-BANs, as HPPM and other physical fields can effectively promote the binding of SPI with BANs, increasing the binding rate of anthocyanins in the complex, while exposing more buried reducing groups in the proteins, thereby greatly enhancing the antioxidant activity of the complex. In summary, treating SPI with HPPM in synergy with BANs can more effectively impart functional activity to SPI. The resulting complex HPPM-SPI-BANs can also serve as a novel protein ingredient in the food industry to enhance the antioxidant activity of products.
4 Effects of HPPM-SPI-BANs on Cake Baking Characteristics
As shown in Table 1, adding HPPM-SPI-BANs significantly inhibits water loss from the cake (P<0.05). Meanwhile, the normal moisture content of chiffon cakes should be between 35% and 44%, with an optimal moisture content of 39% to 40%. By incorporating HPPM-SPI-BANs, which have higher foaming and emulsifying abilities, to replace part of the egg white protein in the cake, the moisture content of the cake can increase to 39.25%, which falls within the optimal moisture range, resulting in better texture and flavor of the cake, with the baking loss rate significantly reduced from 30.14% to 26.88% (P<0.05).
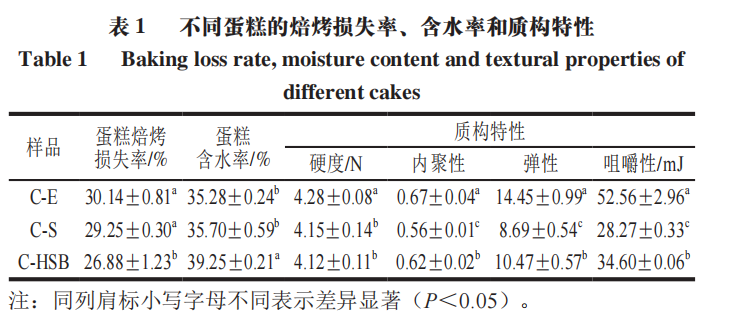
Texture characteristics are also an important indicator of cake quality. The impact of HPPM-SPI-BANs on the texture characteristics of the cake is shown in Table 1. The addition of HPPM-SPI-BANs can enlarge the internal pores of the cake, weakening the support against forces, significantly reducing the hardness of the cake (from 4.28 N to 4.12 N (P<0.05)). For chewiness, it is also negatively correlated with cake quality. When HPPM-SPI-BANs are added, the chewiness of the cake significantly decreases (P<0.05), making the texture softer. Compared to SPI, the addition of HPPM-SPI-BANs can also significantly enhance the cohesiveness and elasticity of the cake, increasing from 0.56 and 8.69 to 0.62 and 10.47 (P<0.05), indicating that the internal binding force of the cake has improved, making the internal texture richer and more elastic. Studies indicate that the change in cake hardness is directly related to the aging of starch molecules; the sensory quality of chiffon cake depends to some extent on its hardness and chewiness, with the softness of the core tissue inversely proportional to hardness and chewiness, and directly proportional to elasticity. The above results indicate that adding HPPM-SPI-BANs can significantly improve the baking loss rate, moisture content, and hardness of chiffon cakes compared to cakes C-E and C-S, and the cohesiveness, elasticity, and chewiness are significantly better than cake C-S, thus enhancing the cake quality.
5 Effects of HPPM-SPI-BANs on Cake Antioxidant Activity
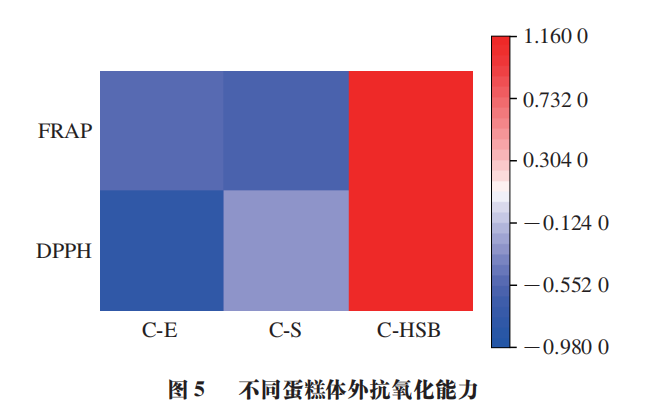 As shown in Figure 5, after replacing part of the egg white with HPPM-SPI-BANs, the antioxidant capacity of the cake extracts is significantly higher than that of the cakes C-E and C-S without HPPM-SPI-BANs. The DPPH radical scavenging rate increased by 3.56 times and 1.29 times, respectively. In terms of iron ion reduction ability, the cake with HPPM-SPI-BANs is 3.79 times and 4.36 times that of cakes C-E and C-S, respectively. The novel protein ingredient HPPM-SPI-BANs, due to its active component anthocyanins, exhibits good antioxidant capacity, which not only improves the baking quality of the cake but also endows it with strong functional activity. Previous studies have shown that replacing part of the egg white with SPI in the cake can balance the amino acid levels of the product, enhancing the nutritional value of the cake. The addition of HPPM-SPI-BANs not only improves the cake’s texture but also increases its added value, allowing the product to meet the higher demands of the current consumer market.
As shown in Figure 5, after replacing part of the egg white with HPPM-SPI-BANs, the antioxidant capacity of the cake extracts is significantly higher than that of the cakes C-E and C-S without HPPM-SPI-BANs. The DPPH radical scavenging rate increased by 3.56 times and 1.29 times, respectively. In terms of iron ion reduction ability, the cake with HPPM-SPI-BANs is 3.79 times and 4.36 times that of cakes C-E and C-S, respectively. The novel protein ingredient HPPM-SPI-BANs, due to its active component anthocyanins, exhibits good antioxidant capacity, which not only improves the baking quality of the cake but also endows it with strong functional activity. Previous studies have shown that replacing part of the egg white with SPI in the cake can balance the amino acid levels of the product, enhancing the nutritional value of the cake. The addition of HPPM-SPI-BANs not only improves the cake’s texture but also increases its added value, allowing the product to meet the higher demands of the current consumer market.
6 Effects of HPPM-SPI-BANs on Cake Storage Quality
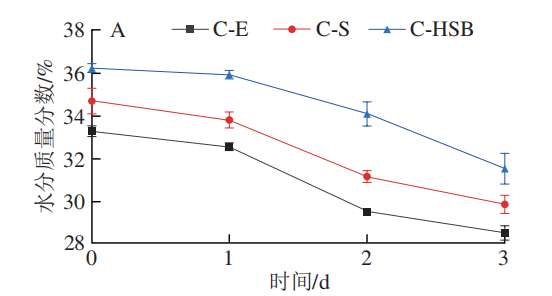
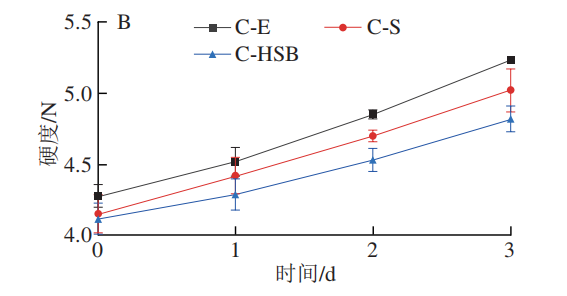
Effects of HPPM-SPI-BANs on Cake Moisture Quality Fraction and Hardness
As shown in Figure 6A, adding HPPM-SPI-BANs can improve the moisture quality fraction of the cake, maintaining a higher moisture state, which is higher than cakes C-E and C-S within 1 to 3 days, positively contributing to preventing the increase in cake hardness. As shown in Figure 6B, the hardness of different cakes significantly increases during the storage period, ultimately reaching 4.75 to 5.25 N, and the trend of hardness change for cakes with HPPM-SPI-BANs is slower than that of cakes C-E and C-S, maintaining at the lowest level, indicating that HPPM-SPI-BANs can effectively resist issues such as starch retrogradation during cake storage, thus improving the storage quality of chiffon cakes. Xia Shuang utilized ultrasound and glycation-modified soybean protein, applying it to heavy oil cakes, also improving the shelf life quality of the cake.
Effects of HPPM-SPI-BANs on Cake Aging Rate
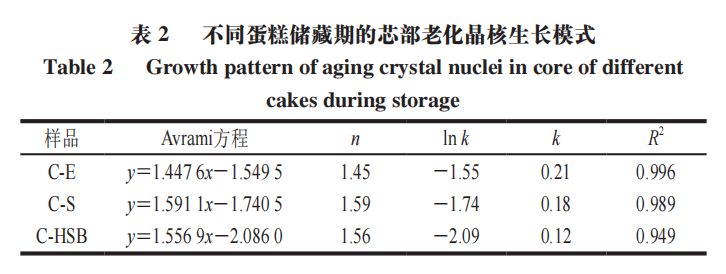
Due to the crystallization during the starch aging process exhibiting characteristics of polymer crystallization, the analysis of the growth pattern of aging nuclei in the cake core during storage can be conducted. The results are shown in Table 2. Within a certain temperature range (-4 to 35 °C), the Avrami index n can be divided into two intervals, where the dimension of crystal growth and its nucleation time determine the size of this value. When n<1, crystallization is primarily instantaneous nucleation; when 1< n≤2, crystallization is primarily spontaneous nucleation. The values of n for different cakes are all within the (1,2) interval, indicating that the retrogradation phenomenon of branched starch in the cake core during storage is mainly formed through spontaneous nucleation. Additionally, the aging rate constant k is closely related to the speed of crystal growth and the density of nuclei, providing a range of information about the formation and growth processes of nuclei. The addition of HPPM-SPI-BANs significantly reduces the k value to just 0.12, which is less than that of cakes C-E and C-S, indicating that HPPM-SPI-BANs can effectively slow the aging rate of the cake core, making it less prone to aging.
This experiment is based on the interaction between SPI and anthocyanins, combined with HPPM physical field treatment, clarifying that HPPM in synergy with anthocyanins can more effectively improve the physical properties of SPI (such as solubility, foaming ability, foam stability, emulsifying ability, and emulsion stability). The resulting HPPM-SPI-BANs complex exhibits higher antioxidant capacity, endowing SPI with the potential to be developed into a new functional food ingredient. By applying HPPM-SPI-BANs in the cake-making process, it is confirmed that this complex can significantly improve the texture characteristics and baking properties of chiffon cakes, enhance their functional activity, and inhibit moisture loss during storage, delaying the aging rate of the cake. This research is beneficial for further realizing the comprehensive utilization of plant protein resources, providing theoretical and scientific basis for gradually expanding the application scope of new non-thermal processing technologies such as HPPM.

Liu Xiaoli, female, PhD, researcher, master’s supervisor. Currently the head of the Food Bioengineering Innovation Team at the Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Mainly engaged in research on functional food bioprocessing, non-thermal processing and cold sterilization technology, and biological preservation of agricultural products.In the past five years, she has led several provincial and ministerial-level projects, including the National Natural Science Foundation project, Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation, Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program, Jiangsu Provincial Agricultural Independent Innovation Fund project, and the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security’s Science and Technology Activities Project for Overseas Students, with over 20 authorized national invention patents, and published over 100 research papers in domestic and international journals, including over 40 SCI-indexed papers, drafted and formulated one industry standard for the Ministry of Agriculture, and three local standards for Jiangsu Province.Her research achievements have won the Jiangsu Provincial Science and Technology Award (third prize), Jiangsu Provincial Agricultural Science and Technology Award (second prize), Ministry of Agriculture Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Award (second prize), China Food Industry Association Science and Technology Award (first prize), and China Industry-University-Research Cooperation Innovation Achievement Award (innovation award).

Zhou Jianzhong, PhD, master supervisor, level-3 researcher. Mainly engaged in research on deep processing and comprehensive utilization of agricultural products, food microbiology, and food biotechnology.In the past five years, he has led over 20 provincial and ministerial-level research projects, formulated five local standards for Jiangsu Province, obtained 23 national authorized invention patents, and published over 100 journal papers.He has received five science and technology awards, including the National Science and Technology Progress Award (4th place), Jiangsu Provincial Science and Technology Third Prize (1st place), and Nanjing City Science and Technology Progress Second Prize (1st place).

Wu Han, female, PhD, assistant researcher, currently working at the Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Institute of Agricultural Product Processing.Mainly engaged in research on the function and mechanism analysis of probiotic lactic acid bacteria, molecular interactions of dietary components, efficient extraction, purification, and activity evaluation of functional factors.She studied in Lille University, France, for two years, and has published nearly 20 research papers as the first author in domestic and international journals, including 9 in SCI source TOP一区, with a cumulative impact factor > 40;She has participated in several provincial and ministerial-level projects, including the National Natural Science Foundation project, Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation, and Jiangsu Provincial Agricultural Independent Innovation Fund project, and has led key research and development programs in Jiangsu Province, Yangzhou City, and Changshu City projects;As a main contributor, her research achievements have won the first prize of the China Food Industry Association Science and Technology Award and the second prize of the Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences Science and Technology Award.
This article “Effects Of High-Power Pulsed Microwave And Anthocyanins On Soy Protein” is sourced from “Food Science”, 2023, Volume 44, Issue 17, Pages 60-66, authors: Wu Han, Liu Haonan, Di Qingru, Xia Yidan·Maimaiti, Liu Xiaoli, Zhou Jianzhong. DOI:10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220801-002.Click belowto read the original textto view the article information.

Intern Editor: Bohai University College of Food Science and Engineering Wang Yuting; Editor: Zhang Ruimei. Click belowto read the original textto view the full text.Images sourced from the original article and Shutterstock.
“Food Science”: Professor Liu Deyong from Bohai University et al.: Research Progress on Temporary Sensory Control Method and Its Application in Food Sensory Evaluation
“Food Science”: Professor Liu Dunhua and lecturer Wei Chaokun from Ningxia University et al.: GC-MS, DSA combined chemometric analysis of volatile flavor substance changes during cream fermentation
“Food Science”: Professor Zhang Yimin and Associate Professor Mao Yanwei from Shandong Agricultural University et al.: Research Progress on the Application of Spectroscopic Technology in Meat Spoilage Detection
“Food Science”: Professor Che Huilian from China Agricultural University et al.: Research Progress on Food Allergen Labeling Management and Its Implications for China
“Food Science”: Professor Ren Guangyue from Henan University of Science and Technology et al.: Construction and Mechanism of Gelatin/Sodium Hexametaphosphate/Transglutaminase Composite Hydrogel Encapsulation System
“Food Science”: Professor Xu Xiaoxi from Northeast Agricultural University et al.: Mechanisms and Regulation Methods of Gut Microbiota Mediating Obesity
“Food Science”: Professor Zhang Jun from Tianjin Agricultural University et al.: Thermal Release Law Analysis of Key Aroma Substances in Pu-erh Ripe Tea
“Food Science”: Researcher Lin Rihui from Guangxi University for Nationalities et al.: Characterization and Pickering Emulsion Stability Analysis of Cassava Starch Stearic Acid Composite Nanoparticles
“Food Science”: Professor Tian Huaixiang from Shanghai University of Applied Sciences et al.: Comparison of Volatile Flavor of Chinese Acid-Curd Cheese Based on Sensory Evaluation, GC-IMS, and GC-MS