1. Introduction to LE Audio
1.1. LE Audio Transmission Protocol
At the end of 2019, the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) released the core protocol for Bluetooth 5.2, which introduced an important feature—LE Audio (Low Energy Bluetooth Audio). Bluetooth application protocols encompass everything from the application layer to the physical layer, and LE Audio is no exception. However, the Bluetooth 5.2 core protocol only defines the link layer transmission method for audio over Bluetooth LE, while the upper layer protocols and the complete LE Audio specifications have been delayed. Recently, the Bluetooth SIG released a more complete specification document for LE Audio.
1.2. Complete Applications of LE Audio
The SIG has defined the following specifications and protocols, which, along with the core protocol, constitute the complete application of LE Audio:
- Basic Audio Profile (BAP)
The Basic Audio Profile is a key specification of LE Audio, defining various roles and the capabilities each role must support, as well as how to use the following services to complete audio application transmission. LE Audio supports both point-to-point audio mode and broadcast audio mode, using different services in each mode.
- Published Audio Capabilities Service (PACS)
The Published Audio Capabilities Service defines the audio capabilities supported by the device, including but not limited to the number of supported codecs and their capabilities. This service allows retrieval of the device’s audio capabilities.
- Audio Stream Control Service (ASCS)
The Audio Stream Control Service defines a set of operation commands for establishing, configuring, and terminating audio streams.
- Broadcast Audio Scan Service (BASS)
The Broadcast Audio Scan Service is used by broadcast audio publishers to inform nearby receivers of broadcast audio parameters. This service is only applicable in broadcast audio scenarios.
- Low Complexity Communication Codec (LC3)
The LC3 codec is used for audio encoding and decoding in LE Audio. As the name suggests, this codec is a low-complexity audio encoder. The LC3 codec supports a wide range of optional parameters, applicable from 8 kHz mono speech to 48 kHz multichannel music, and significantly improves audio quality at the same bit rate compared to the SBC codec used in classic Bluetooth audio specifications.
2. Detailed Explanation of LE Audio
2.1. BAP Specification
The BAP specification serves as the foundational audio specification for LE Audio, located at the following Bluetooth protocol layer.
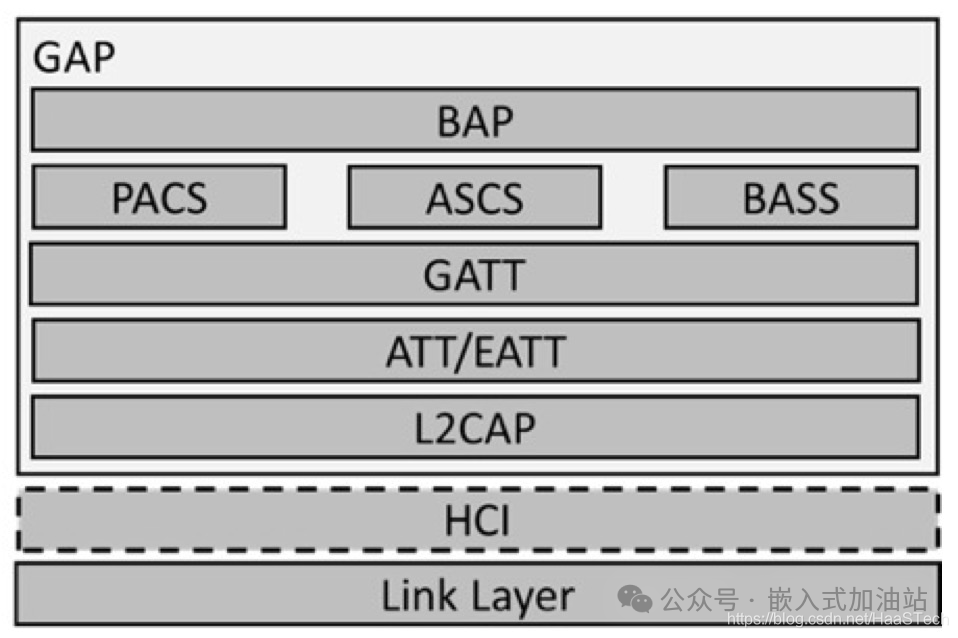
The BAP specification defines the following roles based on support for point-to-point audio and broadcast audio:
|
Unicast Role |
Unicast Server |
Point-to-point audio sink device |
|
Unicast Client |
Point-to-point audio source device |
|
|
Broadcast Role |
Broadcast Source |
Broadcast audio transmitter |
|
Broadcast Sink |
Broadcast audio receiver |
|
|
Broadcast Assistant |
Broadcast audio assisting device |
|
|
Scan Delegator |
Broadcast audio scanning device |
The services supported by each role are as follows (Note: X represents unsupported, M represents must support, O represents optional support):
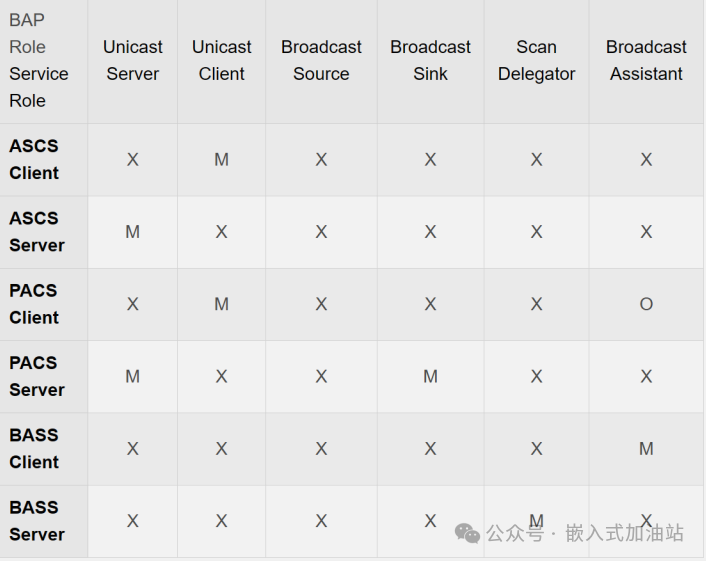 When two devices are in corresponding roles, they can complete service connection and audio transmission service through the operational steps defined by BAP. For example, the steps for Unicast Server and Unicast Client are as follows:
When two devices are in corresponding roles, they can complete service connection and audio transmission service through the operational steps defined by BAP. For example, the steps for Unicast Server and Unicast Client are as follows:
- The Unicast Client discovers the Unicast Server’s PACS service through GATT service discovery and learns the audio parameters.
- The Unicast Client discovers the Unicast Server’s ASCS service through GATT service discovery and learns the current status.
- If the Unicast Client finds that its audio parameters match and the Server’s status is IDLE, it can connect to the audio service.
- The Unicast Client configures audio codec parameters and audio transmission parameters using operation codes defined by ASCS, and then starts audio.
- The Unicast Client initiates the CIS audio transmission stream at the link layer according to the configuration parameters defined by the core protocol 5.2.
- The Unicast Sink notifies the Unicast Source that it is ready to receive audio using ASCS operation codes.
- The Unicast Source activates the LC3 codec and transmits the encoded audio stream to the Unicast Sink via CIS.
- The Unicast Sink receives the audio stream, decodes it, and plays it.
2.2. PACS Service
The PACS service is used for point-to-point audio and defines the audio capabilities of the device. Its service definition is as follows:
|
Characteristic Name |
Requirement |
Mandatory Properties |
Optional Properties |
Security Permissions |
|
Sink PAC |
C.1 |
Read |
Notify |
Encryption required |
|
Sink Audio Locations |
C.2 |
Read |
Notify, Write |
Encryption required |
|
Source PAC |
C.1 |
Read |
Notify |
Encryption required |
|
Source Audio Locations |
C.3 |
Read |
Notify, Write |
Encryption required |
|
Available Audio Contexts |
M |
Read, Notify |
None |
Encryption required |
|
Supported Audio Contexts |
M |
Read |
Notify |
Encryption required |
Among them, the Source PAC is the audio sending capability attribute, which needs to be defined only when the device supports audio sending. Its format is as follows:
|
Parameter |
Size (Octets) |
Description |
|
Number_of_PAC_records |
1 |
Number of PAC records, [i], for this characteristic |
|
Codec_ID[i] |
5 |
Octet 0: Coding_Format value of the [ith] PAC record. Coding_Format values are defined in Bluetooth Assigned Numbers. Octet 1–2: Company_ID value of the [ith] PAC record. Shall be 0x0000 if octet 0 is not 0xFF. Company_ID values are defined in Bluetooth Assigned Numbers. Octet 3–4: Vendor-specific codec_ID value of the [ith] PAC record. Shall be 0x0000 if octet 0 is not 0xFF. |
|
Codec_Specific_Capabilities_Length[i] |
1 |
Length of the Codec_Specific_Capabilities value of the [ith] PAC record. Shall be 0x00 if the Codec_Specific_Capabilities value of the [ith] PAC record is empty. |
|
Codec_Specific_Capabilities[i] |
Varies |
Codec_Specific_Capabilities value of the [ith] PAC record. |
|
Metadata_Length[i] |
1 |
Length of the Metadata field of the [ith] PAC record. Shall be 0x00 if the Metadata value of the [ith] PAC record value is empty. |
|
Metadata[i] |
Varies |
LTV-formatted Metadata applicable to the [ith] PAC record. Shall exist only if the value of the Metadata_Length field is not 0x00. |
The Sink PAC is the audio receiving capability attribute, which needs to be defined only when the device supports audio receiving. Its format is as follows:
|
Parameter |
Size (Octets) |
Description |
|
Number_of_PAC_records |
1 |
Number of PAC records, [i], in this characteristic. |
|
Codec_ID[i] |
5 |
Octet 0: Coding Format of the [ith] PAC record. Coding_Format values are defined in Bluetooth Assigned Numbers. Octet 1–2: Company_ID value of the [ith] PAC record. Company_ID values are defined in Bluetooth Assigned Numbers. Shall be 0x0000 if octet 0 is not 0xFF. Octet 3–4: Vendor-specific codec_ID value of the [ith] PAC record. Shall be 0x0000 if octet 0 is not 0xFF. |
|
Codec_Specific_Capabilities_Length[i] |
1 |
Length, in octets, of the Codec_Specific_Capabilities value of the [ith] PAC record. Shall be 0x00 if the Codec_Specific_Capabilities value of the [ith] PAC record is empty. |
|
Codec_Specific_Capabilities[i] |
Varies |
Codec_Specific_Capabilities value of the [ith] PAC record. |
|
Metadata_Length[i] |
1 |
Length of the Metadata field of the [ith] PAC record. Shall be 0x00 if the Metadata value of the [ith] PAC record value is empty. |
|
Metadata[i] |
Varies |
LTV-formatted Metadata applicable to the [ith] PAC record. Shall exist only if the value of the Metadata_Length field is not 0x00. |
2.3. ASCS Service
The ASCS service is used for audio control, interacting through a defined set of operation codes to achieve control over audio state transitions.
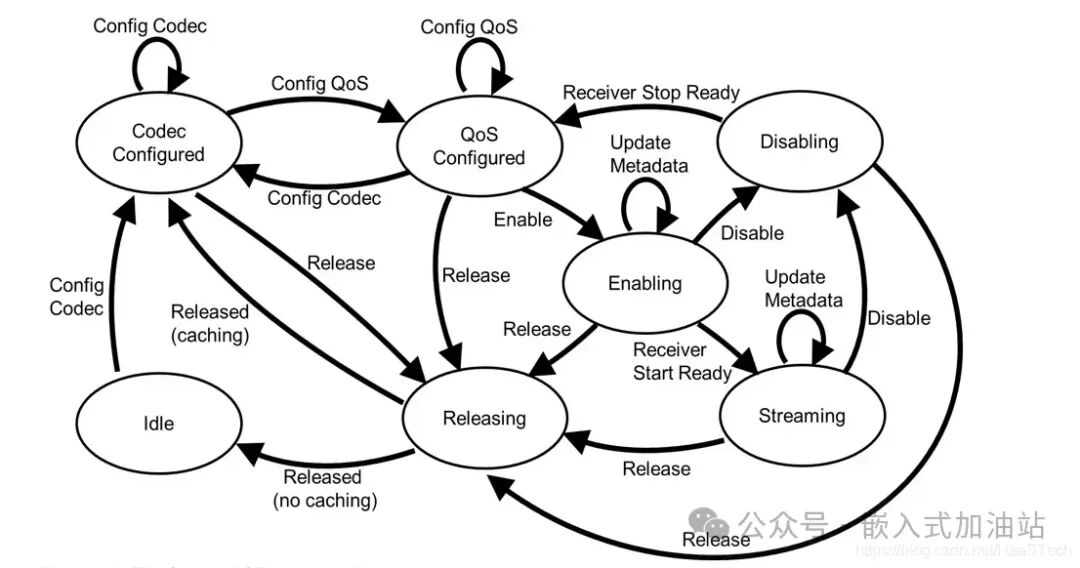 The ASCS service is defined as follows:
The ASCS service is defined as follows:
|
Characteristic Name |
Requirement |
Mandatory Properties |
Optional Properties |
Security Permissions |
|
Sink ASE |
C.1 |
Read, Notify |
None |
Encryption required |
|
Source ASE |
C.1 |
Read, Notify |
None |
Encryption required |
|
ASE Control Point |
M |
Write, WriteWithoutResponse, Notify |
None |
Encryption required |
2.4. BASS Service
BASS is the Broadcast Audio Scan Service, used to inform about some parameters of broadcast audio, and is an auxiliary service defined as follows:
|
Characteristic Name |
Requirement |
Mandatory Properties |
Optional Properties |
Security Permissions |
|
Broadcast Audio Scan Control Point |
M |
Write, Write Without Response |
None |
Encryption required |
|
Broadcast Receive State |
M |
Read, Notify |
None |
Encryption required |
2.5. LC3 Codec
The LC3 codec is used for audio encoding and decoding in LE Audio, similar to MP3 and AAC, belonging to frequency domain encoding. Its encoding efficiency is significantly higher than that of the SBC subband codec, and the short frame structures of 10 ms and 7.5 ms greatly improve audio latency. LC3 introduces technologies such as SNS frequency domain noise shaping, TNS time domain noise shaping, and entropy coding, some of which have been used in AAC, enhancing audio quality. The entire encoding process is as follows:
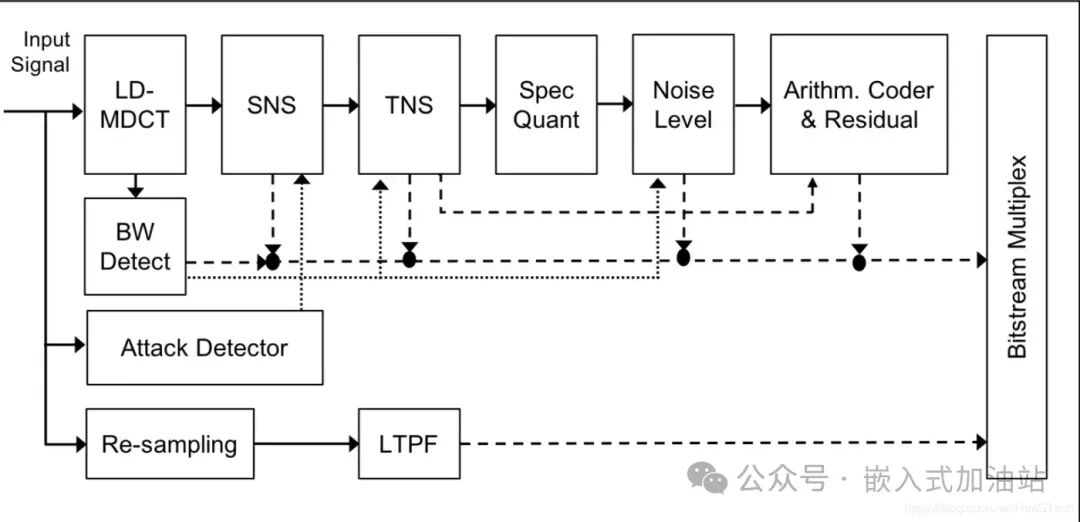
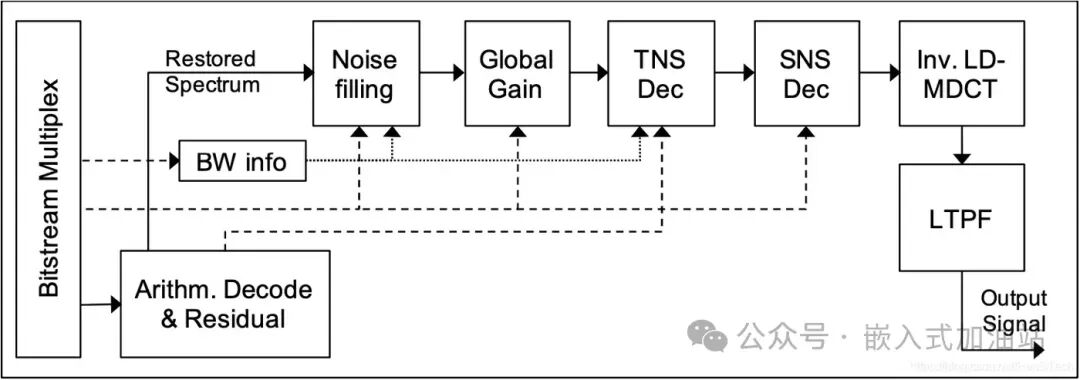
Decoding is the reverse process of encoding, as shown below:
3. Prospects for LE Audio Support
As a very important feature, LE Audio has yet to see widespread application since its release, aside from a few demos. Its large-scale adoption still depends on whether operating system vendors support it, such as Apple’s iOS and Google’s Android. From the current progress (iOS 14 and Android 11), there is still no support for LE Audio. However, looking at the AOSP code, traces of LE Audio can be found in Android 12 (android-s-beta version), as shown below:
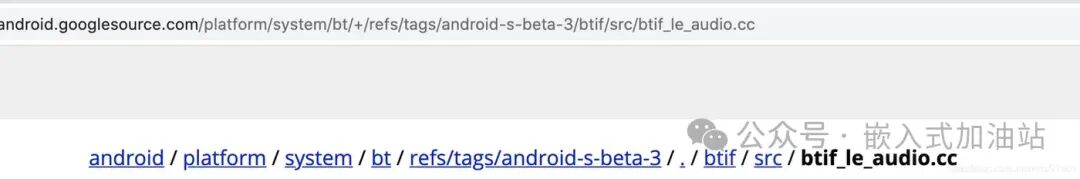 From the current completeness of the code, it does not yet represent full functional support. It is expected that Android 12 will improve and begin to apply it. Once smartphones support it, it is believed that manufacturers will launch headphones that support LE Audio. However, audio applications are general-purpose applications, and support from Apple and other operating systems such as Microsoft’s Windows is also extremely important. From this perspective, it may still take time for LE Audio to achieve widespread adoption.————————————————
From the current completeness of the code, it does not yet represent full functional support. It is expected that Android 12 will improve and begin to apply it. Once smartphones support it, it is believed that manufacturers will launch headphones that support LE Audio. However, audio applications are general-purpose applications, and support from Apple and other operating systems such as Microsoft’s Windows is also extremely important. From this perspective, it may still take time for LE Audio to achieve widespread adoption.————————————————
References
Source | HaaS Technology CommunityThank you for reading. If you need materials, please leave a message in the comments. Or check the original text for downloads.Original content is not easy; please use your wealth to help the editor with likes and hearts, and give the article a boost. Welcome to follow for more exciting and timely updates, and star us for easier access!If you have more technical questions, please follow our public account. Our public account has integrated AI-Deepseek, which can help you answer most questions and even help you write articles and discuss life.If the AI’s answers are not satisfactory, please leave us a message, and we will arrange for an FAE to provide you with professional answers.
1. Chat function upgraded and enhanced;
2. Foreign language translation function;
3. Finding materials and solutions;
4. Writing code and articles;
5. Quick and accurate answers to technical questions
……
 Previous HighlightsGuangming Valley launches S-A5607T serial AT command Bluetooth speaker IC solution supporting USB playback and FM radio SPP/BLE data transmissionVC-S100D-CW smart offline voice recognition warm/cool color monochrome night light IC solution【Solution Recommendation】Guangming Valley launches VC-S100D cost-effective voice-controlled night light solutionGuangming Valley S-BE5607E Bluetooth 5.4 low-cost card/USB/Bluetooth speaker solution【Solution Recommendation】SMP37A-Player low-cost card/USB/USB speaker/MP3 playback/USB sound card solutionBased on Zhongke Lanyun AB5607E low-cost Bluetooth proximity switch timer video introductionZhongke Lanyun AB5607E Bluetooth 5.4 low-cost Bluetooth proximity switch timer solution【Recommended Goodies】Stickman privacy camera AI smart behavior detection fall alarm【Application Solution】Based on MT7628 JN5169-Zigbee-4G smart gateway solutionSmart offline voice recognition whole-house smart voice control solutionBluetooth speaker and headphone mass production considerations and common issuesGuangming Valley launches AT command version of Bluetooth speaker SOC, opening a convenient smart audio development experienceAnalysis of Bluetooth speaker power supply circuit designAnalysis of oscillator circuit design based on Bluetooth SOCBluetooth test box usage precautionsComplete analysis of Bluetooth protocol: a comprehensive understanding of Bluetooth protocolGuide to selecting commonly used audio power amplifiers (amplifier ICs)
Previous HighlightsGuangming Valley launches S-A5607T serial AT command Bluetooth speaker IC solution supporting USB playback and FM radio SPP/BLE data transmissionVC-S100D-CW smart offline voice recognition warm/cool color monochrome night light IC solution【Solution Recommendation】Guangming Valley launches VC-S100D cost-effective voice-controlled night light solutionGuangming Valley S-BE5607E Bluetooth 5.4 low-cost card/USB/Bluetooth speaker solution【Solution Recommendation】SMP37A-Player low-cost card/USB/USB speaker/MP3 playback/USB sound card solutionBased on Zhongke Lanyun AB5607E low-cost Bluetooth proximity switch timer video introductionZhongke Lanyun AB5607E Bluetooth 5.4 low-cost Bluetooth proximity switch timer solution【Recommended Goodies】Stickman privacy camera AI smart behavior detection fall alarm【Application Solution】Based on MT7628 JN5169-Zigbee-4G smart gateway solutionSmart offline voice recognition whole-house smart voice control solutionBluetooth speaker and headphone mass production considerations and common issuesGuangming Valley launches AT command version of Bluetooth speaker SOC, opening a convenient smart audio development experienceAnalysis of Bluetooth speaker power supply circuit designAnalysis of oscillator circuit design based on Bluetooth SOCBluetooth test box usage precautionsComplete analysis of Bluetooth protocol: a comprehensive understanding of Bluetooth protocolGuide to selecting commonly used audio power amplifiers (amplifier ICs)