Traditional/Classic Bluetooth Module (Classic Bluetooth, abbreviated as BT)
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Classic Bluetooth has developed and improved based on earlier versions like Bluetooth 1.0, 1.2, 2.0+EDR, 2.1+EDR, and 3.0+EDR, while Bluetooth Low Energy was developed from Nokia’s Wibree standard, representing two completely different standards.
Classic Bluetooth modules can be further divided into traditional Bluetooth modules and high-speed Bluetooth modules.
-
The traditional Bluetooth module was launched in 2004, primarily represented by modules supporting the Bluetooth 2.1 protocol, which gained wide support during the smartphone explosion.
-
The high-speed Bluetooth module was launched in 2009, increasing the speed to about 24Mbps, which is eight times that of traditional Bluetooth modules.
-
Traditional Bluetooth has three power levels: Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3, supporting transmission distances of 100m, 10m, and 1m respectively.
BLE technology adopts a very fast connection method, allowing it to remain in a “non-connected” state most of the time (saving energy). At this time, both ends of the link only know about each other and only open the link when necessary, then close it in the shortest time possible (transmitting a maximum of 20 bytes each time). Bluetooth Low Energy has no power levels, with typical transmission power at 7dBm.
Here is a software layer distinction between classic Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy, with dual-mode in the middle:
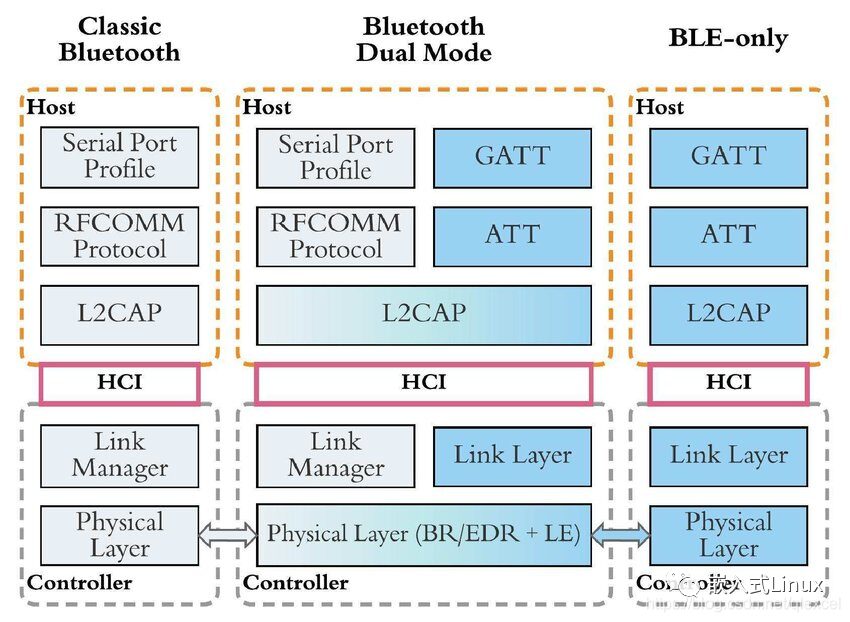
Comparison of Characteristics Between Classic Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy:
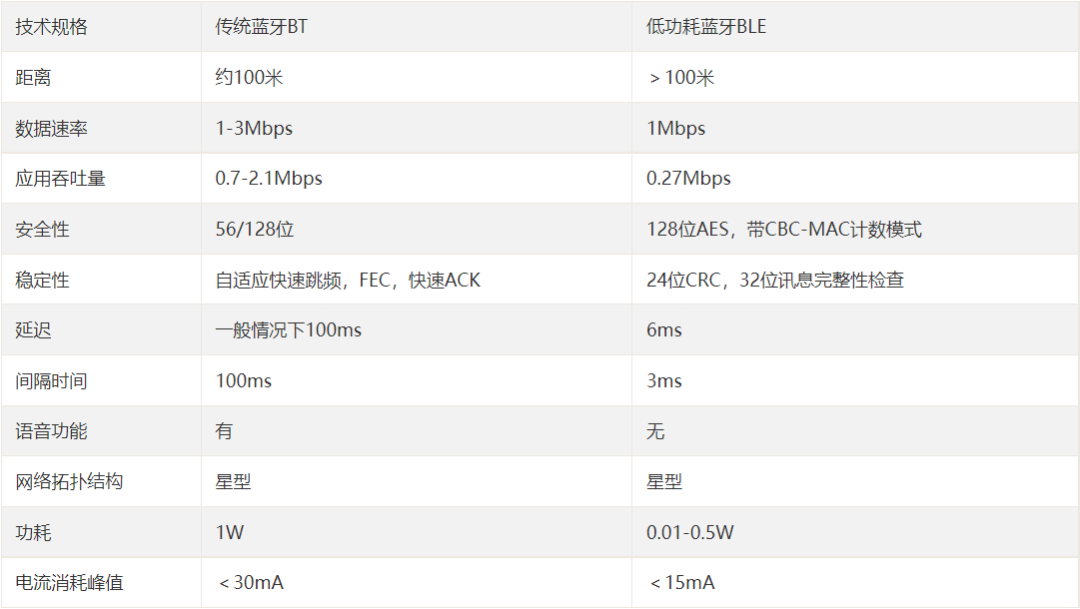
What are the differences in their applications?
First, Classic Bluetooth
1. Audio Transmission: Such as Bluetooth headsets and Bluetooth speakers. Bluetooth was designed primarily for audio transmission, making it the best choice for short-distance audio transmission. There are now audio transmission solutions based on Wi-Fi, such as Airplay, but Wi-Fi consumes much more power than Bluetooth, making it impractical for portable devices. Therefore, fixed audio systems may use Wi-Fi, but portable devices like headsets and portable speakers predominantly use the classic Bluetooth protocol.
2. Large Data Transmission: For example, in certain industrial control scenarios, using Android or Linux as the main control, external Bluetooth remote control devices can use the SPP protocol in classic Bluetooth as a wireless serial port. The speed is much faster than BLE transmission.
Second, Bluetooth Low Energy
1. Low Power Consumption, Small Data Volume: Such as remote control devices (mouse, keyboard), sensing devices (heart rate monitors, blood pressure monitors, temperature sensors, shared bicycle locks, smart locks, anti-loss devices, indoor positioning).
2. Currently, the most cost-effective means of communication between smartphones and smart hardware, with a direct distance of about 50 meters, a single AA battery can last a year, and transmission module costs are low, making it much more practical than communication protocols like Wi-Fi and 4G that handle large data volumes. Although Bluetooth has a shorter range, its advantage lies in direct connection to smartphones at a very low price. For example, in indoor positioning, each store in a shopping mall can hang a Bluetooth beacon, achieving meter-level indoor positioning accuracy for smartphones, and Bluetooth 5.1 can even achieve centimeter-level indoor positioning.
Third, Dual-Mode Bluetooth
1. Smart TV Remote Control: Many smart TVs come with remote controls that have voice recognition, requiring classic Bluetooth to transmit sound. However, for complex key functions that are not originally on the keyboard, the HID key protocol of classic Bluetooth is insufficient, requiring BLE to create a private protocol.
2. Noise-Canceling Headphones: Many noise-canceling headphones use an app to adjust noise cancellation effects, also using BLE for private communication protocols.
Bluetooth 5.0
Compared to the previous generation Bluetooth 4.2, Bluetooth 5.0 offers a longer transmission distance and faster speed. The theoretical effective distance is 300 meters, allowing stable connections for mobile devices throughout an entire home or office. The fastest speed can reach 2Mbps, making faster response times and higher performance Bluetooth devices more likely to be used. Additionally, it significantly enhances Bluetooth broadcast data transmission, providing better prospects for commercial Bluetooth and strengthening the use of Bluetooth as a standard for IoT applications.
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (Bluetooth SIG) recently announced the launch of Bluetooth Mesh technology, which will transform the traditional one-to-one pairing of Bluetooth devices into a many-to-many signal transmission model. This technology will not only be applied in Bluetooth 5.0 but will also extend to previous versions. The Bluetooth SIG states that Bluetooth Mesh technology is a new networking technology based on Bluetooth Low Energy, which will transform networks for commercial and industrial devices and make existing IoT technologies more complete and stable.