Click the blue text
Follow us
Shanghai Society of Civil Engineering
As we enter the era of Industry 4.0, with the introduction and practice of concepts such as sensors, wireless networks, 5G technology, information models, general algorithms, and cloud platforms, modern tunnel engineering faces new trends and challenges in achieving digitalization, informatization, intelligence, and even wisdom in the construction and operation processes while building deeper and longer tunnels. Today, a young scholar will share her insights and thoughts from her research in this field.

Author Business Card
Author business card
Zhu Mengqi, a PhD student in the Department of Underground Architecture and Engineering at Tongji University, is jointly trained as a PhD student in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at the Colorado School of Mines in the USA, under the supervision of Academician Zhu Hehua and Professor Zhu Jianwen. She mainly conducts research on the theories and applications of artificial intelligence, big data, and machine learning technologies in the fields of underground and tunnel engineering, and has published several academic papers as the first author in top journals such as Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering.
A tunnel from design to completion and operation,
and finally to disposal,
forms a complete closed loop.
Throughout the entire lifecycle of a tunnel,
information is recorded in the form of data.
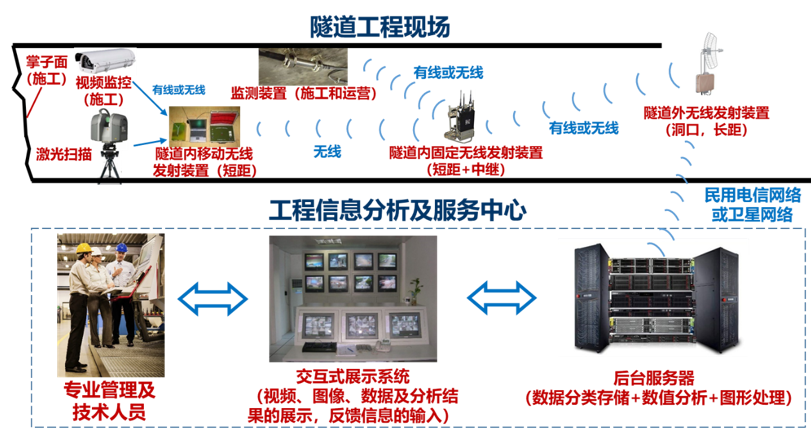
Data collection, transmission, analysis, and service flowchart
The intelligence of tunnels is mainly reflected in the processing and mining of IoT data, utilizing AI technology for automatic decision-making. More specifically, it can be divided intointelligent planning and design, intelligent construction, and intelligent operation and maintenance three aspects. I will illustrate the process of data collection, processing, expression, and analysis during the construction and maintenance phases of tunnels in the IoT era through two examples, as well as how different hardware and software play roles in this process.Mountain tunnel under construction Traditional rock excavation face information collection usesgeological sketching methods, requiring operators to approach the rock face and use geological compasses, tape measures, etc., which poses high risks in large areas that cannot be directly measured.

Geological sketching method for collecting rock excavation face information With the development of image processing technology and computer vision,laser scanning and evendigital photography can generate three-dimensional point clouds, achieving precise collection of rock information. Based on the collected information, three-dimensional point cloud reconstruction technology can digitize the discontinuities of the rock, obtaining information such as excavation face traces and roughness, significantly reducing the uncertainty of the geological environment and ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment during construction.
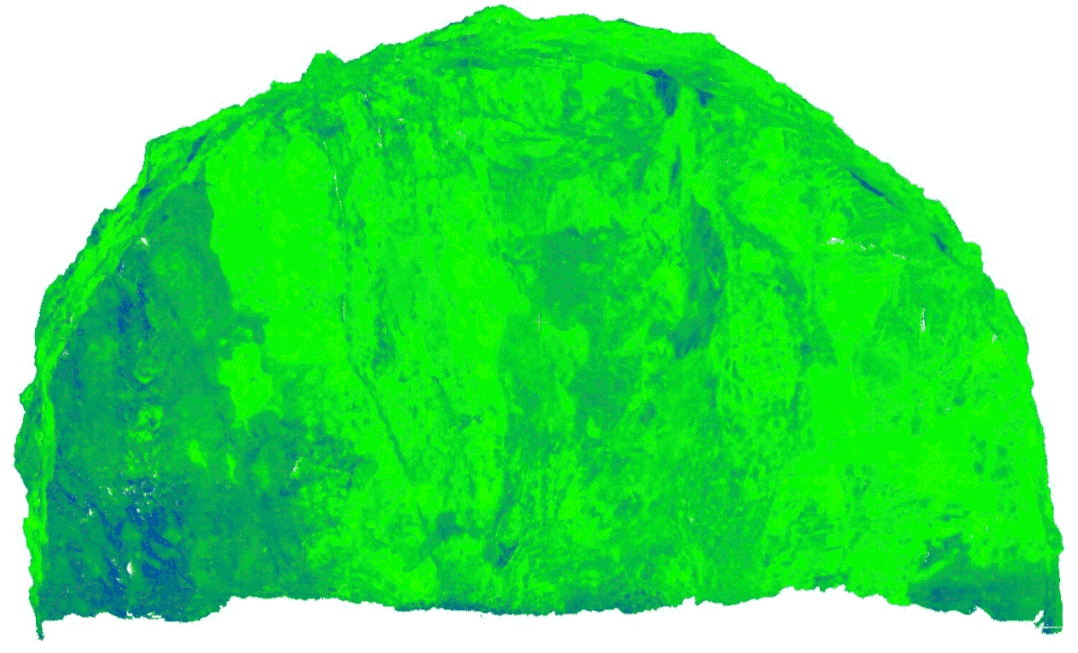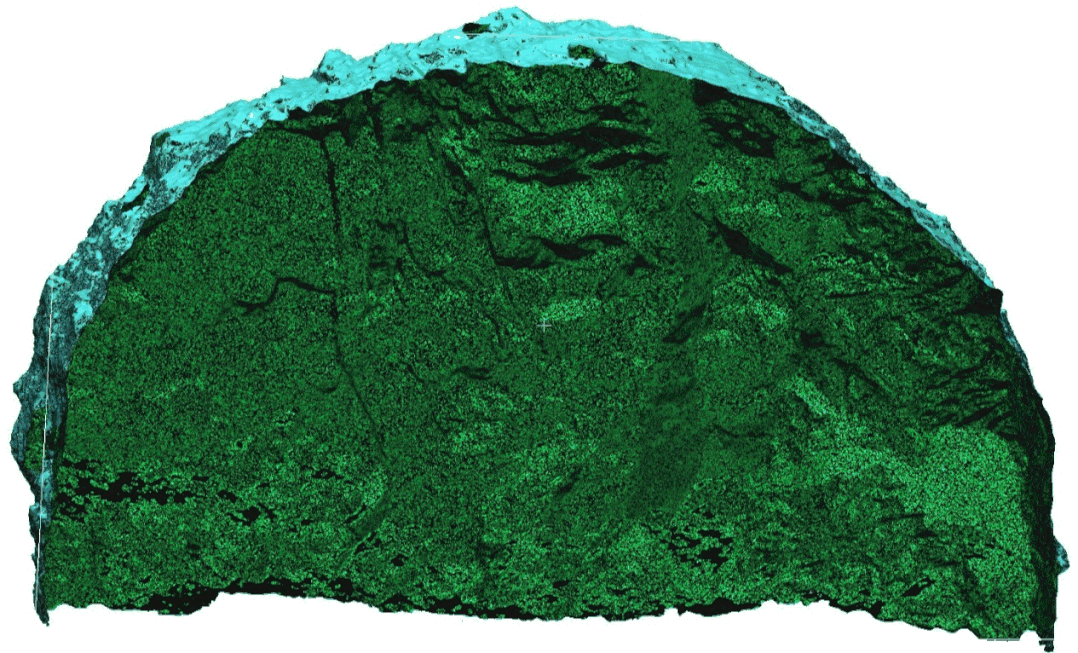

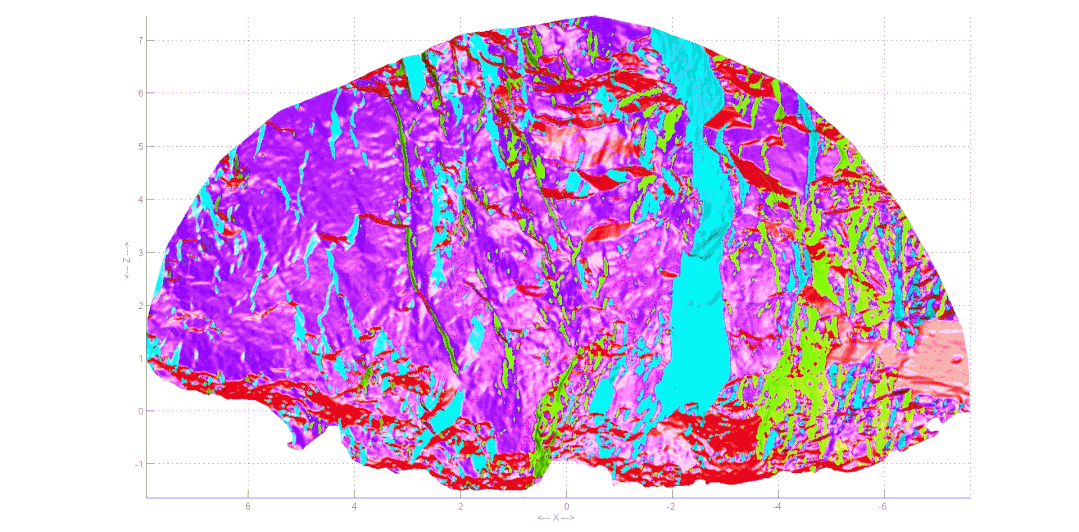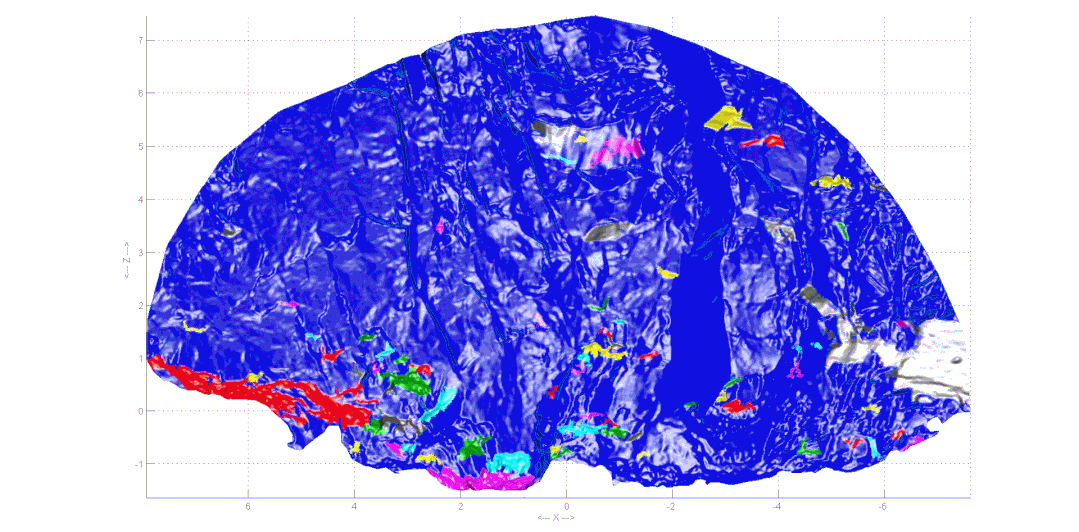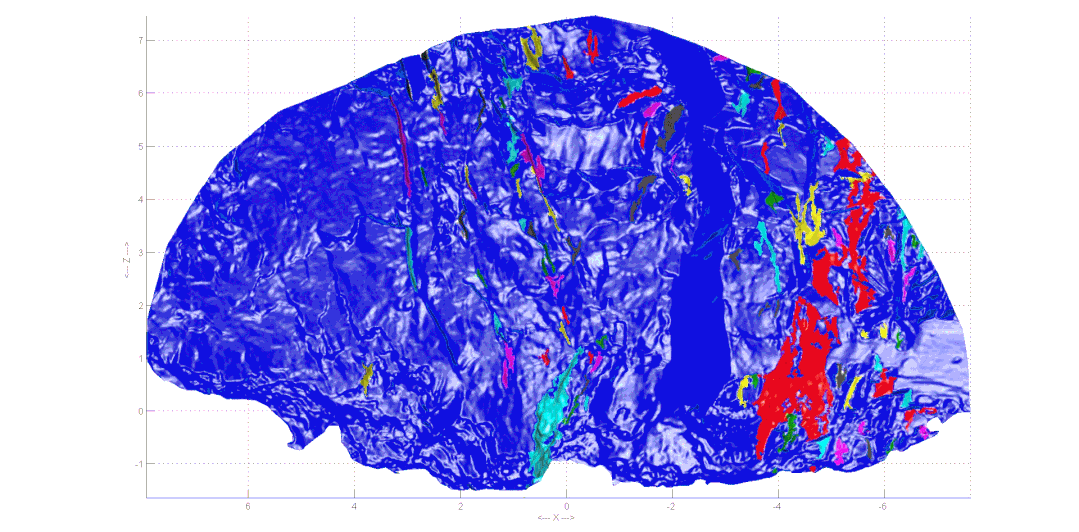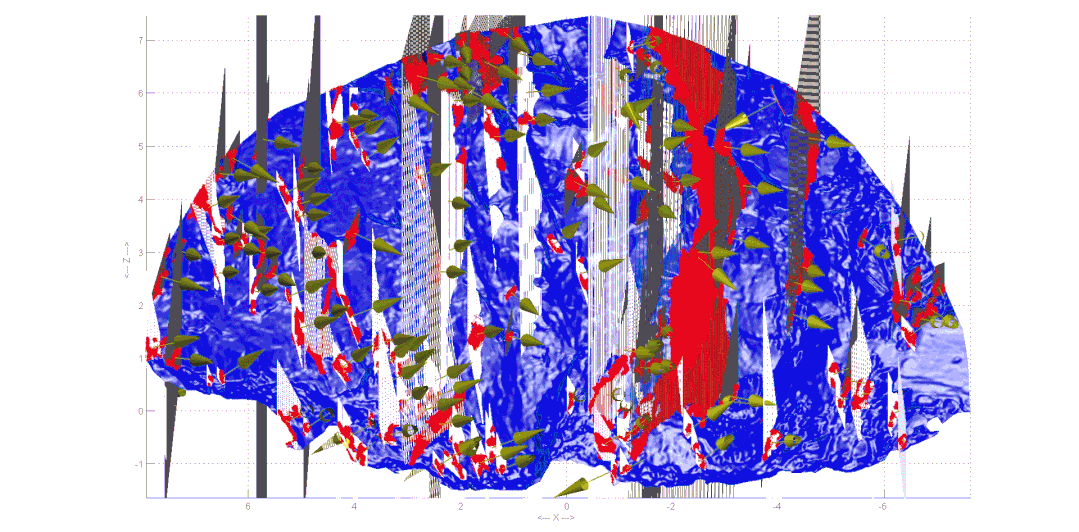

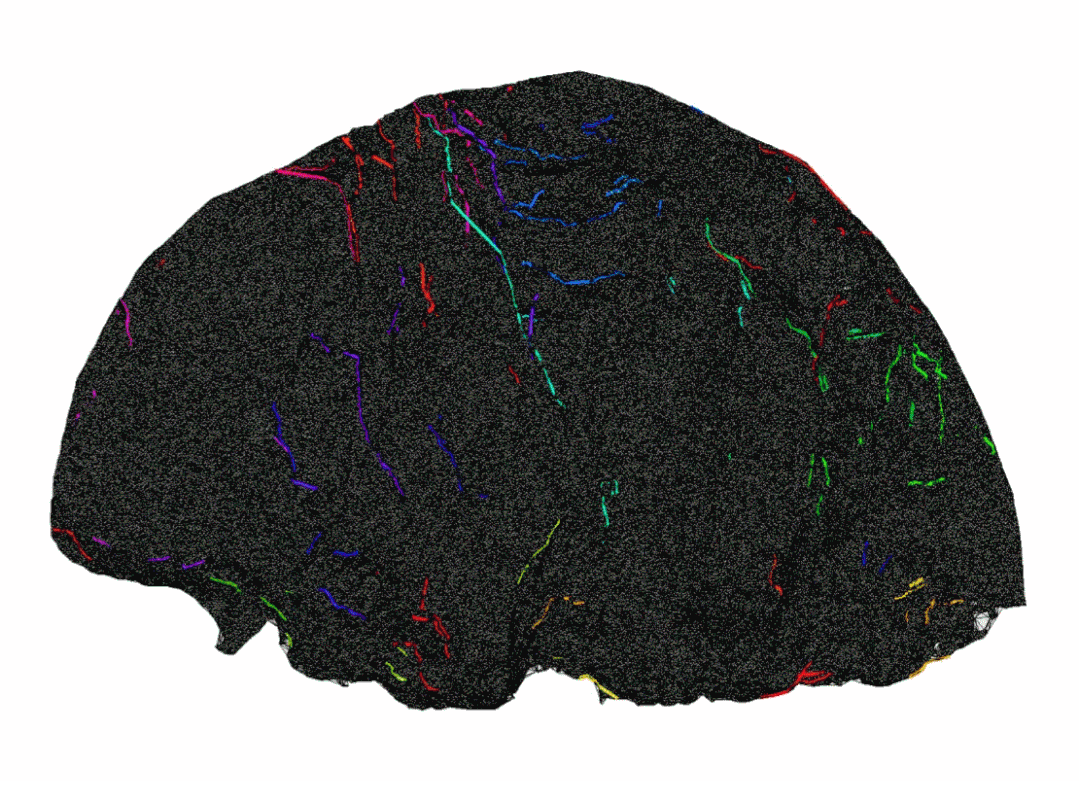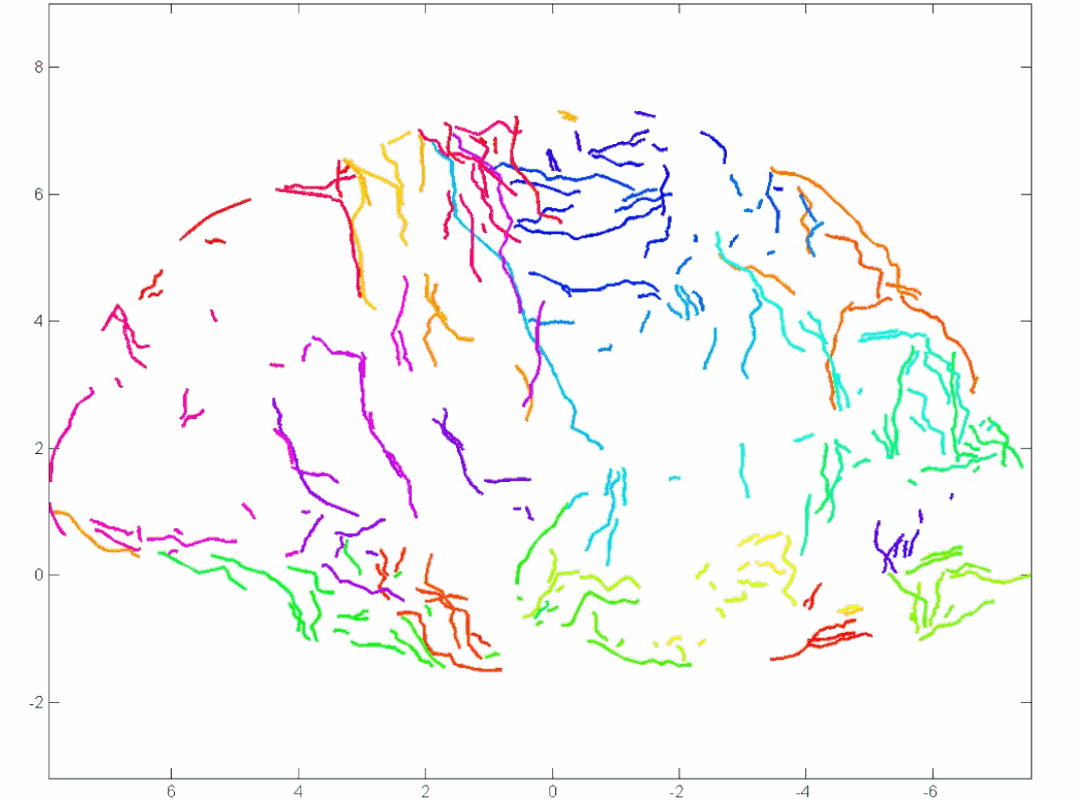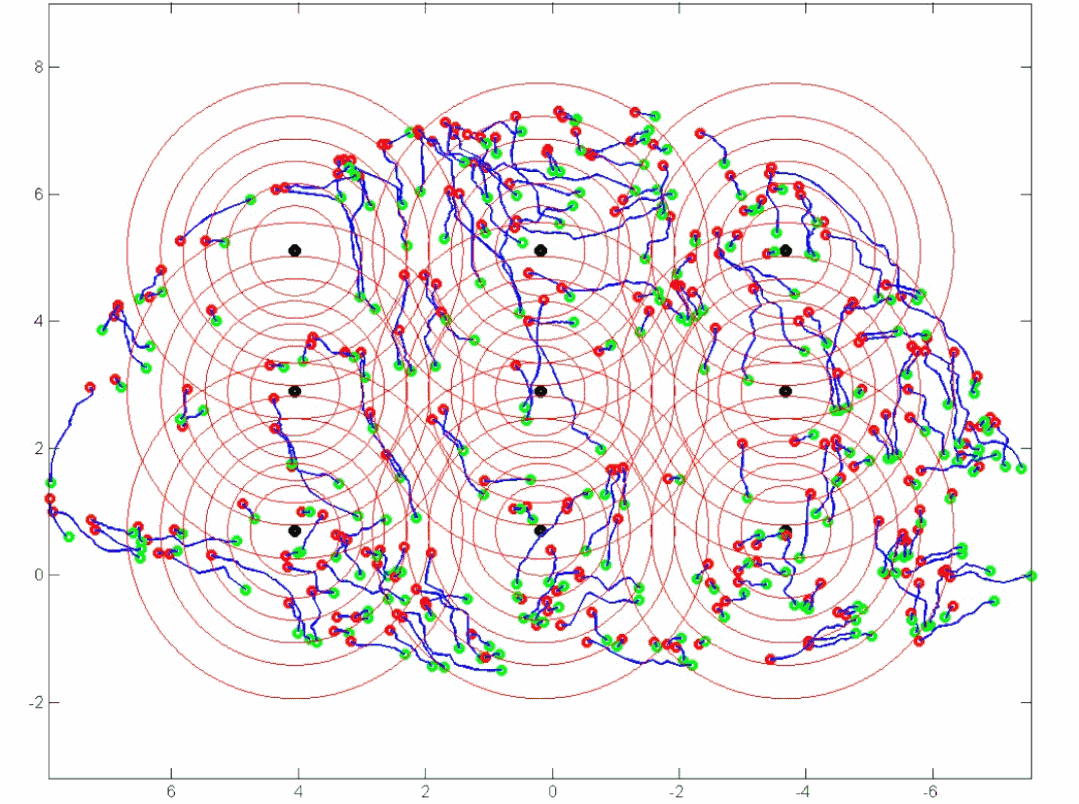
Automatic extraction of structural plane occurrence and traces
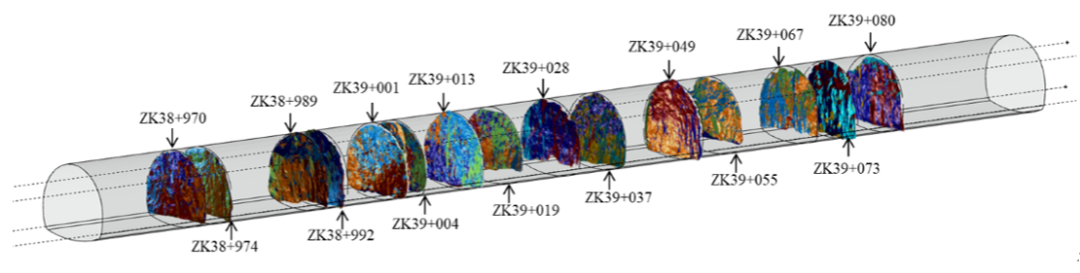
Dynamic modeling of tunnel geological environment When usingtunnel boring machines (TBM) as the main construction method, the sensor system widely distributed on the machine records valuable operational data: such as cutter head torque, total thrust, advance speed, penetration rate, etc.By monitoring the changes in machine operating parameters in real-time, accidents can be effectively prevented and mitigated. For example, changes in methane concentration detected by sensors in the operating room can indicate variations in methane concentration in the stratum where the tunneling machine is located; when the concentration reaches a certain level, a warning is issued to ensure the safety of operators’ lives and property. Additionally, changes in some machine operating parameters also reflect the machine’s different responses to varying surrounding rock conditions during different tunneling stages.
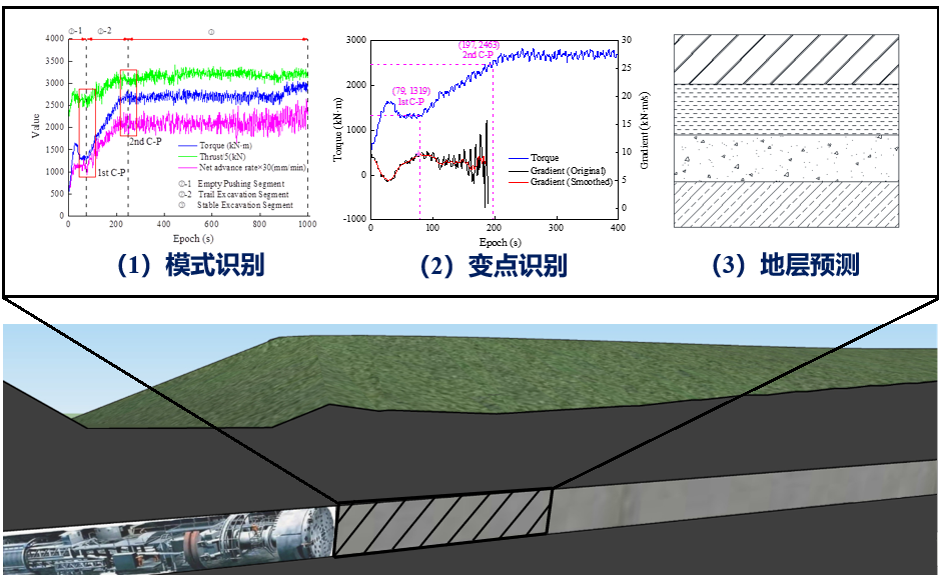
TBM operational data for stratum predictionOperational subway tunnels Currently, the safety inspection of subway shield tunnels mainly relies on:manual inspections, machine detection, and sensor monitoring. For tunnel structural deformation, monitoring data is mainly obtained by installing sensors at key locations; for defects such as cracks and water leakage, data can be obtained through manual inspections or machine detection. Currently, the Shanghai subway tunnel’s daily operation and maintenance inspections use the GRP5000 tunnel inspection vehicle from Amberger Company. This inspection vehicle performs full cross-section scanning of the tunnel surface using a high-speed rotating laser emitter, analyzing the emitted and received laser signals to obtain images of the inner surface of the tunnel lining and the location information of various points, and processing images to obtain defect information of the tunnel lining.

Tunnel inspection vehicle scanning and identifying tunnel lining defect information However, the speed of manual track inspection vehicles is less than 5 km/h, which is inefficient, and the contour scanning accuracy is limited, with a long data processing cycle. Therefore, on one hand, the sensor field is accelerating the development of sensors such aswater leakage sensors, crack sensors, and tilt sensors; on the other hand, rail-mounted tunnel inspection vehicles relying on area array cameras have emerged.
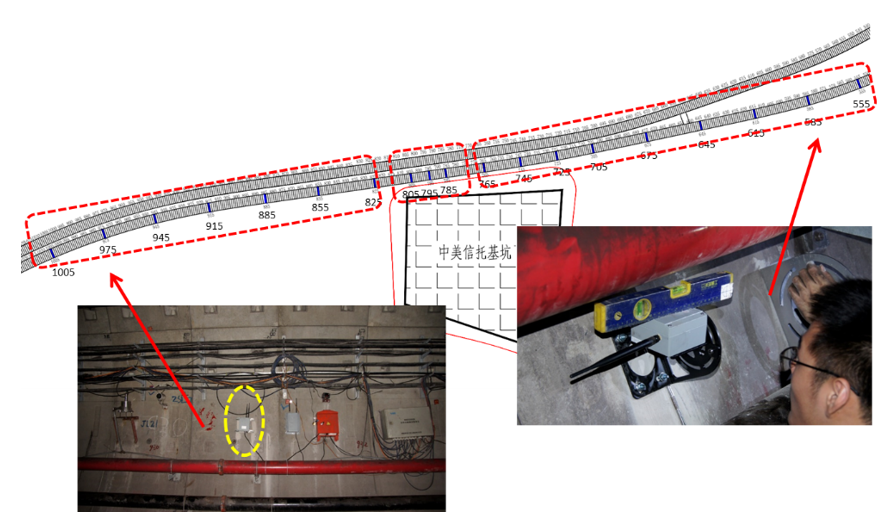
Application of tilt sensors
Rail-mounted tunnel inspection vehicle operation diagram Developed jointly byTongji University and Shanghai Tongyan Civil Engineering Technology Co., Ltd., the rail-mounted tunnel inspection vehicle can achieve computerautomatic identification, automatic measurement, and automatic labeling of cracks, joints, and water leakage, solving various safety status indicators and the challenge of quickly obtaining high-precision automation in a short time. Among them, the detection accuracy error for tunnel segment ring convergence deformation is2mm, the measurement accuracy error for cracks is0.1mm, and the identification accuracy error for water leakage area is1cm2.

Rail-mounted tunnel inspection vehicle physical image

Automatic identification of tunnel lining cracks and joints based on cascade networks
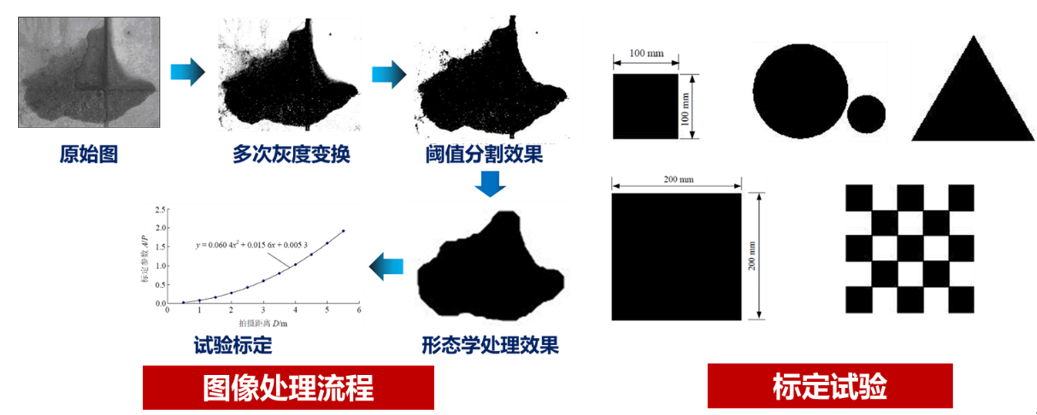
Automatic identification of tunnel structure water leakage based on infrared thermal imaging
To achieve integrated services from data collection, processing, to expression and analysis,Academician Zhu Hehua of Tongji University proposed and established theSmart Infrastructure Platform (infrastructure Smart Service System, iS3), realizing intelligent management of infrastructure from the perspective of information flow. The iS3 system includes database modules, analysis tool modules, finite element software modules, GIS and BIM modules, UI interface modules, and API modules; it can provide three service forms including PC, mobile, and cloud; and supports most mainstream programming languages such as C#, Python, and MATLAB.
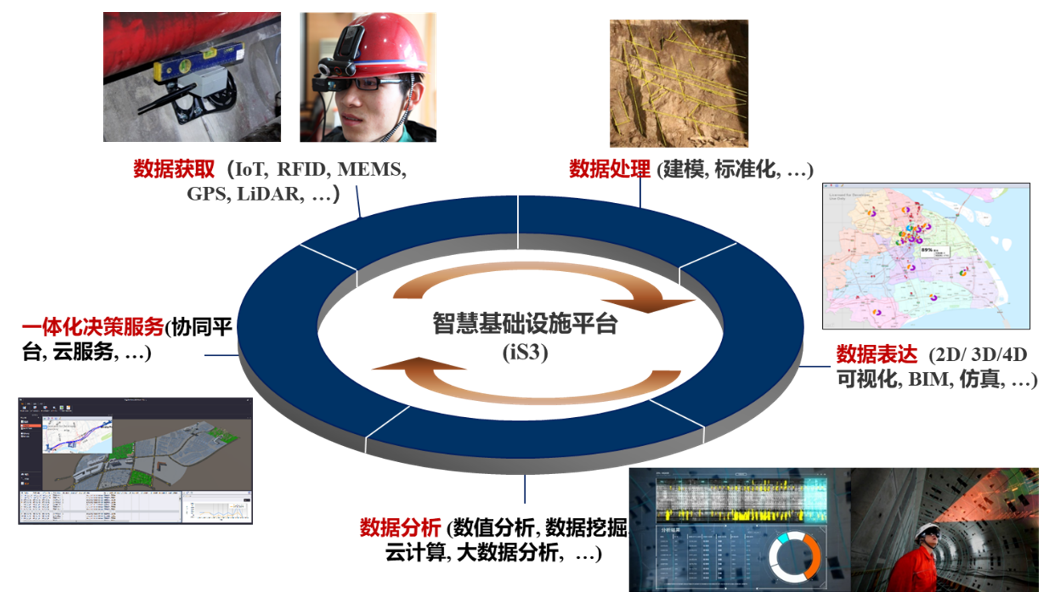
Smart Infrastructure Platform (iS3)
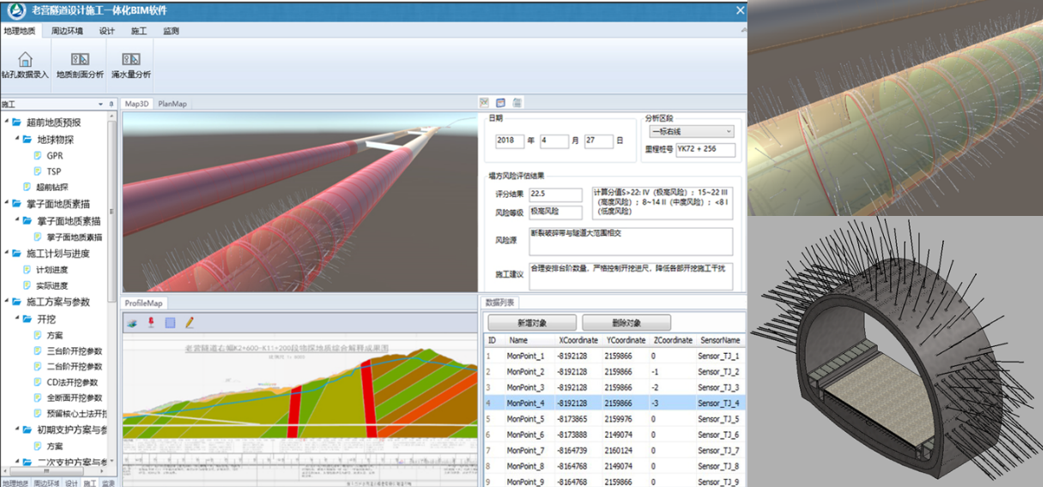
iS3 Service Example
Based on the iS3 platform, the concept ofDataHub has been proposed. On one hand, the current engineering data recording and management are not standardized, making it difficult to call data between departments, and historical engineering data is unverifiable. On the other hand, both the realization of construction intelligence and operation and maintenance intelligence require a large supply of high-quality historical data for algorithms.DataHub aims to provide a platform for encrypted storage and calling of engineering data, ensuring data privacy while providing database services.
Author’s Remarks
We are a fortunate generation, experiencing the transformation of infrastructure from nothing to something, and from weak to strong in all aspects of life; while enjoying the convenience brought by infrastructure, you may not have thought that everything presented to you today is just the tip of the iceberg of technological progress, with infinite possibilities in the future.
Remember to star ⭐️ and pin the public account!
Expand
Read
More
Articles

· Notice on recommending and applying for the 2022 Shanghai Society of Civil Engineering Science and Technology Progress Award and Engineering Award
· Notice on recommending and applying for the 2022 Shanghai Society of Civil Engineering Talent Award
· [Ten-year appointment, reschedule] The 2021 (10th) International Bridge and Tunnel Technology Conference and the “Belt and Road” High-end Forum on Transportation Infrastructure will be postponed
· [Reschedule] The 2021 International Conference on Sustainable Development in Construction Engineering (3rd) will be postponed
· Cover Story | Expo Cultural Park: Shanghai Central Park, Ecological City Business Card
· Expert Viewpoint | Wang Rulu: Risk Control of Underground Engineering in Shanghai Rail Transit

The Engineer’s Home for Civil Engineers

Electronic Journal Online Reading
Statement: Unless otherwise noted as original or sourced, this account’s content is compiled from the internet by the Shanghai Society of Civil Engineering, and the copyright belongs to the original author, with thanks to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact us for deletion or related processing!
Articles and images are not to be reproduced or used commercially without permission.