The application of modulus (<span><span>%</span></span>) and integer division (<span><span>/</span></span>) in C language.
- Code section:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
/*(Sum of Digits) Write a function that takes an integer and returns the sum of its digits. For example, given the number 7631, the function should return 17 (Explanation: 7 + 6 + 3 + 1 = 17).*/
int get_reversed_num(int num);
int get_digit_length(int num);
int get_digit_pos_sum(int num);
int main(void){
unsigned int num;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%u", &num);
unsigned int sum = get_digit_pos_sum(num);
printf("The sum of %u for every position is %u\n", num, sum);
return 0;
}
int get_reversed_num(int num){
// Reverse the number, for example 7631 -> 1367
int reversed = 0;
int temp = num;
while(temp > 0){
reversed = reversed * 10 + temp % 10;
temp /= 10; // Remove the last digit
}
return reversed;
}
int get_digit_length(int num){
unsigned count = 0;
while(num > 0)
{
num /= 10;
count++;
}
return count;
}
int get_digit_pos_sum(int num){
int reversed_num = get_reversed_num(num);
unsigned count = get_digit_length(num);
// printf("%d\n", count);
unsigned int d;
unsigned int sum = 0;
for(int i = count; i > 0; --i)
{
printf("%u %s%s", reversed_num % 10, (i > 1 ? "+" : ""), (i > 1 ? " " : ""));
sum += (reversed_num % 10); // Extract the last digit
reversed_num /= 10; // Remove the last digit
}
printf(" = %u\n", sum);
return sum;
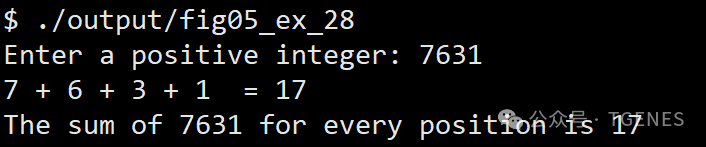
}- Example Run 1:
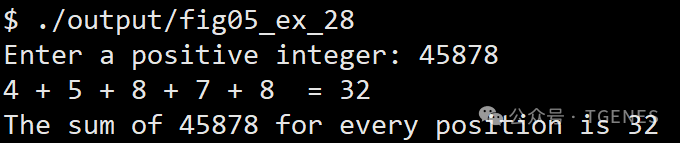
- Example Run 2: