





Proteus vulgaris and Proteus penneri, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus hauseri, and Proteus myxofaciens belong to the Enterobacteriaceae family. Currently, the main pathogens reported are Proteus vulgaris and Proteus mirabilis, with Proteus vulgaris infecting a wide range of animals, causing cystitis, food poisoning, and wound infections. In aquaculture, it can infect California bass, channel catfish, tilapia, shrimp, largemouth bass, Chinese soft-shelled turtle, red-spotted grouper, and crocodiles, leading to lesions and death; while Proteus mirabilis mainly infects poultry, causing death. In nature, Proteus vulgaris has a wide range of hosts, can infect both invertebrates and vertebrates, even humans, and has strong pathogenicity. Research on its pathogenic mechanisms shows that this bacterium adheres to the host cell surface via its fimbriae, rapidly proliferates its flagella and polysaccharide capsule, and enters the host cells to produce a large amount of virulence factors, leading to host death and lesions.
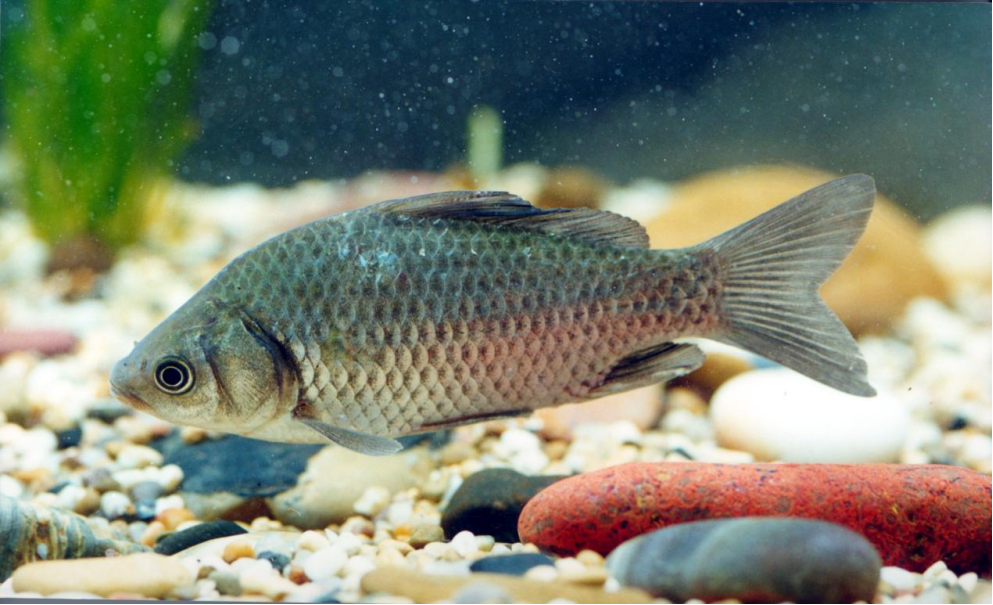

Nanjing Comprehensive Experimental Station conducted field sampling and analysis for a case of carp disease. The symptoms of the diseased carp mainly include ulceration on the body surface, with a light yellow fluid oozing from the anus upon slight pressure on the abdomen. Necropsy revealed a large amount of light yellow abdominal fluid in the abdominal cavity, and the liver appeared earthy yellow. An investigation into the cause of disease in the affected carp was conducted, along with an analysis of the pathogenic characteristics of the bacteria, providing a theoretical basis for the prevention and control of carp diseases.
By isolating and purifying bacteria from the liver and intestines of the diseased carp, conducting 16S rRNA sequence analysis, artificial infection tests, physiological and biochemical identification, and phylogenetic tree construction, as well as antibiotic susceptibility tests using the paper disk diffusion method, sensitive drugs were screened. Strain A was isolated from both the liver and intestines of the diseased fish, and the 16S rRNA sequence analysis and physicochemical characteristics were consistent with Proteus vulgaris. The artificial infection test confirmed that strain A is a pathogenic bacterium, with an LD50 of 9.77×106 CFU/fish. Strain A is highly sensitive to cephalexin, cefalexin, florfenicol, kanamycin, azithromycin, doxycycline hydrochloride, and resistant to amoxicillin, erythromycin, and clindamycin. Test results indicate that strain A is Proteus vulgaris, the main culprit in this carp disease, and clinical treatment can be based on the antibiotic susceptibility test to select highly sensitive antibiotics for treatment.
No reports have been seen domestically regarding Proteus vulgaris infection in carp. This study also confirms for the first time that Proteus vulgaris can infect carp, causing disease. Proteus vulgaris exists not only in nature but also in the intestines of animals. The intestinal microbiota of fish forms a stable state, normally being a relatively balanced microbial system coexisting with the host without affecting each other. However, once the balance is disrupted, some bacteria can become pathogenic, leading to fish diseases. Currently, the treatment of bacterial diseases still relies on the use of antibiotics, but during clinical treatment, the amount of antibiotics used must be controlled. Excessive use of antibiotics can also have counterproductive effects, disrupting the balance of intestinal flora, thus causing other diseases.

Symptoms of Infection: When fish are infected with Proteus vulgaris, a series of symptoms may appear. For example, the ulceration on the fish’s body surface may not be obvious, but the intestines may exhibit edema or even necrosis, and the liver may show spotty necrosis. These symptoms can severely affect the health of the fish and even lead to death.
High Mortality Rate: In some cases, infection with Proteus vulgaris may lead to a high mortality rate in fish. For instance, studies have shown that at certain concentrations, test fish may experience continuous death shortly after infection, with the final mortality rate potentially reaching a high level.
Impact on Farming Efficiency: Infection with Proteus vulgaris not only leads to fish deaths but also affects farming efficiency. On one hand, outbreaks of disease increase farming costs, including treatment and medication expenses; on the other hand, the disease also affects the growth rate and quality of the fish, thereby reducing farming efficiency.
Scientific Farming: Implement scientific and standardized farming practices, preferentially selecting disease-resistant fish species to control pathogens from the source and reduce incidence rates.
Water Quality Management: Strengthen water quality management, maintain excellent water quality and sufficient dissolved oxygen, and adjust the water environment suitable for fish growth. Regularly change water, adding water in small amounts multiple times, avoiding large-scale drainage and filling.
Disinfection Treatment: Regular disinfection of farming ponds, production tools, etc., is essential to prevent cross-infection. Disinfect ponds, tools, and seedlings before stocking to prevent pathogens from being introduced with the seedlings.
Rational Feeding: Flexibly control the feeding amount based on weather, water quality, and fish activity, using fresh feed and avoiding spoiled feed. Improve feed quality and regularly add immune enhancers to the feed to boost fish resistance.
Drug Treatment: Under the guidance of veterinarians or aquaculture experts, use antibacterial drugs sensitive to Proteus vulgaris for treatment, such as florfenicol, doxycycline hydrochloride, etc. When using drugs, strictly follow the instructions or the veterinarian’s advice to avoid overdose or abuse of drugs.
Chinese herbal medicine has natural, safe, and residue-free advantages, showing great potential for application in treating fish diseases. For Proteus vulgaris infections, some herbs with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and immune-boosting effects can be selected for feeding or soaking treatment. However, it should be noted that the therapeutic effects of herbal medicine may be relatively slow, and combinations and dosage adjustments should be tailored to different symptoms.
Water Quality Adjustment: Use quicklime or chlorine-containing disinfectants to disinfect the farming water, killing pathogenic bacteria in the water. Adjust water quality to maintain suitable pH and dissolved oxygen levels, which helps fish recovery and healthy growth.
Farming Management: During the treatment period, strengthen farming management, observe changes in fish activity, feeding, and coloration, and timely adjust feeding amounts and types. Maintain cleanliness and hygiene in the farming environment, promptly removing debris and leftover feed from the farming pond.

Accurate Diagnosis: Before treatment, an accurate diagnosis of the fish should be made to determine if it is an infection of Proteus vulgaris, avoiding misdiagnosis and mistreatment.
Scientific Medication: During treatment, medication should be used scientifically to avoid misuse or overdose, which may cause unnecessary harm to the fish.
Observe Treatment Effects: During treatment, closely observe the recovery of the fish. If the condition does not improve or worsens, timely adjust the treatment plan.
This article is copyrighted by the Journal of Scientific Aquaculture
Author: Nanjing Comprehensive Experimental Station, Zhao Yanhua
Editor:Liu Le Dan (WeChat ID: Editor-Liu9, for news tips and reprint authorization, please add WeChat)
★ Winter hit! Many places drop more than 10°C in a single day! Typhoon “Ginkgo” forms
★ Prices of yellow catfish and grass carp plummet; prices of California bass drop; bullfrogs and black-spotted frogs remain sluggish in the market
★ Shrimp ponds cleared of dirt flooded wheat fields, resulting in disputes! This is how it was resolved!
★ Tight supply of Ecuadorian white shrimp drives up prices in the Chinese market!

1. Conference Theme
New Quality Productivity Empowering the Shrimp and Crab Industry for a New Future
2. Conference Content
1. Paradigm shift promoting the development of new quality productivity in fisheries
Academician Gui Jianfang, Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
2. Techniques for reducing costs and improving quality in shrimp farming
Professor He Jianguo, National Shrimp and Crab Industry Technology System
3. Current status of river crab breeding in China and new variety breeding
Researcher Xu Pao, Freshwater Fisheries Research Center, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences
4. Current status of crayfish industry in Jiangsu Province and main efficient farming models
5. Progress in new variety breeding of green shrimp and efficient farming models
Researcher Fu Hongtuo, Freshwater Fisheries Research Center, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences
6. Scalable green farming and quality control techniques for river crabs
Researcher Ge Jia Chun, Jiangsu Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture
7. Development and application techniques of functional feed for shrimp and crabs
Researcher Liu Bo, Freshwater Fisheries Research Center, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences
8. Overview of river crab farming in Hunan and efficient farming models
Professor Wang Chun, Shanghai Ocean University
9. New trends in disease occurrence in shrimp and crabs under continuous high temperatures and prevention measures
Researcher Fang Ping, Jiangsu Fisheries Technology Promotion Center
10. Nutritional requirements and feeding techniques for juvenile crayfish
Professor Wang Aimin, Yancheng Institute of Technology
11. Exploration and reflection on coupling technology for shrimp and crabs (river crabs and crayfish)
Researcher Zhang Fengxiang, Modern Agricultural Development Service Center, Xinghua City
3. Conference Time
November 14-15, 2024, registration on the 14th, conference on the 15th.
4. Conference Location
Jinling International Hotel, Taizhou, Location: No. 298, Hailing South Road, Hailing District.
5. Organizers
Freshwater Fisheries Research Center, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences
National Shrimp and Crab Industry Technology System
Jiangsu Haorun Biological Industry Group Co., Ltd.
……
6. Co-organizers
China Fisheries Association Input Products Branch
Jiangsu Fisheries Association
Jiangsu Shichang Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Group Co., Ltd.
Hunan Yumekang Biotechnology Group Co., Ltd.
Jiangsu Hengtai Environmental Protection Technology Development Co., Ltd.
Guangdong Hengxing Feed Industry Co., Ltd.
Yancheng Tianbang Feed Technology Co., Ltd.
……
7. Support Units
Jiangsu Haiwei Feed Co., Ltd.
……
8. Sponsoring Units
Tianjin Fish Life Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Wuxi Zhongshui Fish Medicine Co., Ltd.
Merck Animal Health Products (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Nanjing Siyuan Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Jiangsu Haibo Feed Technology Co., Ltd.
Fujian Runhe Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Technology Co., Ltd.
Jiangsu Yihui Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Huai’an Chengxin Fish Public Crab Industry Technology Co., Ltd.
Guangdong Lijian Biological Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Huai’an Guochang Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Sheyang Chengxin Changjiang Crab Ecological Seedling Farm
Shanghai Fulangte Animal Health Co., Ltd.
Su Zhou Anmaikang Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Huai’an Zhengchang Feed Co., Ltd.
Huai’an Fish Butler Aquatic Technology Co., Ltd.
……
9. Friendly Support Units
Tian Nong Biological Engineering Research (Tianjin) Co., Ltd.
Jiangyin Baichuan Oxygen Equipment Co., Ltd.
Mingguang Green Clean Environmental Technology Co., Ltd.
Taizhou Aohua Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Wuhan Chutian Aike Biotechnology Group Co., Ltd.
Yangzhou Hongda Feed Co., Ltd.
……
10. Undertaking Units
Journal of Scientific Aquaculture, Chinese Fisheries Society
11. Sponsorship Contact



Important Reminder: Recently, some authors have found counterfeit submission websites through search engines. After submitting, they not only received no response but also some were scammed out of page fees. The correct submission website for this journal is: kxyy.fish.cn, which does not charge any form of review fee. Once the manuscript is accepted, remuneration will be paid! Please choose the correct website for submission!