Today, I will outline various low-power wide-area network technologies and their corresponding alliances. Different organizations or alliances manage different protocols, including IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), ETSI (European Telecommunications Standard Institute), 3GPP (The Third Generation Partnership Project), IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force), WEIGHTLESS-SIG (WEIGHTLESS Special Interest Group), LoRa™ Alliance, and DASH7 Alliance. I will provide a brief introduction to each alliance and its main technologies.
1
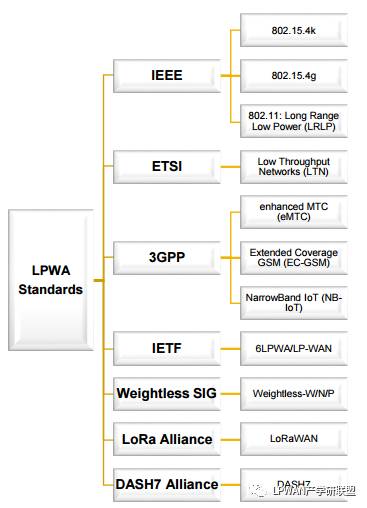
IEEE
IEEE has introduced two long-range, low-power network standards: 802.15.4 and 802.11. 802.11 is the original wireless local area network standard developed by IEEE, primarily used to address wireless access for users and terminals in office and campus networks. The IEEE 802.15.4 standard is designed for low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPAN). This standard focuses on low power, low-rate transmission, and low cost, aiming to provide a unified standard for low-speed interconnection between different devices within personal or home environments.
2
ETSI
ETSI focuses on the development of narrowband standards and proposed a bidirectional low-rate LPWA standard called LTN (Low Throughput Network) in 2014. For example, LPWA technology providers such as Sigfox, TELENSA, and Semtech are actively participating in the standardization of ETSI standards.
3
3GPP
3GPP, which focuses on the M2M and IoT markets, has evolved its existing cellular standards to reduce complexity and cost, improve signal penetration and coverage, and significantly extend battery life. Its multiple authorization schemes, such as eMTC (enhancements for Machine Type Communications), EC-GSM (Extended Coverage GSM), and NB-IoT (Narrow-Band IoT), evolved from LTE (Long Term Evolution), balance cost, coverage, data rate, and energy consumption to meet the diverse application needs of IoT and M2M.
4
IETF
IETF aims to provide a proprietary technology LPWA ecosystem by standardizing IP-based end-to-end connectivity to serve low-power devices and applications. IETF proposed 6LoWPAN (IPv6 stack for Low power Wireless Personal Area Networks), but the 6LoWPAN standard based on IEEE 802.15.4 has a relatively higher rate compared to other LPWA technologies, but a relatively smaller coverage range.
5
WEIGHTLESS-SIG
The WEIGHTLESS Special Interest Group has proposed three open LPWA standards: WEIGHTLESS-W, WEIGHTLESS-N, and WEIGHTLESS-P, each with different characteristics, coverage, and power consumption. These standards can be used in both unlicensed and licensed frequency bands.
6
LoRa™ Alliance
LoRa is a proprietary physical layer for LPWA connectivity, while the upper layer and system structure are defined and regulated by the LoRa™ Alliance, an open, non-profit technology alliance focused on LPWA. Over the past two years, the LoRa™ Alliance has rapidly developed, and the deployment and application promotion of LoRaWAN networks globally have accelerated.
7
DASH7 Alliance
The DASH7 Alliance, composed of over 20 RFID suppliers, users, and researchers, has proposed a standard that defines a complete LPWA connection vertical network stack called D7AP (DASH7 Alliance Protocol). Based on the ISO/IEC 18000-7 standard for active RFID device air interfaces, D7AP introduces a stack for providing medium to long-range connectivity for low-power sensors and actuators.

LPWAN Industry-Academia-Research Alliance
WeChat ID: LPWAN-NIOT

The Internet of Things is no longer a dream.
Please long press the QR code to follow.
