Definition of Concepts:
STEAM education is essentially an educational approach that integrates multiple disciplines, balancing theory and practice, aimed at enhancing students’ comprehensive problem-solving abilities.
Global Overview:
The United States focuses on management, funding, and top-level design macroscopically, while emphasizing teacher and student training and keeping content up to date in execution; Finland provides a conducive environment for STEAM education with a well-developed teaching, learning, and curriculum design; Japan’s STEAM education ecosystem consists of diverse roles from government and society, with curriculum design following the “Programming + X” integration concept.
Development Drivers:
Policies at the level of teachers, teaching, and curriculum have been introduced; in terms of talent cultivation, interdisciplinary development is gradually gaining momentum in China; technological advancements such as AIGC and XR are enhancing learning experiences.
Ecological Interpretation:
China’s STEAM education industry mainly includes regulatory policies, competition activities, and the core industrial chain across upstream and downstream. Currently, midstream enterprises are the backbone of the entire industry’s development, collaborating with regulators to establish standards, deeply involved in operating competition activities, expanding upstream for R&D in software and hardware, and promoting the dissemination of STEAM educational concepts downstream. Competition activities are currently the cornerstone for ensuring the healthy and sustainable development of the industry, but issues such as questionable credibility, vague intrinsic value of competitions, and a singular existing evaluation system still exist. The entire industry continues to iterate and update in terms of educational concepts, curriculum development, and teacher training with the advancement of technologies like artificial intelligence.
Industry Pain Points:
The lack of systematic design in course resources, a shortage of interdisciplinary capabilities among teachers, and users’ focus on externalized results are prevalent issues.
Practical Implications:
Currently, China’s STEAM education practices are mainly categorized into three types: software programming, hardware programming, and scientific literacy.
Market Size:
In 2024, China’s STEAM education market size is approximately 64.71 billion RMB, with a CR5 market concentration of about 10-15%. By 2029, the market size is expected to grow to 101.51 billion RMB.
Business Models:
Currently, the mainstream business models and profit channels in the market are primarily in the directions of courses and hardware. Among course-oriented enterprises, those targeting C-end users have a relatively mature business model, while those targeting B/G-end users still need further exploration; hardware enterprises improve their influence by sponsoring competitions to become official equipment suppliers, which is currently a common business model. Additionally, enterprises can explore business model expansion by identifying market positioning for small and medium-sized institutions, collaborating on-campus and off-campus, and diversifying their business types to enhance profitability.
User Level:
As the demand from lower-tier cities begins to emerge and various local primary and secondary schools start offering scientific literacy courses, the user base is steadily expanding.
Regional Level:
Capital outflow can achieve rapid overseas market layout, hardware export can effectively reduce capital costs, and content export is optimal with lightweight AI courses.
Scope Level:
Collaborating with undergraduate and vocational education to enhance research capabilities and vocational education while actively exploring issues related to the connection between basic education and industry collaboration.

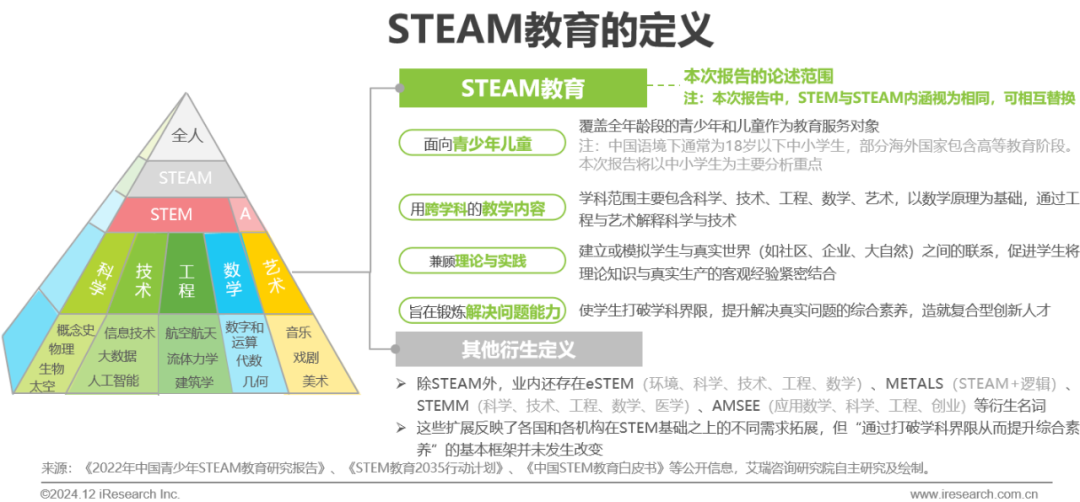
Definition of Concepts – What is STEAM Education
Integrating knowledge from science, technology, engineering, arts, and mathematics into a comprehensive educational approach aimed at enhancing students’ problem-solving abilities.
STEAM is an acronym for the first letters of Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics. STEAM education integrates knowledge from these five disciplines, emphasizing the integration, diversity, and inclusivity of subjects, aiming to break down the boundaries of disciplines and cultivate children’s ability to identify problems and solve them based on multidisciplinary approaches.
In the 1980s, the National Science Board of the United States proposed STEM education, which evolved into a national strategy aimed at encouraging more students to choose STEM-related subjects in higher education to maintain the U.S.’s leading position in technological innovation and international competitiveness. Professor Yakman from Virginia Tech noted that STEM has certain limitations in the breadth and depth of interdisciplinary knowledge and lacks engagement, contextual relevance, and artistic elements in its teaching process. Therefore, she organically integrated the arts with STEM and proposed the concept of STEAM education in 2006. Around 2014, the concept of STEAM education was introduced to China, sparking a wave of STEAM education in the country.
Overview of the United States – Development Characteristics
Macroscopically focuses on management, funding, and top-level design, while execution emphasizes teacher and student training and keeping content up to date.
The National Science Foundation of the United States released the report “Undergraduate Education in Science, Mathematics, and Engineering” in 1986, marking the beginning of STEM education in the U.S.; after Obama took office, STEM education expanded from higher education to K12, and various educational planning and teacher training documents were subsequently issued. Since then, U.S. STEAM education has formed characteristics in macro governance such as “multi-party participation under overall coordination at the management level,” “high funding investment,” and “gradually increasing emphasis on top-level design,” along with characteristics at the teacher level focusing on teacher training and providing multi-dimensional support, at the student level providing diverse learning scenarios and paying attention to disadvantaged groups, and at the content level emphasizing vocational education integration and keeping pace with the times..

Overview of Finland – Development Characteristics
The macro educational environment provides a good foundation for STEAM education, with well-developed teaching, learning, and curriculum design.
Finland is one of the countries providing the best foundational education for STEAM education. The complete curriculum design at the basic education stage starts with integrated subjects, requiring all teachers at this level to master the ability of “interdisciplinary teaching”. Additionally, the latest round of curriculum reform in Finland has further enhanced the importance of integrated teaching, providing a solid foundation for the development of STEAM education through good curriculum design and teacher training. Consequently, the implementation of STEAM education in Finland primarily involves integrating programming and other content into existing subjects, providing a complete and closed-loop training system for teachers while emphasizing awareness cultivation among students.

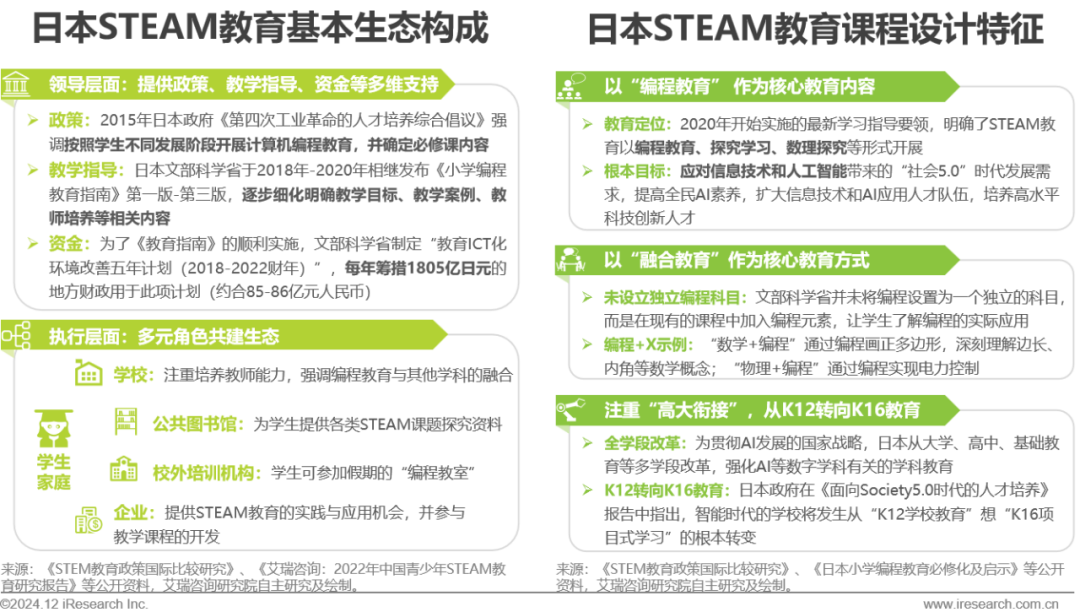
Overview of Japan – Development Characteristics
The basic ecology is composed of diverse roles from the government and society, with curriculum design adhering to the “Programming + X” integration concept.
Japan’s STEAM education started relatively late, appearing in national strategies such as the “Fourth Science and Technology Basic Plan” only in 2010. Therefore, Japan’s STEAM education policies, teaching concepts, and curriculum designs are highly related to the promotion of information technology and artificial intelligence development. The basic ecology of STEAM education in Japan consists of diverse roles, including government, schools, public libraries, extracurricular training institutions, and social enterprises. The curriculum design of STEAM education in Japan mainly follows the principles of “programming education as the core content, integration education as the core approach, and emphasizing high-level connections.” Considering the relatively short implementation period and the predominance of public institutions in promotion, this report does not provide case studies of Japanese enterprises.

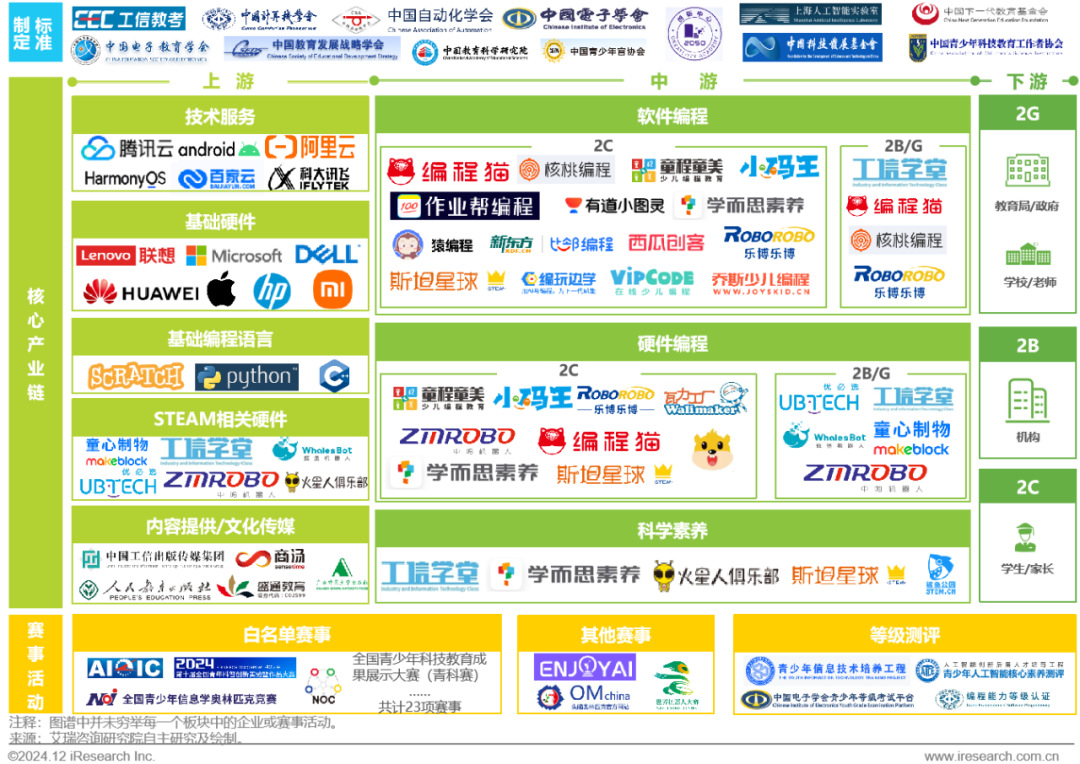
Industry Ecosystem – Overview of the Industrial Map
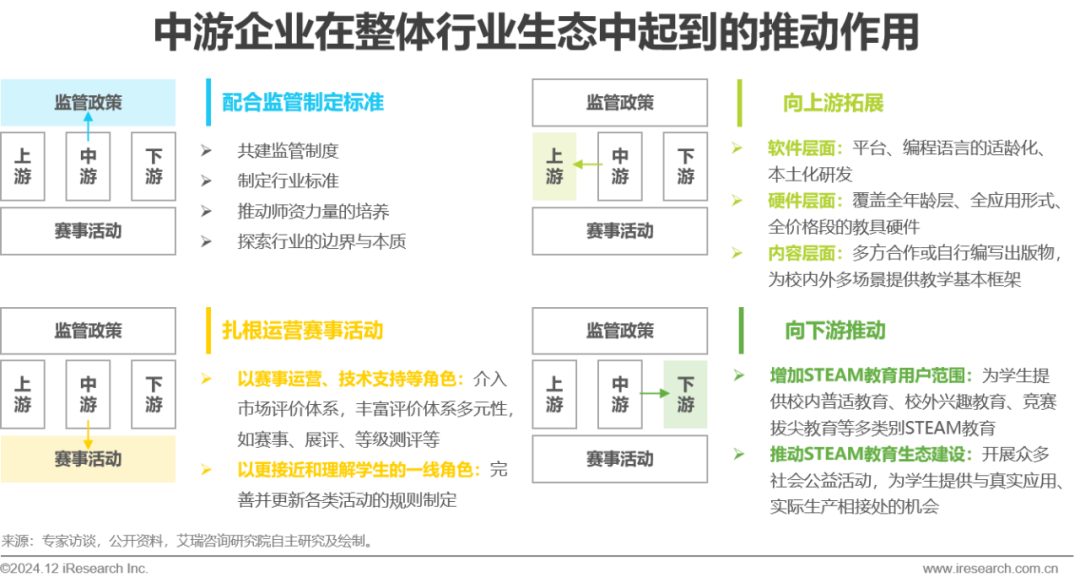
Midstream Interpretation – The Backbone of the Industry
Collaborating with regulators to establish standards, deeply involved in operating competition activities, expanding upstream for R&D in software and hardware, and promoting the dissemination of STEAM educational concepts downstream.
In 2017, the Chinese Academy of Education Sciences released the “China STEM Education White Paper,” which mentioned that the rise of STEM in China is more of a grassroots movement under national policy trends, with various STEM product companies being the first to launch products and gradually carry out related educational activities to promote the development of STEM education in society. To this day, midstream enterprises in China’s STEAM education industry still integrate and consolidate diverse roles such as education departments, education experts, teachers, and industry partners. They can collaborate to build regulatory systems and industry standards, deeply engage in various competition activities, expand upstream for R&D in software and hardware, and promote the dissemination of STEAM educational concepts among students, continuously building and improving the new ecology of STEAM education.
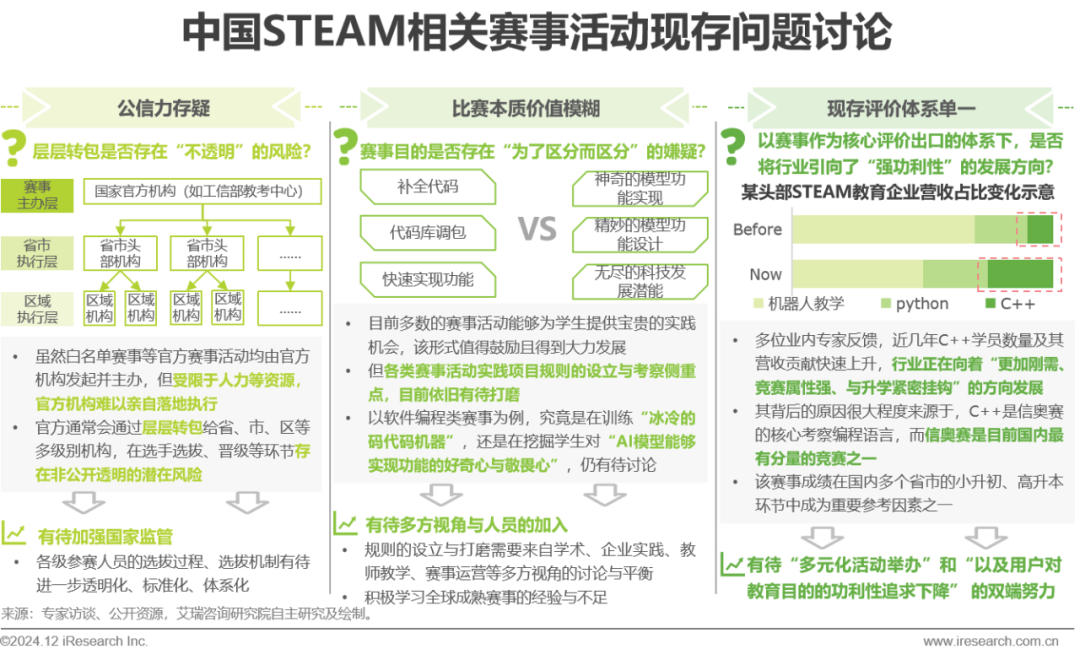
Competition Activities Interpretation – Basic Introduction
The whitelist is one of the most prestigious competitions, with software and hardware programming, and scientific literacy as the main assessment content, where theory and practice coexist as the primary assessment method.
Currently, the competition activities related to STEAM education in China mainly consist of whitelist competitions, commercial competitions, and level assessment activities. Among these, the “Natural Science Literacy” category, which has accounted for more than half of the whitelist competitions for five consecutive years, is currently one of the most prestigious competition categories in STEAM education. The assessment content of various competition activities primarily focuses on software and hardware programming, and scientific literacy, continuously evolving new competition items as technology develops; the emergence and development of new competition items to some extent lead the direction and focus of STEAM education in domestic education. The assessment methods of various competition activities are primarily based on a combination of theory and practice and result showcases, but there are potential issues such as lack of transparency in assessments and insufficient credibility in result showcases.

Competition Activities Interpretation – Value Analysis
The export nature of competition activities makes them a cornerstone for ensuring the healthy and sustainable development of the industry.
The awards and certificates from various competition activities are currently the largest output for verifying achievements in China’s STEAM education, thus becoming a cornerstone for ensuring the healthy and sustainable development of STEAM education. At the national level, competition activities to some extent embody the official advocacy of educational direction, thus playing a guiding role in educational direction and teacher training at a macro level. At the enterprise level, competition activities become an important link in the commercial closed loop, providing an engine for profit growth. At the user level, competition activities provide students with the most direct incentives and positive feedback, while also offering valuable practical opportunities and exposure to real industry development under the existing educational system.

Competition Activities Interpretation – Existing Problems
Issues such as questionable credibility, vague intrinsic value of competitions, and a singular existing evaluation system urgently need to be resolved.
It is undeniable that competition activities have become an important support for the development of STEAM education in China, but there are still issues that need discussion and resolution. Issue one: official competitions have a phenomenon of layered subcontracting in the actual implementation process, resulting in risks such as lack of transparency in participant selection. Issue two: the intrinsic value of competitions is vague; although competition activities provide students with practical opportunities, the quality of practice and focus of assessment still need refinement and optimization. Issue three: the existing evaluation system is singular, and under the influence of commercial profit-seeking, the industry is developing towards a direction characterized by “strong necessity and competitive attributes,” which requires the hosting of more diversified activities and a shift in the mindset of all users.
Industry Iteration Interpretation – Artificial Intelligence
The development of artificial intelligence puts forward iterative requirements for educational concepts, curriculum construction, and teacher training.
With the development of artificial intelligence, the demands placed on children by society are changing rapidly, and both the industry and users need to continuously iterate and keep pace with the times. Firstly, at the grassroots level, parents and children should strive to participate in diverse activities to ensure that family members update their concepts, forming a basic consensus that values emerging technologies and principles exploration within the family. Secondly, the overall society and enterprises should synchronize their iterative development across multiple dimensions such as curriculum, teacher capabilities, and software and hardware, ensuring that societal needs, school/institutional training, and family progress at a synchronized pace.

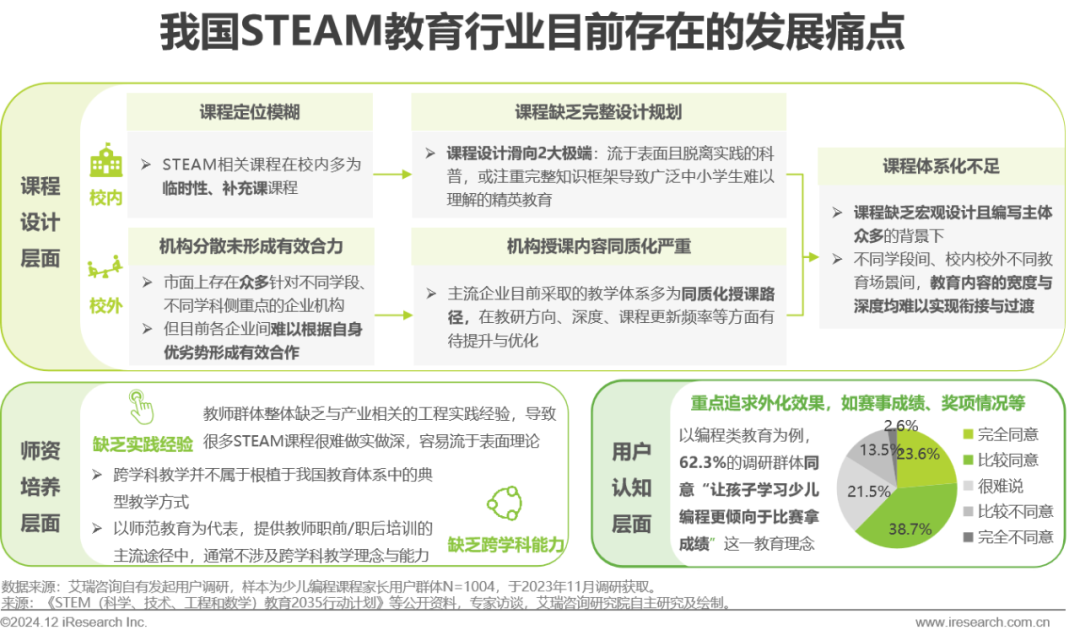
Industry Pain Points Interpretation – Curriculum, Teachers, Users
Lack of systematic design in course resources, teachers lack interdisciplinary capabilities, and users primarily pursue externalized results.
Although China’s STEAM education is actively catching up with the development of the times, there are still numerous developmental pain points in the existing ecology regarding courses, teachers, and user cognition. Firstly, in terms of course design, the STEAM-related courses offered in schools are often temporary or supplementary, lacking comprehensive design planning. Meanwhile, the teaching content among off-campus institutions is highly homogenized, leading to an overall lack of systematic structure in China’s STEAM course resources. Secondly, in terms of teacher training, teachers generally lack practical experience and interdisciplinary teaching capabilities, making it easy for classes to remain superficial. Finally, in terms of user cognition, despite the promotion of quality education concepts over the past few decades, users still generally focus on pursuing externalized results such as competition scores.

Subcategories of STEAM Education in China
In STEAM education practices, based on different educational focuses, it is mainly divided into software programming, hardware programming, and scientific literacy, with the same institution often offering multiple types of courses.

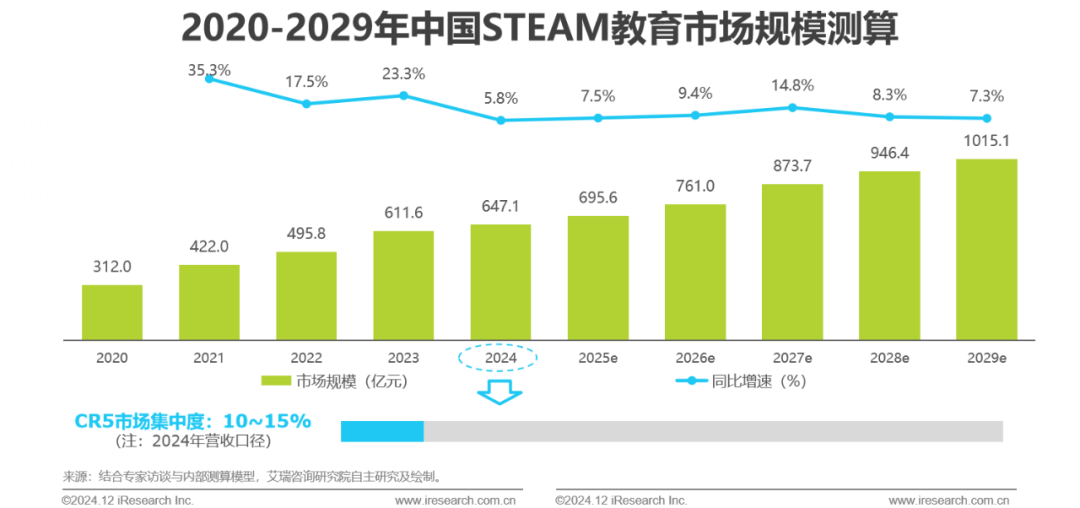
Overall Market Size Estimation
In 2024, the market size is about 64.71 billion, and it is expected to exceed 100 billion by 2029.
As of 2024, the market size of STEAM education in China is approximately 64.71 billion RMB, with a CR5 market concentration of only about 10-15%, indicating that it is still a market with low concentration and significant long-tail effects. Although the entire market faces challenges such as a decrease in the total number of eligible users due to declining birth rates and an unclear growth trend in user consumption, positive factors such as the increase in penetration rates driven by national promotion of technology-related education and the increase in average revenue per user driven by enterprises developing study tours make it possible for the market size of STEAM education in China to exceed 100 billion by 2029, with a projected CAGR of about 9.4% over the next five years.
The forward estimation logic for market size is: market size = total number of eligible users * STEAM education penetration * average revenue per user; the reverse estimation logic for market size is: market size = annual revenue of leading enterprises / market share of leading enterprises. The market size in this report has been validated through both forward and reverse estimation.
Overview of Commercial Practices in China
Courses and hardware are the mainstream profit channels, while positioning for small and medium-sized institutions, on-campus and off-campus cooperation, and expanding business types provide new ideas for enterprises to explore business models.
Currently, the mainstream business models and profit channels in the market are primarily in the directions of courses and hardware, with course-oriented enterprises further divided into “enterprises originating from STEAM education” and “enterprises gradually expanding their educational scope to the STEAM education field,” with typical representatives including Gongxin Academy, Programming Cat, etc.; hardware enterprises are further divided into “education enterprises” and “technology enterprises,” with typical representatives including UBTECH, Whale Robot, etc. Additionally, enterprises can explore business model expansion by identifying market positioning for small and medium-sized institutions, collaborating on-campus and off-campus, and diversifying their business types to enhance profitability.

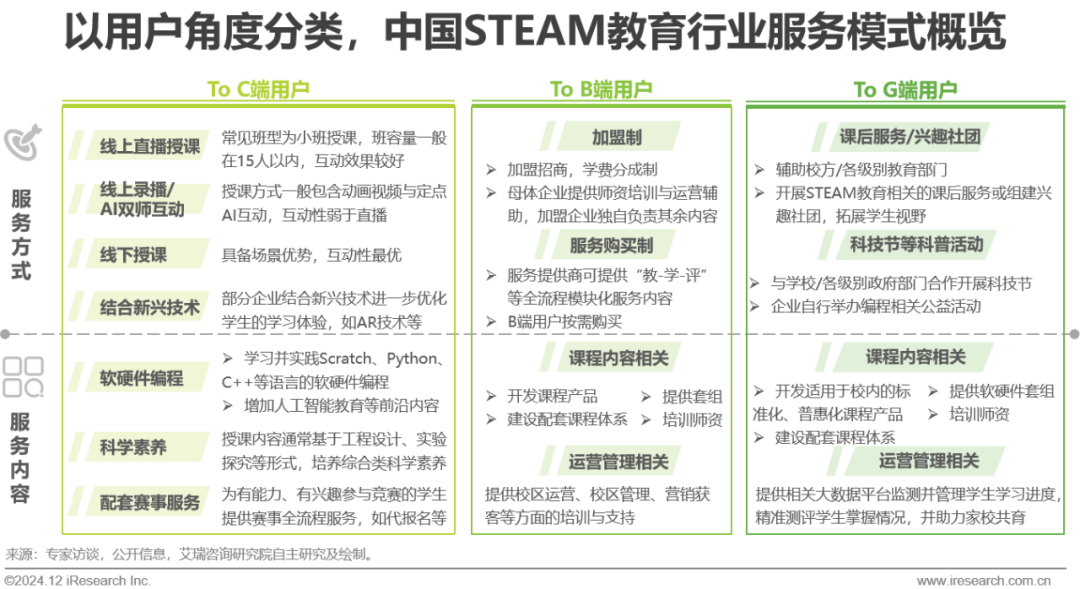
Commercial Model Analysis of Course-Oriented Enterprises – Overview
Users are divided into C/B/G ends, with a service model combining online and offline, and service content covering courses and operations.
The service methods and contents involved in the STEAM education industry vary significantly based on the target users. C-end users mainly refer to students and parents, with the services provided by enterprises primarily through various teaching formats, offering programming courses, scientific literacy courses, and supporting competition services. B-end users mainly refer to franchisees of large enterprises or small STEAM education institutions, with service methods including franchising and service purchasing, and service content mainly including course development and teacher training services, campus operations, and customer acquisition services. G-end users mainly refer to schools or education-related departments at various levels, with service methods primarily including after-school services, interest clubs, and science popularization activities, covering the entire teaching process, such as course development, teacher training, student management, and assessment.
Commercial Model Analysis of Course-Oriented Enterprises – Advantages and Disadvantages
Among enterprises originating from STEAM education, the C2B business model is relatively mature but significantly affected by policies, while the B/G business model is relatively a blue ocean but requires high resource integration capabilities.
Currently, the enterprises in the STEAM education industry that can successfully develop with courses as the main business can be divided into two categories based on their business origins: “originating from STEAM education” and “gradually expanding their educational scope to the STEAM education field.” The former can be further divided based on user types and revenue capabilities into three subcategories: the first category consists of large enterprises primarily targeting C-end users, which were established earlier but face risks of difficulties in transitioning if they maintain a single business; the second category consists of small enterprises primarily targeting C-end users, which have a lower profit burden and can easily establish a high influence in certain regions, but their growth potential is limited; the third category consists of enterprises primarily targeting B/G-end users, which are currently in a blue ocean competition stage, and the user types determine that this business requires high resource integration capabilities, but successful benchmark projects have obvious marginal effects.

Enterprises gradually expanding their educational scope to STEAM education possess a strong human resources foundation, but their operational model is less replicable.
Currently, the enterprises in the STEAM education industry that can successfully develop with courses as the main business can be divided into two categories based on their business origins: “originating from STEAM education” and “gradually expanding their educational scope to the STEAM education field.” The latter primarily consists of internet education enterprises that have accumulated a large student base and teacher resources, as well as rich operational experience with enterprises and users before entering the STEAM education field. The operational model in the STEAM education field has externalized effects, enhancing the circulation capabilities of different sub-businesses within the enterprise, which also determines that the operational model of these players is less replicable and has lower reference value.

Commercial Model Analysis of Hardware-Oriented Enterprises – Overview
Education enterprises expand users and enhance profitability around competitions, while technology enterprises enhance influence through competitions.
Currently, there are primarily two types of enterprises in the market that focus on STEAM education-related hardware as their main business. The first type is education enterprises, with typical representatives including but not limited to UBTECH, Whale Robot, and Mars Club, which become official equipment suppliers for large competitions through sponsorships, significantly enhancing their brand influence and driving purchases from B/G end clients, while gradually improving their production capabilities and reducing costs, eventually enhancing sponsorship levels or starting to host competitions themselves to create a closed business model. The second type consists of technology enterprises, including but not limited to DJI, Arduino, and SenseTime, but student/competition hardware is not a significant profit point for these enterprises and is typically only used in high-level competitions or university-level events, thus not analyzed in detail in this report.

Commercial Model Analysis of Hardware-Oriented Enterprises – Advantages and Disadvantages
The high-end professional path effectively increases user average revenue per user, while the low-price inclusive path can expand user awareness.
The two types of hardware-oriented enterprises currently generally show two development paths. The first path is towards “high-end and professional”; the advantage of this path is that the product is highly recognizable and difficult for other enterprises in the industry to replicate, effectively increasing the user’s lifetime value; however, the products of such enterprises typically establish a moat through closed-source models, leading to lower market compatibility and challenges in future market cooperation expansion. The second path is towards “low-price and inclusive”; this path’s advantage is the ability to quickly establish widespread user awareness, and low-priced, low-age products are also conducive to reaching a large number of users through entertainment cross-industry collaborations; however, the products of such enterprises are easier to replicate, leading to a weaker product moat and higher demands for cost control capabilities, and furthermore, low-price strategies may lead to insufficient profits, slowing down product iteration speed and increasing the risk of being eliminated from the market.

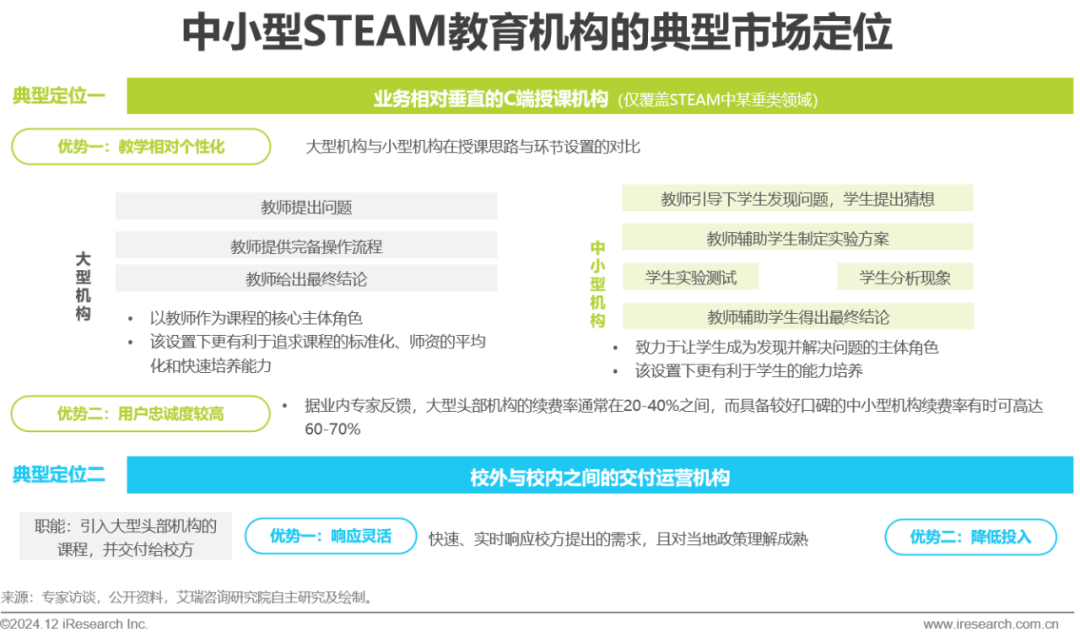
Exploration of Market Positioning for Small and Medium-Sized Institutions
Covering only a specific vertical field of teaching or becoming an operational role between on-campus and off-campus to secure a place in the market.
The STEAM education industry currently exhibits characteristics of low concentration and diversified institutions in the domestic market, thus retaining numerous small and medium-sized institutions. These institutions currently have two main positioning types in the market. The first typical positioning is “C-end teaching institutions with relatively vertical business,” usually characterized by more personalized teaching and higher user loyalty. The second typical positioning is “delivery operational institutions between on-campus and off-campus,” where these enterprises’ roles involve introducing courses from large leading institutions and delivering them to schools, allowing for more flexible responses to local policies while effectively reducing enterprise investment and focusing on cultivating operational capabilities.
Exploration of Cooperation Between On-Campus and Off-Campus
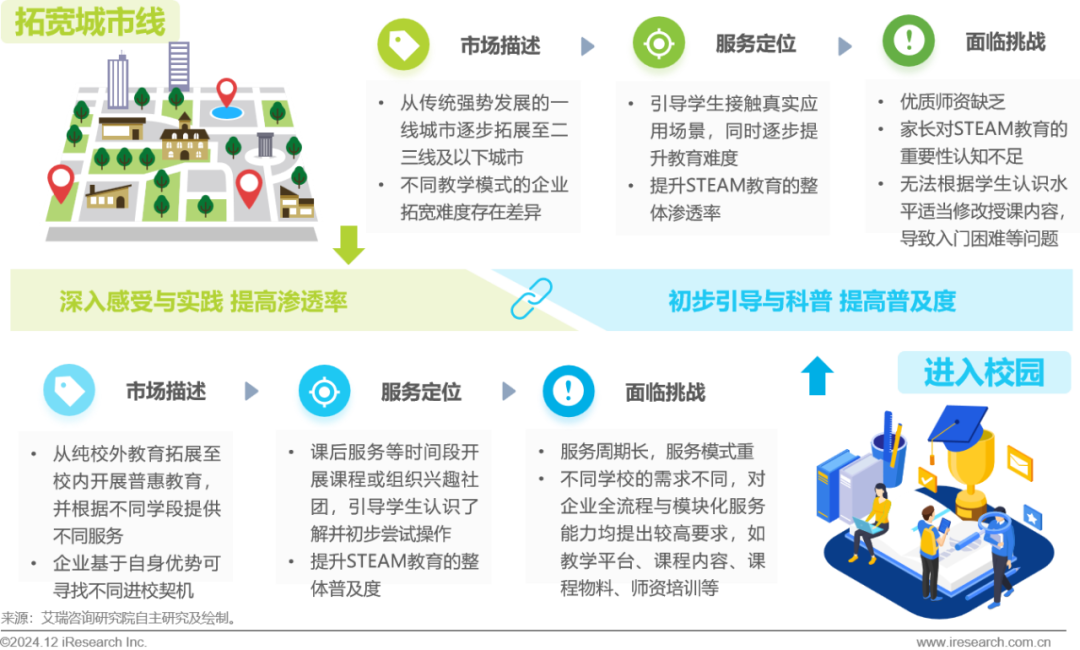
On-campus construction of characteristics leveraging off-campus resources, while off-campus leveraging on-campus resources for user education.
Although there is currently a demand for actively conducting scientific education and artificial intelligence education in schools due to policy requirements, the current education in these areas lacks sufficient rigidity in terms of “subjectification”; thus, the optimal development route becomes “on-campus leveraging off-campus resources for construction, while off-campus leveraging on-campus resources for user education.” However, there are still three major issues in implementing this route: firstly, enterprises need to flexibly adjust operational strategies according to local policies to resolve the issue of “how to enter schools”; secondly, enterprises need to conduct some subjects based on mainstream teaching practices suitable for local conditions to resolve the issue of “what to teach in schools”; finally, enterprises need to actively balance “cost of entering schools” and “teaching quality” to resolve the issue of “how to commercialize.”

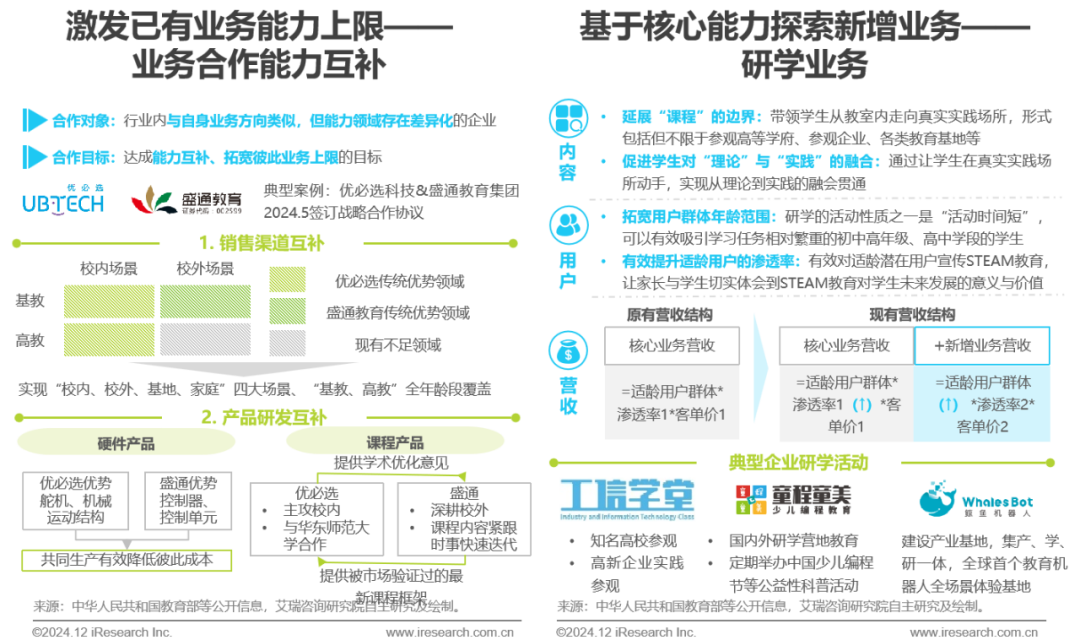
Exploration of Business Type Expansion
Finding complementary partners to stimulate the upper limit of existing business capabilities and exploring new business through research and study.
STEAM education enterprises can further stimulate the upper limit of existing business capabilities by seeking partners with complementary businesses in the industry across dimensions such as educational scenarios, user age, and product development; on the other hand, they can also explore new businesses such as research and study around their core STEAM education business, achieving business upgrades in terms of content, users, and revenue.

User Level – Expanding to Lower-Tier Cities and Schools
As the penetration rate in first and second-tier cities rises, the demand from lower-tier cities begins to emerge, and the development of scientific literacy-related courses in primary and secondary schools across regions steadily expands the potential user base.
Regional Level – Attempting Various Forms of Going Abroad
Capital outflow can achieve rapid overseas market layout, hardware export can effectively reduce capital costs, and content outflow is optimal with lightweight AI courses.
Considering factors such as policy changes in the domestic education industry and declining population, going abroad has become one of the second growth curves sought by many enterprises. From the perspective of domestic players’ profit models and advantageous capabilities, there are currently three main approaches to going abroad, with increasing difficulty: capital outflow, hardware export, and content/educational solution export. Capital outflow can achieve rapid overseas market layout but requires the largest amount of capital; hardware export has the lowest localization transformation cost but may face direct competition from established overseas brands; content export requires the most localization adaptation and transformation but, compared to hardware, has the potential for single-user repurchase and a higher average revenue per user.

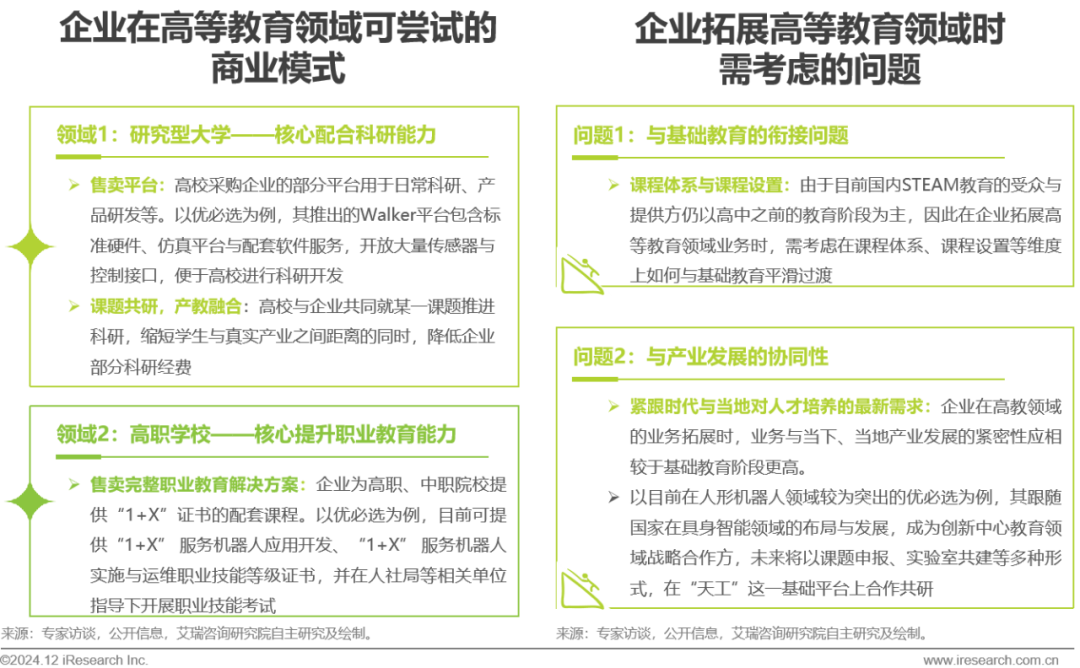
Scope Level – Expanding into Higher Education
Collaborating with research universities and vocational schools to enhance research capabilities and vocational education while actively exploring issues related to the connection between basic education and industry collaboration.
On one hand, starting from 2017, the declining birth rate in China has led to a decrease in the audience for basic education; on the other hand, the “National Digital Literacy and Skills Development Research Report (2022)” mentioned that there is currently a lack of compound talent in China. Under the influence of multiple factors, STEAM enterprises capable of cultivating compound talents in hardware and software are beginning to gradually expand their focus from the basic education stage to the higher education field, seeking sales platforms, collaborative research projects, and integration of industry and education as new growth curves for enterprises.
Appendix – Summary of Mainstream Competition Activities in the Market
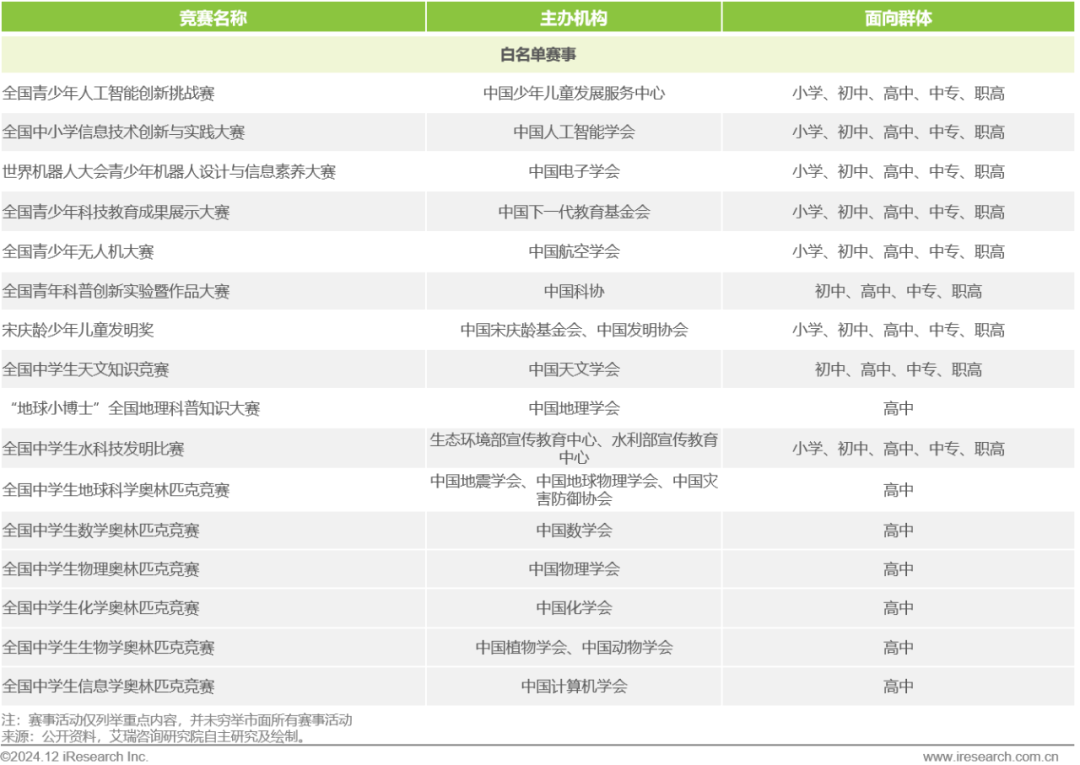
Appendix – Summary of Mainstream Competition Activities in the Market

This article is reprinted from: iResearch Consulting
More Topics

① Why have LEGO and DJI abandoned educational robots?
② Don’t use the brand to deceive money without investing 100 million.
③ Three years later, there will not be educational robots costing more than 1000 yuan.
④ In the past 20 years, has the development route of robot education gone wrong?
⑤ Robot education is an industry with certain growth in the next 20 years.
⑥ Let’s do the math: what services can you get for a franchise fee of 200,000?
⑦ I just want to open a small store, do I need financing? – Insights after six rounds of financing.
⑧ Ministry of Education: Non-subject class “programming” is the most expensive and still rising.
Add a friend


Read the original text to obtain the source file download link