
Sensor Technology Editor Compilation
Sensors are like the eyes, ears, mouth, and nose of a human, but they are not just as simple as human senses; they can even collect more useful information. Therefore, it can be said that these sensors are the foundation of the entire Internet of Things (IoT) system, and it is because of sensors that the IoT system has content to transmit to the “brain”.
In the past, sensors were more commonly used in industry. But over time, they have gradually entered our lives.
Sensors Are the Cornerstone of IoT Development
With the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issuing the official commercial license for 5G on June 6, the arrival of 5G seems to have pushed the IoT to a tipping point, and what are the small wings of the IoT? Perhaps different people have different answers, but sensors are undoubtedly one of the important options.
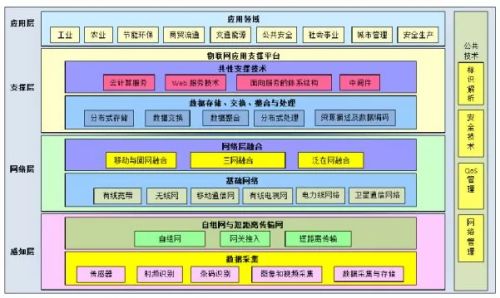
IoT Hierarchy
From the IoT hierarchy diagram, it can be seen that the IoT is mainly composed of four parts: the perception layer, the network layer, the support layer, and the application layer. There is a saying: the foundation of the lower layer determines the upper structure. Sensors, as one of the important components of the IoT perception layer, are the foundation of the entire IoT, and their importance is self-evident.
The massive data information in the IoT system comes from terminal devices, and the data from terminal devices can be traced back to sensors. Sensors give everything the “sensory” function. Just as humans rely on vision, hearing, smell, and touch to perceive their surroundings, objects can also perceive their environment through various sensors. And they are more accurate and have a wider range of perception than humans. For example, humans cannot accurately perceive the specific temperature of an object through touch, cannot sense thousands of high temperatures, and cannot distinguish subtle temperature changes, but sensors can. It can be said that sensors are the “language” for communication between objects in the era of “Internet of Everything”.
The Role of Sensors in the IoT Industry
The Internet of Things is a huge network formed by combining various information sensing devices with the Internet. It is an upgrade of the Internet and the core of the information age. The development of the IoT requires technical support for intelligent sensing, identification, and communication, and the key to sensing is sensors and related technologies. It is not an exaggeration to say that without the progress of sensors, there would be no prosperity of the IoT. As the IoT develops, the sensor industry will also usher in an explosion. Sensors are the key components for data collection in the IoT, playing an indispensable role.
As the world begins to enter a rapidly developing information age, the first thing to solve in the process of acquiring and processing information is to obtain reliable and accurate information, and sensors are the main means and ways to obtain information. For example, in the era of Industry 4.0, sensors are needed to monitor and control parameters in the production process to keep equipment in a normal working state; in the smart home field, sensors are the basis for interaction between users and home appliances (lighting, television, refrigerator, audio, etc.); in autonomous driving, sensors are needed to collect and process traffic and environmental data to ensure the safe operation of vehicles on the road… It can be said without exaggeration that the larger the market for the future IoT, the greater the role sensors will play.
With the increasing demand for IoT, the domestic sensor market is currently showing a trend of rapid growth. According to statistics, it is expected to reach 593.7 billion yuan by 2021, with an average annual compound growth rate of about 30% in the next five years, far exceeding the global average level.
Development History of Sensors
The IoT has been proposed for more than twenty years, but the scale of sensor deployment has not yet been popularized, resulting in an insufficient physical layer and limiting industrial development from the source. Sensor deployment, as the infrastructure of the IoT, has been proposed by the state for a trillion sensor revolution many years ago, aiming to promote the use of 1 trillion sensors in social infrastructure and public services each year, and it is expected to embed 100 trillion sensors in various places after 2030.
China began to engage in the sensor manufacturing industry as early as the 1960s, and after years of development, it can be roughly divided into three generations:
The first generation: is structural sensors, which use changes in structural parameters to sense and convert signals.

The second generation: Sensors began to develop solid-state sensors in the 1970s. These sensors are composed of solid components such as semiconductors, dielectrics, and magnetic materials, made using certain properties of materials.

The third generation: Sensors are intelligent sensors that just developed in the 1980s. The so-called intelligent sensors refer to those that have certain detection, self-diagnosis, data processing, and self-adaptive capabilities for external information, characterized by high precision, low cost, diversified functions, and strong automation. They are the product of the combination of microcomputer technology and detection technology.

Intelligent sensors have multiple integrated circuits with information collection, processing, exchange, and storage functions, and are system-level products that integrate sensing chips, communication chips, microprocessors, drivers, software algorithms, etc.
In the era of intelligent sensing of the IoT, intelligent sensors are one of the key technologies to realize the IoT. Sensors in many IoT scenarios have the characteristics of intelligent sensors, and they will play a huge role in fields such as industry, agriculture, healthcare, and transportation. In the future sensor market, the proportion of intelligent sensors will continue to grow.
Development Requirements for Sensors in the IoT Era
Since their birth in the 1960s, sensors have a history of over 150 years. In the era of mobile internet, the popularity of smartphones has promoted the rapid development of sensors, but it has also determined that many types of sensors are designed specifically for smartphones. The “things” in the IoT era have significant differences in their demand for sensing and connectivity compared to smartphones, so they also place more and higher requirements on sensing technology. In summary, sensors are evolving towards high precision, miniaturization, low power consumption, and intelligence.
1. High Precision and High Quality
If the data information collected by the sensor is incorrect, it means that there is an error from the source, and the subsequent data transmission, analysis, and application will be meaningless. Therefore, the precision and quality of the sensor are an important baseline for ensuring the vision of the IoT. Imagine if the precision and quality of a smart connected car’s sensor do not meet standards; this means that during those crucial milliseconds in an emergency, the system cannot make the correct decision, thus seriously threatening the safety of the driver.
As mobile devices centered around smartphones develop towards multifunctionality and high performance, the number of components within circuit boards requires more and smaller sizes. Therefore, sensors are gradually adopting integrated technology to achieve high performance and miniaturization. Integrated temperature sensors, integrated pressure sensors, etc., have long been widely used, and more integrated sensors will be developed in the future.
We are already accustomed to the daily need to charge our smartphones due to the high power consumption of social media, videos, and games. But can you imagine how awkward it would be if smoke alarms, smart cameras, and other connected devices also required daily battery replacements? Unlike smartphones, many IoT devices are located in areas not frequently accessed by people, so they have extreme power consumption requirements, which determines that the power consumption of sensors must also be very low; otherwise, the operating costs would be too high.
With the explosive growth of connected devices, data is growing exponentially, and centralized cloud systems have become “overburdened.” More importantly, for applications such as smart manufacturing or intelligent transportation, delays in cloud analysis can cause the value of data to drop dramatically, leading to the rise of edge intelligence.
Sensors are excellent edge nodes, integrating sensors with microprocessors through embedded technology, making them intelligent data terminal devices with environmental perception, data processing, intelligent control, and data communication functions. This is what is known as intelligent sensors. These sensors have self-learning, self-diagnosis, and self-compensation capabilities, composite perception capabilities, and flexible communication abilities. In this way, the data that sensors feed back to the IoT system when sensing the physical world will be more accurate and comprehensive, achieving precise perception goals.
Surge in Demand for Intelligent Sensors Across Five Key Areas
Intelligent sensors possess high precision, low cost, diverse functions, and strong automation. They are sensors with information processing capabilities, products of the integration of sensors and microprocessors. In many IoT scenarios, sensors exhibit characteristics of intelligent sensors, and in the future IoT era, intelligent sensors will be the market mainstream.
Among the most promising IoT scenarios in the future are smart industry, smart home, smart healthcare, smart vehicles, and smart agriculture.
1. Smart Industrial Sensors Are the Foundation for Industry 4.0
It is well known that Industry 4.0 has become part of national strategy, and smart manufacturing is key to national industrial transformation. The role of smart industrial sensors in manufacturing is becoming increasingly important. Industrial sensors are characterized by high performance specifications and precision requirements, with no room for errors in data collection and processing. Unlike traditional industrial sensors, smart industrial sensors will be used in smart manufacturing, and they impose stricter requirements on precision, stability, and impact resistance.
In the future, the demand for smart industrial sensors based on Industry 4.0 will increase significantly, which is also the biggest opportunity for industrial sensor manufacturers.
2. Smart Homes Provide Growth Space for These Sensors
A major feature of smart homes is the control of home products. As the IoT develops, more and more sensors will be used in home appliances such as washing machines, televisions, refrigerators, lighting, air conditioning, and range hoods. Products that previously did not have sensors will become the main battlefield for sensors due to the popularity of smart homes.
Sensors will be standard in smart home products. For example, pressure sensors can monitor the amount of foam in washing machines; photoelectric sensors can control lighting in light bulbs; electromagnetic sensors can achieve the movement of spray arms in dishwashers, and flow sensors, smart gas sensors, etc., will also have great utility.
3. Smart Healthcare Requires Various Intelligent Sensors
Smart healthcare uses IoT technology to achieve interaction between patients, medical personnel, and medical devices. The core part of its work is to collect, store, transmit, and process patient information. During image transmission and massive data computation, various intelligent sensors with processing capabilities are needed, such as MEMS pressure sensors for measuring blood pressure, thermoelectric sensors for studying sleep apnea, and temperature sensors for monitoring and measuring body temperature.
With the development of IoT technology, wireless medical sensors are gradually evolving towards intelligence, miniaturization, and low power consumption, and the application of sensors in smart healthcare will become increasingly widespread. According to foreign media reports, scientists have studied a new type of sensor that can be used to diagnose eye injuries, which determines the severity of the injury based on the concentration of vitamin C in human tears. Recently, scientists also researched a swallowable heart rate sensor that is the size of a capsule, which can measure vital signs after being swallowed and transmit information to a receiver for remote monitoring by doctors.
With technological advancements, the types of sensors used in smart healthcare will continue to increase, but they will all share the common characteristic of being intelligent sensors.
4. Intelligent Sensors Support the Intelligence of Vehicles
Although many cars in China have achieved some basic networking functions, they are not truly smart vehicles. With the development of AI and IoT technology, smart cars will become the mainstream in the future. Smart cars are comprehensive systems that integrate environmental perception, multi-level assisted driving, and other functions, and a major feature is the ability to achieve networked control. The key to control and operation lies in intelligent sensors, and the popularity of smart cars will lead to an increase in intelligent sensors.
In smart cars, the most commonly used intelligent sensors in the future will be airflow sensors, odometer sensors, oil pressure sensors, brake pressure sensors, position sensors, and collision sensors.
5. The Smart Agriculture Sensor Market Has Broad Prospects
Smart agriculture is key to China’s goal of becoming a strong agricultural country. In future agricultural production, many types of IoT sensors and related technologies will be needed. The components of IoT agriculture include smart water quality sensors, wireless sensor networks, wireless communication, etc., which together form a complete smart agriculture system, with sensors being the first step to achieving this.
The characteristics of IoT agriculture are based on information technology, collecting data through sensors during agricultural production, conducting quantitative analysis and intelligent decision-making. The agricultural production environment is very complex, and different scenarios require different sensors, such as air temperature, humidity, light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, etc. The collection of these data requires the corresponding smart agricultural sensors.
Sensors are playing an increasingly important role in the fields of science and technology, industrial and agricultural production, and daily life. The growing demand for sensors in human society is a powerful driving force for the development of sensor technology, while modern technology’s rapid advancement provides a strong backing for its development.
Under the IoT strategy, the demand for domestic sensor production is urgent, and domestic leaders in the sensor industry receive more government support; as the key to the IoT, sensors become a competitive advantage in the entire industrial chain and represent the core competitiveness of enterprises.









