Today, smart connected vehicles have become a hot field, giving rise to numerous new technologies, products, and services. After the Chinese automotive industry established the development goals of intelligence and connectivity, key technologies such as onboard operating systems, emerging automotive electronics, vehicle communication, service platforms, and safety have gradually become research hotspots.
From the perspective of industrial chain development, the industrial chain of smart connected vehicles is divided into three levels: Upstream mainly includes perception systems, control systems, and execution systems, which can be used to collect and process data; Midstream mainly includes intelligent cockpits, autonomous driving solutions, and complete vehicle solutions, used for information exchange with other vehicles, roads, people, and networks; Downstream mainly includes travel services and data value-added services, which receive commands from midstream systems and respond accordingly.

【Upstream: Three Key Systems of Smart Vehicles】
The upstream of the smart connected vehicle industrial chain encompasses three key systems: perception systems, decision-making systems, and execution systems. Each system has different responsibilities but plays an important role.
1) Perception System
The perception system of smart connected vehicles can sense and collect various data, providing accurate and comprehensive information support for smart connected vehicles and comprehensive environmental data for the perception system. Data collection is mainly accomplished through LiDAR, optical cameras, intelligent navigation systems, etc.
2) Decision-Making System
The control system of smart connected vehicles is responsible for route planning and real-time navigation, mainly involving high-precision maps and communication systems. Smart connected vehicles have high requirements for map accuracy and information volume, and these maps are known as high-precision maps, which differ significantly from ordinary navigation maps. The positioning accuracy of high-precision maps is generally at the centimeter level, and they are three-dimensional, covering a wealth of information such as lane markings and the coordinates of surrounding devices.
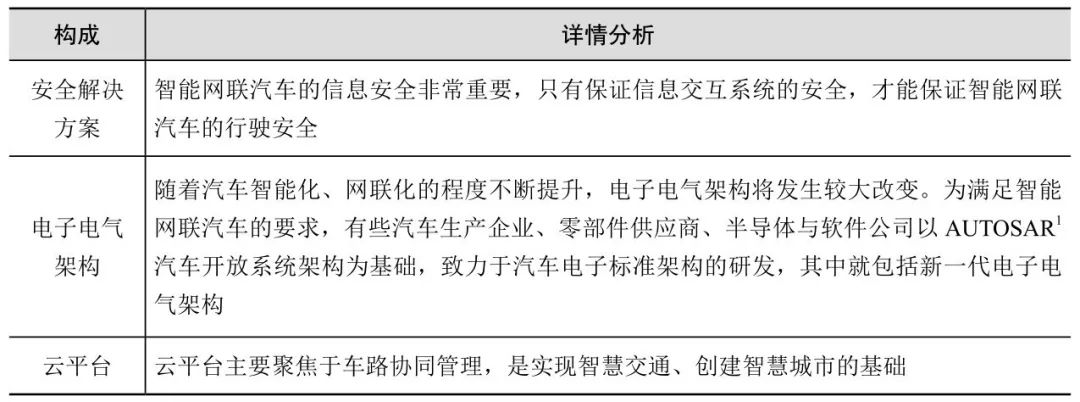
The communication system of smart connected vehicles allows vehicles to connect with other vehicles, roads, pedestrians, cloud platforms, etc., including V2X communication systems, safety solutions, electronic and electrical architecture, and cloud platforms.

With the support of high-precision maps and communication systems, smart connected vehicles can utilize search algorithms to study the feasibility of various autonomous driving solutions, including waiting times at traffic lights, road congestion, and road maintenance conditions, thus determining the optimal driving path.
3) Execution System
In the system architecture of smart connected vehicles, the execution system belongs to the lower-level control system and can perform operations such as braking, acceleration, and steering.
Engineers control the steering wheel, accelerator, and other components of autonomous vehicles through specialized “drive-by-wire devices”, enabling the vehicle to achieve autonomous driving, thereby “liberating” the driver, and using subsystems built with multiple processors to provide accurate and stable control of the vehicle’s mechanical systems.

【Midstream: Automotive Component Integration Suppliers】
The midstream of the smart connected vehicle industrial chain involves integrated systems from different fields, including intelligent cockpits, autonomous driving solutions, and vehicle manufacturing.
(1) Intelligent Cockpit
The core components of the intelligent cockpit include full LCD instrument panels, large screen central control systems, in-vehicle infotainment systems, head-up display systems, and streaming media rearview mirrors. The intelligent cockpit serves two main purposes: to enhance the technological feel and comfort inside the vehicle; and to improve the customer’s riding experience.
(2) Intelligent Airbags
In the event of a collision, intelligent airbags can adjust the timing and intensity of deployment based on the collision situation, as well as the conditions of the driver and passengers, maximizing safety for the driver and passengers. In addition to intelligent airbags, smart connected vehicles must also be equipped with driver detection systems and tire pressure monitoring systems, utilizing in-vehicle cameras, tire pressure monitoring systems, etc., for real-time monitoring.
(3) Intelligent Lighting Systems
Intelligent lighting systems mainly include adaptive cornering lights, curve lighting, and night vision systems, which help drivers widen their field of vision and improve the recognition of vehicles and pedestrians, thereby maximizing driving safety.
(4) Thermal Management Systems
Compared to traditional automotive thermal management systems, the thermal management system of smart connected vehicles adds two subsystems—battery thermal management system and motor electronic control cooling system, and also imposes higher performance requirements on the vehicle’s air conditioning system. The thermal management system is an essential part of the composition of smart connected vehicles.

【Downstream: Various Application and Service Providers】
The downstream of the smart connected vehicle industrial chain mainly consists of various application and service providers, including travel services and data value-added services.
(1) Travel Services
Traditional travel services mainly include three types: purchasing a vehicle, renting a vehicle, and taking a taxi. The emergence of ride-hailing services has enriched the types of travel services, greatly enhancing the flexibility of vehicle use and effectively addressing the inconveniences of traditional travel vehicle usage.
The emergence of corporate travel service platforms has led corporate travel services into a new development stage. With the support of this platform, corporate employees can book rides online and enjoy travel services without personally paying the fare, as it is settled by the company, providing great convenience for companies to manage travel costs and data.
In recent years, ongoing public vehicle reforms, improving ride-hailing policies, and tax reforms have driven the innovative development of corporate travel services, specifically reflected in three aspects: first, public vehicle reforms have released a large demand for travel services; second, in order to regulate the ride-hailing market, transportation departments have introduced many regulatory policies, promoting new vitality in the ride-hailing market and guiding it towards a more standardized and safer direction; third, with the continuous advancement of tax reforms, the VAT deduction chain has been improved, leading to increased profits for companies providing travel services, thus promoting more stable development of travel service platforms.
(2) Data Value-Added Services
Smart connected vehicles continuously generate data during operation, and these data types are quite rich, including decision control data, connectivity interaction data, and industrial service data. Companies can utilize big data, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence technologies to conduct in-depth analysis of this data, providing users with more value-added services and effectively enhancing the commercial value of smart connected vehicles.
In recent years, with the joint efforts of complete vehicle manufacturers, leading component manufacturers, and leading internet companies, significant breakthroughs have been made in fields such as algorithm chips and sensors, resulting in an increasing number of smart connected vehicle products and the gradual commercialization of autonomous driving technology, all of which will drive the development of smart connected vehicles into the fast lane.