This article is applicable to Tactile Intelligence development boards that support the Buildroot system. This article takes the Purple Pi OH as an example. The Tactile Intelligence Purple Pi OH motherboard is a recommended Harmony development board from the Huawei Laval official community.
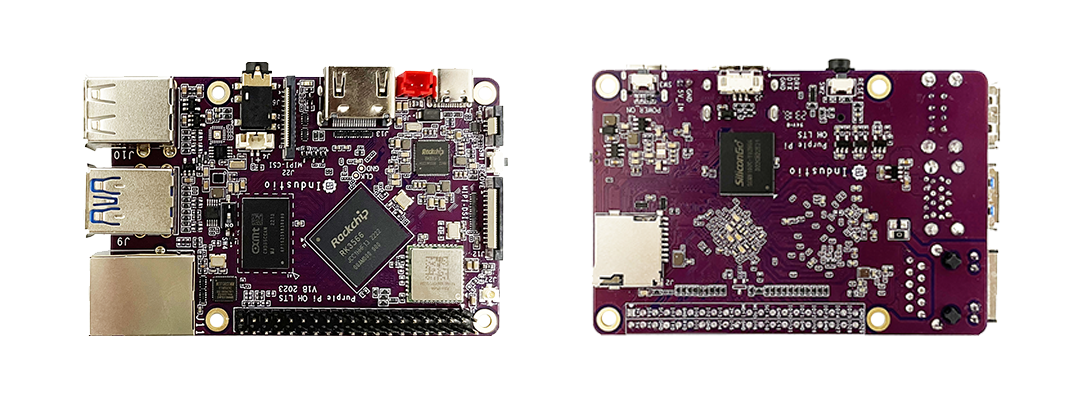
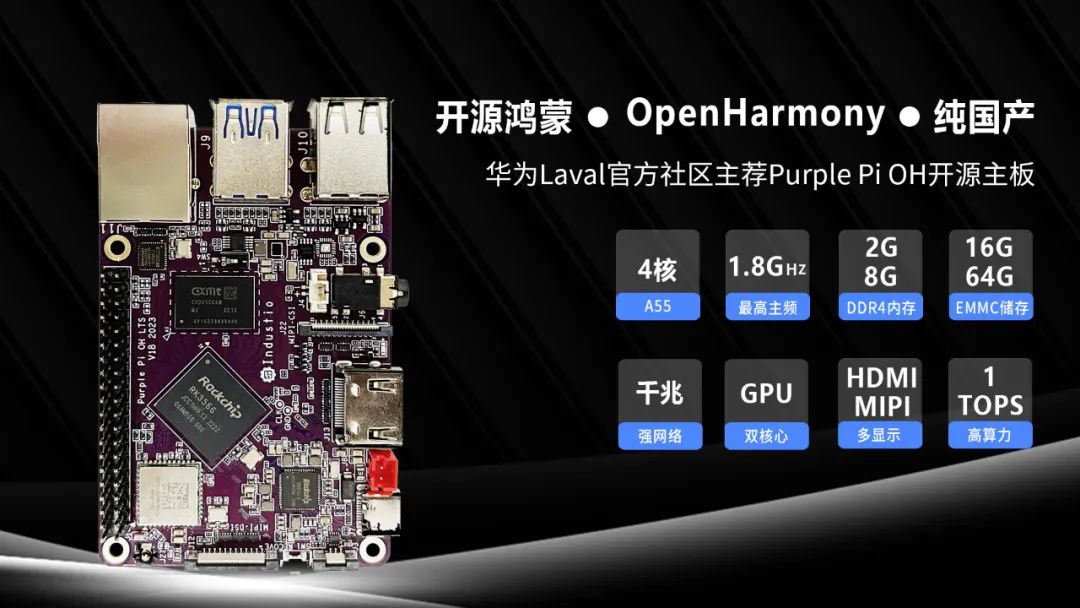
This motherboard is mainly aimed at students, geeks, and engineers, greatly lowering the entry barrier for open-source Harmony developers, and has the following advantages:
-
Supports open-source Harmony/Linux/Android 11/Kirin, compatible with Raspberry Pi;
-
Quad-core A55, up to 1.8G main frequency Mali G52-2EE GPU;
-
Supports OpenGL/CL/Vulkan/1T NPU/8MISP;
-
Supports TensorFlow/MXNet/PyTorch/Caffe;
-
Supports 1*Gigabit Ethernet, 3*USB2.0, 1*USB3.0, 3*UART, 2*SPI, 2*I2C, 28*GPIO, 1*MIPI DSI, 1*HDMI;
-
Supports OpenHarmony 3.2/4.0/4.1 versions, open SDK source code;
-
Active developer community, more experts online for technical support;
-
Ultra-small size, extreme cost performance, only 249 yuan;
In the field of computer storage, TRIM is a command used for Solid State Drives (SSD), which informs the SSD about which data blocks are no longer used by the operating system and can be erased. This typically occurs when files are deleted or the recycle bin is emptied; the operating system notifies the SSD that it no longer needs to retain these data blocks, allowing the SSD to safely erase these blocks during future garbage collection processes.
The main benefits of the TRIM command include:
Performance Maintenance: TRIM helps maintain the performance of SSDs, as SSDs need to erase existing data before writing new data. If the operating system does not inform the SSD via TRIM which blocks are free, the SSD’s controller may mistakenly believe that some blocks still contain important data and avoid erasing them, leading to decreased write performance.
Extended Lifespan: TRIM helps extend the lifespan of SSDs. Each storage cell in an SSD (or “cell”) has a limited number of erase/write cycles. By effectively reclaiming data blocks that are no longer in use, TRIM reduces unnecessary erase/write operations, thereby extending the lifespan of the SSD.
Space Optimization: TRIM ensures that the SSD’s garbage collection process can work more efficiently, helping to free up space and providing more available storage cells for new data writing.
Avoid Write Amplification: Without TRIM, SSDs may retain deleted data blocks until new data needs to be written, which can lead to the phenomenon of “write amplification,” where the actual amount of data written to the SSD is much larger than the original data amount. TRIM helps reduce this occurrence by marking data blocks as free in advance.
In modern operating systems, such as Windows 7 and later, macOS, Linux, etc., TRIM is usually enabled by default. Users can check whether TRIM is enabled and manually trigger TRIM operations using specific system commands or tools.
Using the TRIM command in a system built with Buildroot mainly involves two steps: ensuring that your file system supports TRIM operations and enabling TRIM functionality in the system.
Here are the general steps to use TRIM in a Buildroot system:


Most modern file systems (such as ext4, XFS, Btrfs, and F2FS) support TRIM.
In the Buildroot .config configuration file, ensure that the correct file system and TRIM support options are selected.
For example, if you are using the ext4 file system, ensure that Buildroot is configured with CONFIG_EXT4_FS to use this feature.


In a Buildroot built system, you can enable TRIM through the following methods:
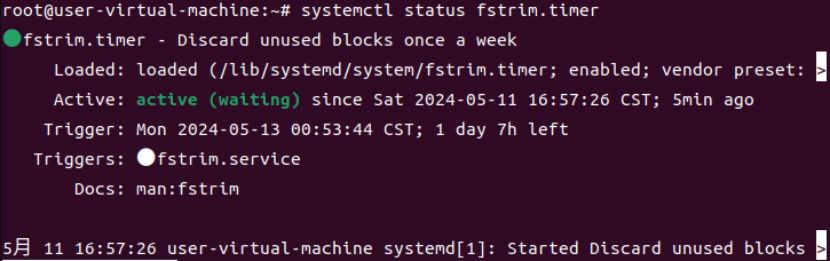
Fedora Linux implements a service that runs a systemd timer weekly. To check if it exists and its current status, run systemctl status.
$sudo systemctl status fstrim.timerThe result of executing this statement is shown in the following image:
Now, enable the service.
$sudo systemctl enable fstrim.timerThis will enable TRIM when the file system is mounted.
Finally, you can verify whether the timer has been enabled by listing all timers.
$ sudo systemctl list-timers --all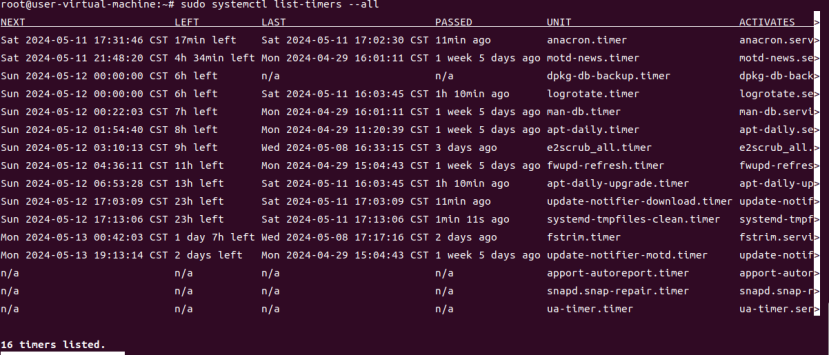
Please note that different versions of file systems and operating systems may have different details regarding TRIM support. Be sure to consult the documentation for the file system and operating system you are using for more detailed guidance. Additionally, TRIM operations for SSDs should be used with caution, as improper use may shorten the lifespan of the SSD.
Purple Pi OH Purchase Link
https://m.tb.cn/h.g1qerYc?tk=ahOAWGe64ky

