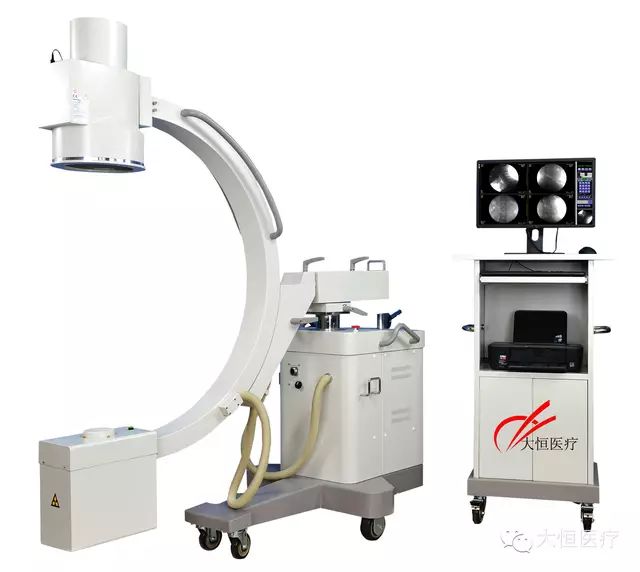
1.High-frequency mobile C-arm, widely applicable in clinical settings: can be used for interventional imaging/bone surgery/gastroenterology intervention/vascular intervention/neurosurgery intervention/tumor intervention/pain intervention.
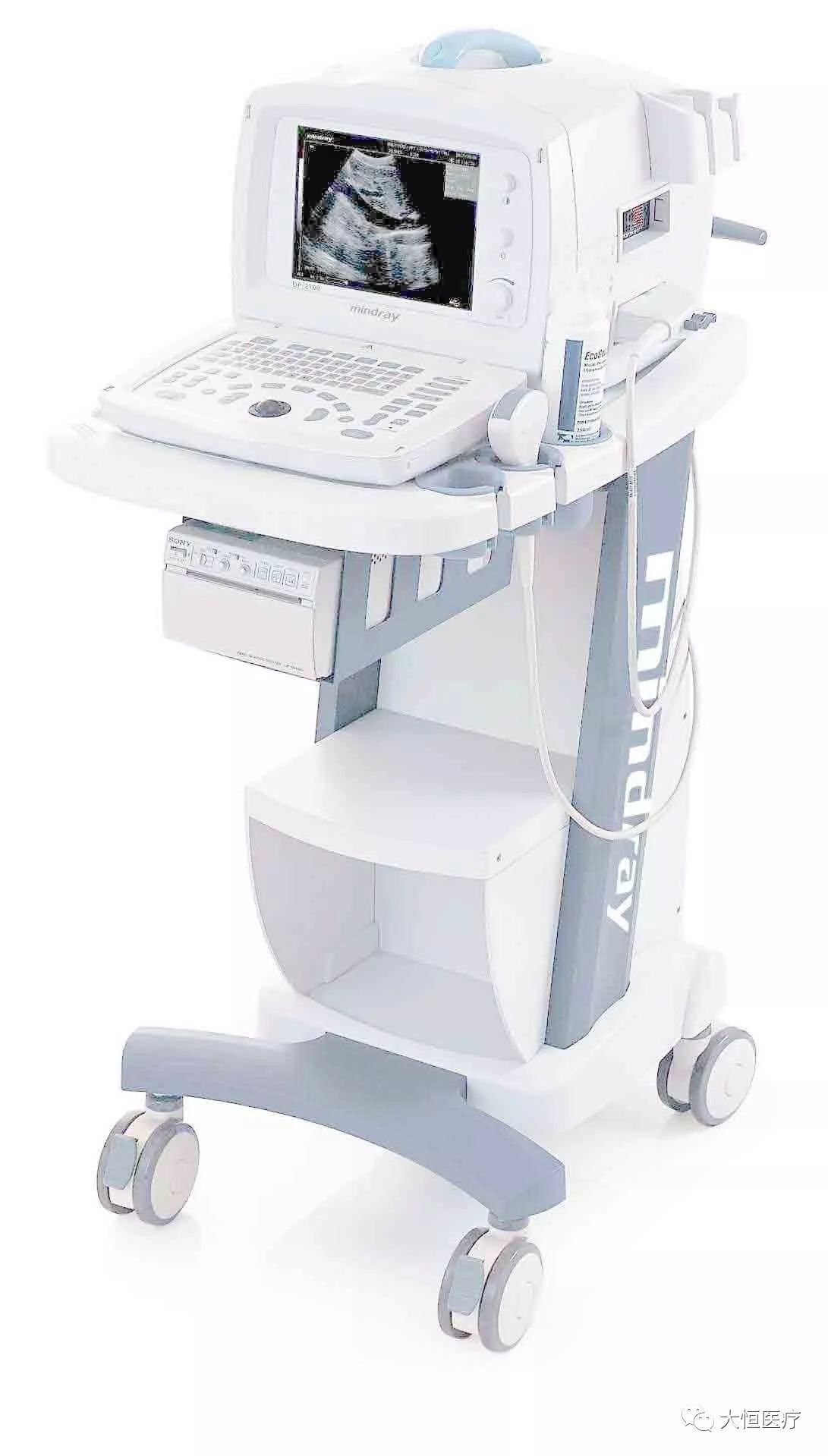
2.B ultrasound is a technology that uses ultrasound to detect the human body, constructing organ images based on the feedback from sound waves.
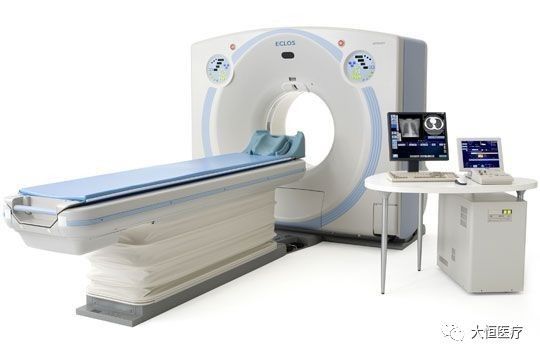
3.CT (Computed Tomography) is a type of electronic computer tomography that uses precisely collimated X-ray beams, gamma rays, and ultrasound, along with highly sensitive detectors, to perform sequential cross-sectional scans around a specific part of the body. It features fast scanning times and clear images, making it suitable for various disease examinations; it can be classified based on the type of radiation used: X-ray CT (X-CT), ultrasound CT (UCT), and gamma-ray CT (γ-CT).
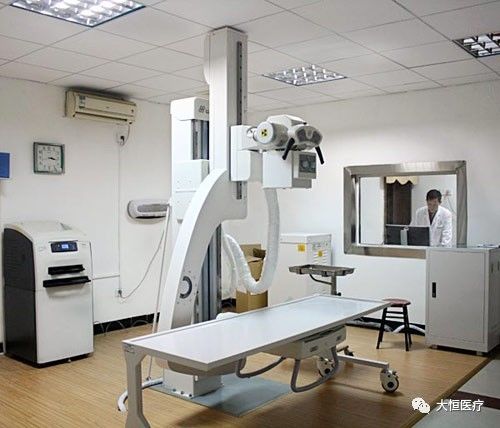
4.DR system, or Direct Digital Radiography system, consists of an electronic dark box, scanning controller, system controller, and imaging monitor. It directly converts X-ray photons into digital images through the electronic dark box, representing a broad definition of direct digital X-ray photography. The narrow definition refers to DDR (Direct Digit Radiography), which typically indicates digital radiography using flat-panel detector technology, representing a true direct digital X-ray photography system. It can be mainly classified into amorphous silicon flat-panel DR (mainstream).
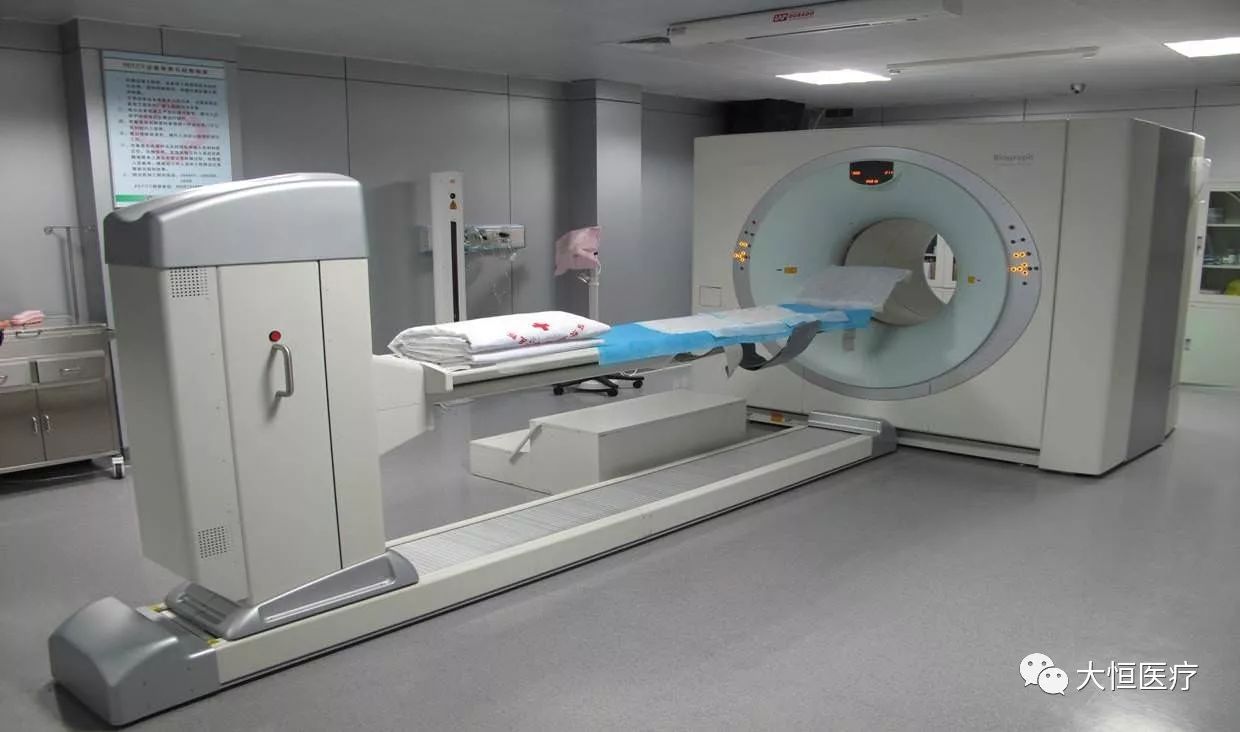
5.PET: Positron Emission Tomography is a relatively advanced clinical imaging technique in nuclear medicine. The general method involves labeling a substance, usually essential for biological metabolism, such as glucose, proteins, nucleic acids, and fatty acids, with short-lived radioactive isotopes (e.g., F18, carbon 11), injecting it into the body, and reflecting the metabolic activity based on the accumulation of this substance to achieve diagnostic purposes.
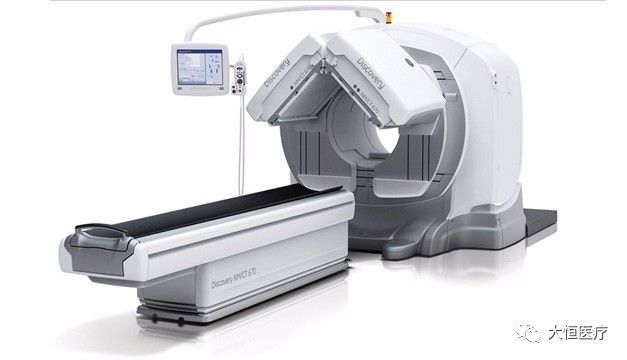
6.ECT (Emission Computed Tomography) is a single-photon emission computed tomography device, abbreviated in English for isotope emission computer-assisted tomography. Its principle is to use the instrument to detect the dynamic distribution of isotopes within the human body for imaging; it can observe functional and metabolic aspects. ECT combines electronic computer tomography (CT) with the principles of nuclear medicine tracing technology. ECT includes SPECT and PET (as shown in the above image).
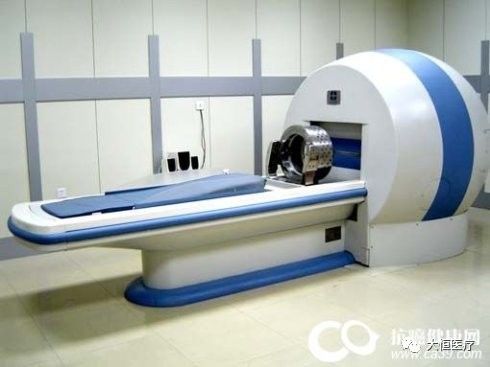
7.The Gamma Knife, also known as the stereotactic gamma radiation therapy system, is a therapeutic device that integrates modern computer technology, stereotactic technology, and surgical techniques. It focuses gamma rays emitted from cobalt-60 geometrically to concentrate on the lesion, destroying the tissues within the target in a single, lethal dose, while causing almost no harm to the normal tissues through which the rays pass, making the boundary between the treatment area and normal tissues very distinct, resembling a cut from a knife, hence the name “Gamma Knife”.
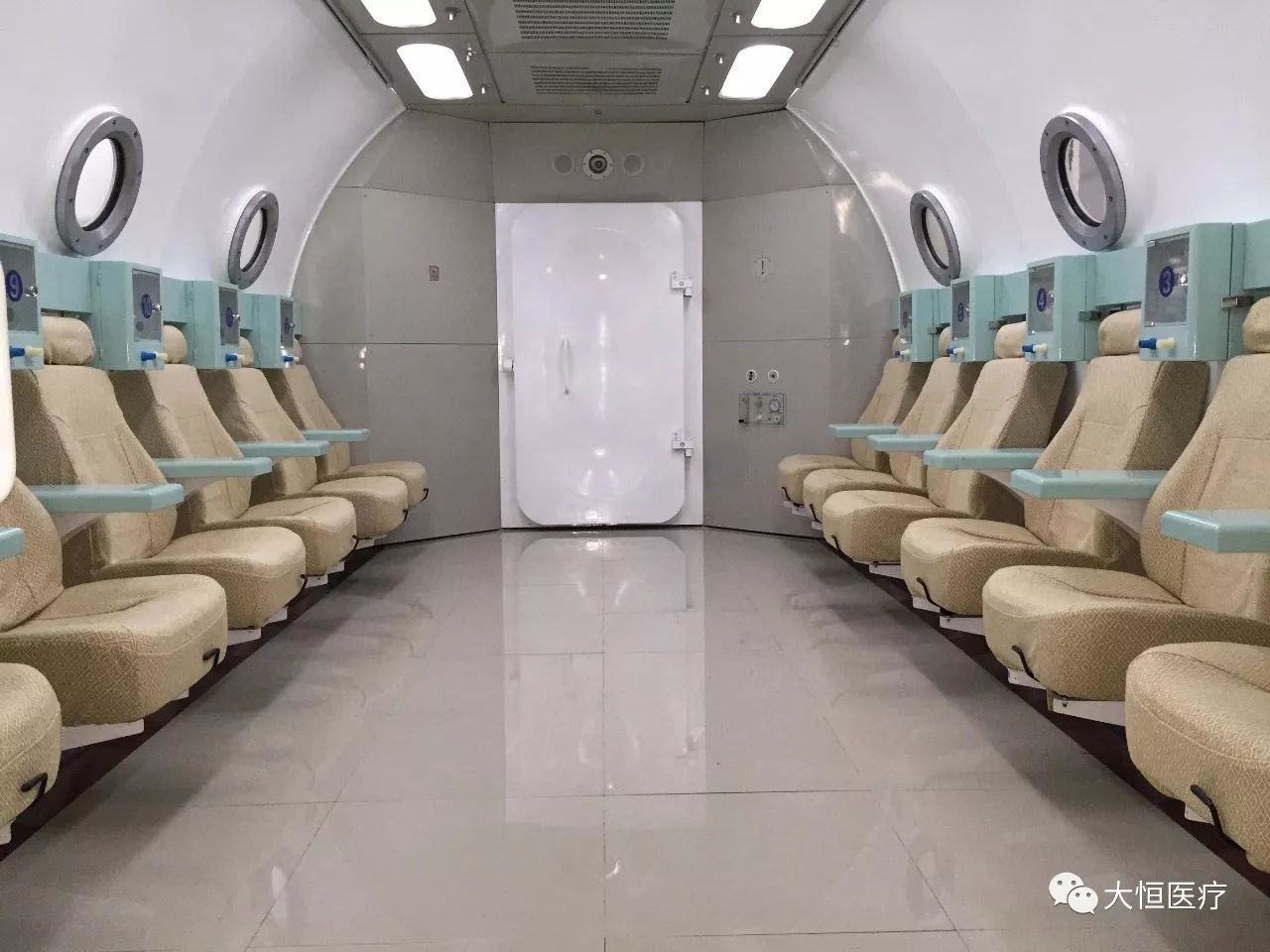

8.Hyperbaric oxygen chamber, a treatment device for various hypoxic conditions. The chamber is a sealed cylinder that inputs pure oxygen or purified compressed air through pipes and control systems. Doctors outside the chamber can communicate with patients through observation windows and intercoms. Large oxygen chambers can accommodate 10 to 20 seats.

9.The X-ray machine is a device that produces X-rays, mainly consisting of an X-ray tube and an X-ray machine power supply. The X-ray tube consists of a cathode filament (Cathode) and an anode target (Anode), along with a vacuum glass tube. The X-ray machine power supply can be divided into high-voltage power supply and filament power supply, where the filament power supply is used to heat the filament, and the high-voltage power supply applies high voltage across the cathode filament and anode target, creating a high-voltage electric field that accelerates active electrons from the filament towards the anode target, forming a high-speed electron flow. The resulting X-ray penetrates the body to create an image.
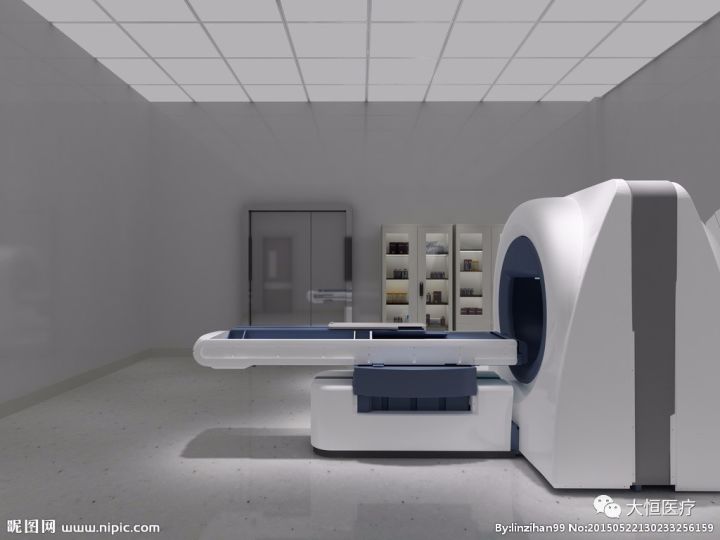
10.Nuclear magnetic resonance application: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has become a common imaging examination method. As a new type of imaging technology, MRI does not impact human health, but there are six groups of people who should not undergo MRI examinations: individuals with pacemakers, those with or suspected of having metallic foreign bodies in the eyes, those who have undergone aneurysm clipping surgery, individuals with retained metallic foreign bodies or prosthetics, critically ill patients in life-threatening conditions, and patients with claustrophobia. Monitoring instruments and emergency equipment should not be brought into the MRI examination room. The principle is mainly based on proton resonance.
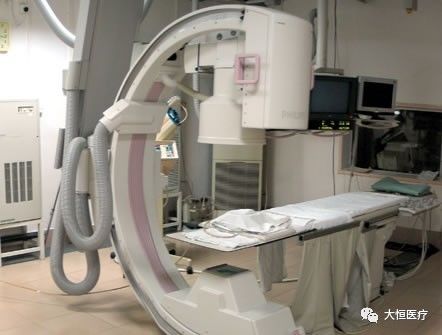
11.Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is an angiography method assisted by electronic computers, a new X-ray examination technology applied clinically since the 1970s. It involves two imaging processes completed by computer programs. Before injecting the contrast agent, the first imaging is performed, and the image is converted into a digital signal for storage. After injecting the contrast agent, a second imaging is done and converted into a digital signal. The two digital images are subtracted to eliminate identical signals, revealing an image of the blood vessels containing only the contrast agent.

12.Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) uses an extracorporeal lithotripter to generate shock waves, which are focused by a machine to target stones, releasing energy multiple times to break the stones within the body, allowing them to be expelled through urine. Since the first extracorporeal lithotripter was developed by Dornier in the early 1980s, millions of cases of extracorporeal lithotripsy have been performed abroad, making it the routine first-choice method for treating urolithiasis.
13.Medical electronic cyclotron, used in conjunction with PET and others.
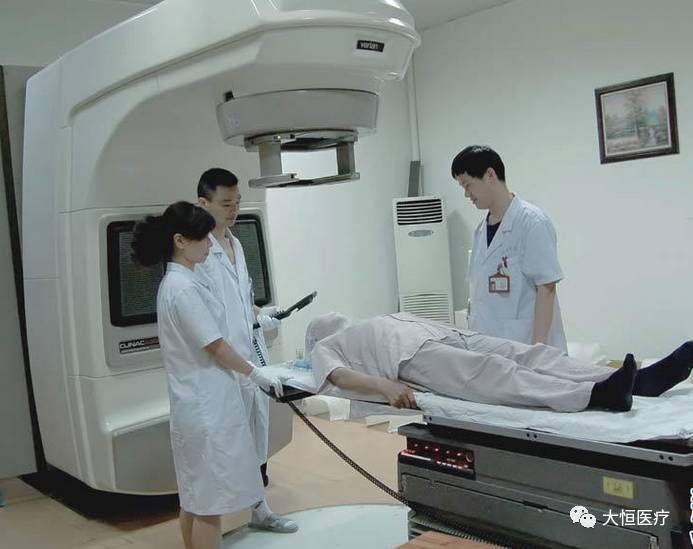
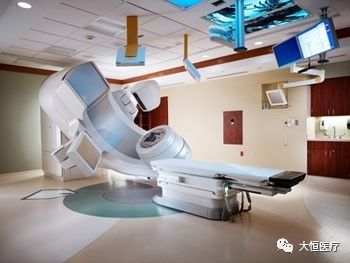
14.Medical accelerator is a type of particle accelerator device used in biomedical applications for radiation treatment of tumors. Charged particle accelerators use artificial methods to accelerate various types of charged particles to higher energies using different forms of electric fields, commonly referred to as “particle accelerators” or simply “accelerators.” To energize charged particles, an accelerating electric field is required. Depending on the type of accelerated particle and the shape of the accelerating electric field, as well as the trajectory followed during the acceleration process, various types of accelerators are classified. Currently, the most widely used in radiation therapy is the electron linear accelerator.
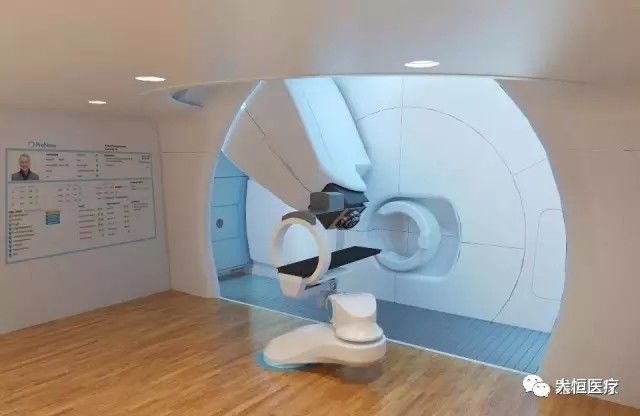
15.Proton therapy system: The proton knife is a commercial application of the proton accelerator; its primary application in medicine is for the radiation treatment of cancer tumors, while in semiconductor or solar science, it is used for cutting wafers or solar substrates.
Conveying Positive Energy, Embracing a Powerful Life!
Beijing Daheng Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. (Xuan)
Equipment staging, equipment deployment, department co-construction and physician groups
Stock code: 600288
Service phone: 400-6805-120