1. What is Industry 4.0?
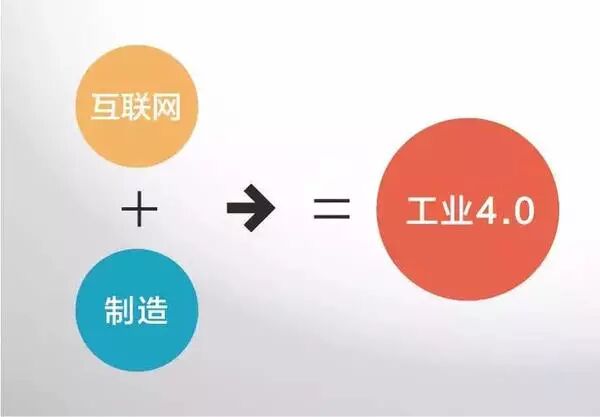
”Internet + Manufacturing” is Industry 4.0. The concept of “Industry 4.0” was introduced by Germany, referred to as the “Industrial Internet” in the United States, and as “Made in China 2025” in China. The essence of these three concepts is consistent, all pointing to a core idea: intelligent manufacturing.
In 2015, several concepts became very popular in China: the first was mass entrepreneurship and innovation, the second was Industry 4.0, and the third was “Internet +”.
”Internet +” is an enormous concept, encompassing “Internet + Finance” known as Internet Finance, “Internet + Retail”, and “Internet E-commerce”. Among these, “Internet + Manufacturing” is Industry 4.0. It will drive the transformation of Chinese manufacturing into Chinese creation, which is why many people say that Industry 4.0 is a revolutionary change for the entire era of China.
2. What are the characteristics of Industry 4.0?
Connectivity: The core of Industry 4.0 is connectivity, which aims to closely link equipment, production lines, factories, suppliers, products, and customers.
Data: Industry 4.0 connects product data, equipment data, R&D data, industrial chain data, operational data, management data, sales data, and consumer data.
Integration: Industry 4.0 will form an intelligent network through ubiquitous sensors, embedded mid-range systems, intelligent control systems, and communication facilities via CPS (Cyber-Physical Systems). This intelligent network enables connections between people, machines, and services, achieving high levels of horizontal, vertical, and end-to-end integration.
Innovation: The implementation process of Industry 4.0 is a process of innovative development in manufacturing, with innovations emerging in manufacturing technology, products, models, business formats, and organizations, ranging from technological innovation to product innovation, model innovation, liquid innovation, and finally organizational innovation.
Transformation: For traditional manufacturing in China, transformation means shifting from traditional factories, from 2.0 and 3.0 factories to 4.0 factories. The entire production form shifts from mass production to personalized customization. In fact, the entire production process becomes more flexible, personalized, and customized. This is a very important feature of Industry 4.0.

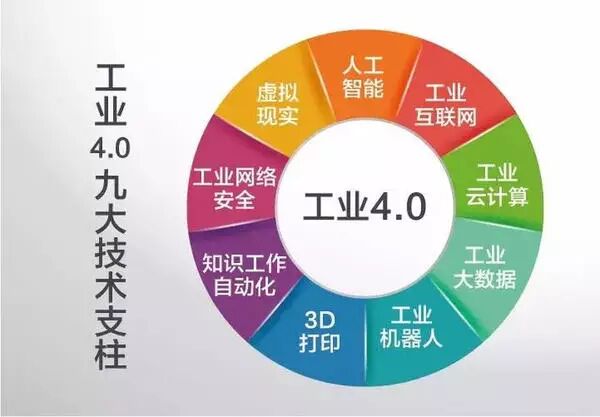
3. What are the technological pillars of Industry 4.0?
The nine technological pillars of Industry 4.0 include the Industrial Internet of Things, cloud computing, industrial big data, industrial robots, 3D printing, knowledge work automation, industrial cybersecurity, virtual reality, and artificial intelligence. Countless business opportunities and public companies will emerge from these nine pillars.
4. Which types of companies have the best prospects?
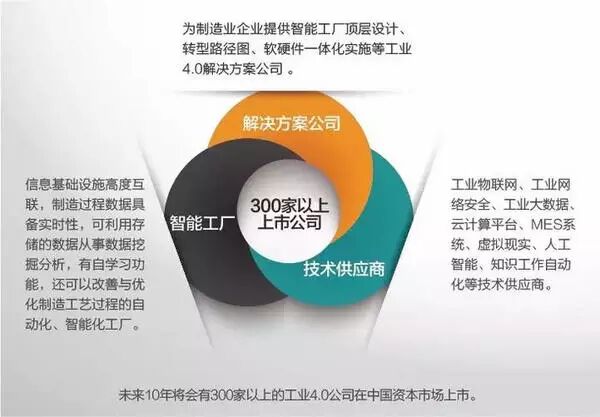
Considering the current state of Chinese industry, the three types of companies that will have ample development in the field of Industry 4.0 over the next decade are:
The first type is smart factories, which can be divided into two categories: the first is traditional factories transforming into smart factories, and the second is those that are born as smart factories;
The second type is solution companies, which provide smart factory top-level design, transformation roadmaps, and integrated software and hardware implementation solutions for manufacturing companies;
The third type is technology suppliers, including those in the fields of industrial IoT, industrial cybersecurity, industrial big data, cloud computing platforms, and MES systems.
In addition to these three types, technology suppliers in virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and knowledge work automation will also face tremendous development prospects.
【Solutions】 include both software and hardware. Software encompasses industrial IoT, industrial cybersecurity, industrial big data, cloud computing platforms, MES systems, virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and knowledge work automation; hardware includes industrial robots (including high-end components), sensors, RFID, 3D printing, machine vision, smart logistics (AGV), PLCs, data collectors, industrial switches, etc.
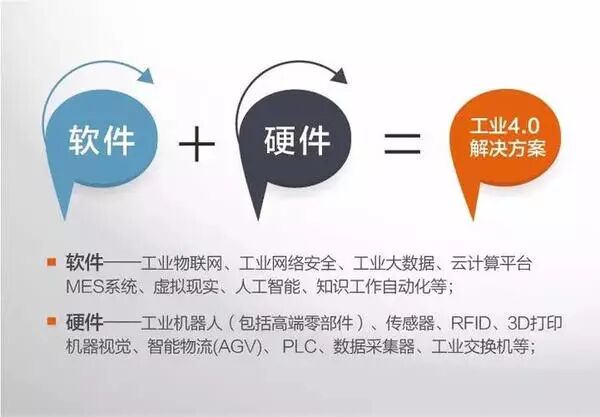
This is a massive industrial revolution; missing out on Industry 4.0 means missing out on this era!
5. Who will ultimately win the dominance in the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is marked by the Hannover Messe in Germany in 2013, announcing that this round of work revolution centers on intelligent manufacturing.
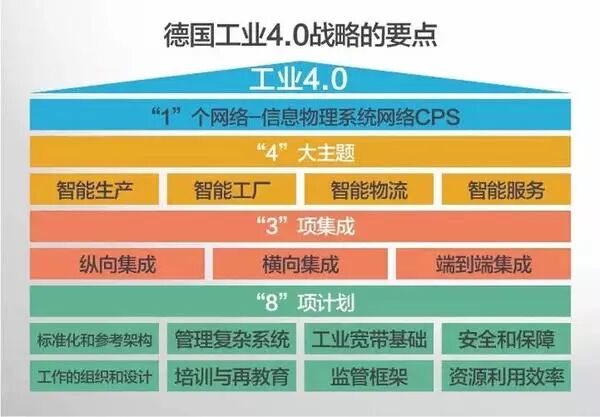
The framework defined by the German government for Industry 4.0 consists of one information network, four major themes, three integrations, and eight plans. The overall framework proposed by the German government for Industry 4.0 differs in many aspects from China’s actual national conditions, and there is still a certain distance in terms of implementation.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is expected to last approximately 30 to 40 years, so the disruption, reconstruction, and integration of Chinese industry by Industry 4.0 and the mobile internet have only just begun.
The essence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is the competition for the industrial standards that will dominate the future of the world, driven by Germany and the United States according to their own logical paths and expressions.
The United States has proposed standards for the Industrial Internet, focusing on equipment connectivity, data analysis, and business insights based on data. Their focus on traditional industrial internet connectivity emphasizes big data and cloud computing.
Germany has proposed Industry 4.0, leveraging its strong mechanical manufacturing technology and advanced capabilities in embedded and control equipment, with a keen focus on the profound changes in the intelligent and virtualized production processes.
It can be seen that the paths and logic of the American Industrial Internet and German Industry 4.0 are opposite, but their goals are the same. The U.S. is supported by companies like GE and IBM, focusing on bridging hardware from a software perspective; Germany is led by companies like Siemens, KUKA, and SAP, aiming to connect software from a hardware perspective.
Whether from software to hardware or from hardware to software, the goal of both is the same: to achieve intelligent manufacturing and the integration of mobile internet and industry.
6. Why does China choose the German standard?

First, the Chinese government believes that the German path is easier to achieve than the American path; second, the U.S. has a serious hollowing out of its industry. IT companies face significant challenges in implementing Industry 4.0 due to a lack of infrastructure. Germany has a strong industrial technology base, being a manufacturing hub with suppliers of production equipment and IT business solution providers. In the strategic choice of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the Chinese government’s strategy is to closely follow the new round of industrial development trends, choose Industry 4.0, launch the Chinese version of Made in China 2025, and seek opportunities for leapfrogging and proactive measures.

Industry 4.0 represents a brand new era, with the first phase just beginning, expected to take 30 to 50 years for development and introduction. According to the Minister of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Germany transitioned from Industry 3.0 to Industry 4.0, while China is parallelly transitioning from 2.0 and 3.0 to 4.0.
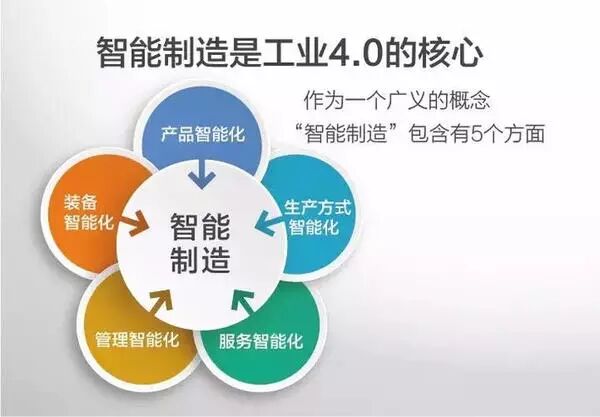
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the Chinese Academy of Engineering have defined the core goal of the Chinese version of Industry 4.0 as intelligent manufacturing, a term that is very accurate. Extending from intelligent manufacturing to specific factories, it refers to smart factories. Intelligent manufacturing and smart factories are the two major goals of Industry 4.0.

In the future era of Industry 4.0, which is more important: software or hardware? The answer is very simple: software determines everything; software defines machines. All factories are software companies and data companies. All industrial software will be crucial in the era of Industry 4.0, hence software defines everything.

The path of Industry 4.0 has just begun, but it has provided us with a general direction. In the future, enterprises will become data-driven, innovative, integrated, and rapidly changing companies. For the entire manufacturing industry, this is a tremendous disruption, which is not an exaggeration to call an industrial revolution.

Note: This article is based on the “Le Xue” lecture series at Zhaoyin University titled “Industry 4.0 and Bank Transformation”. For more information, please read the book “Industry 4.0: The Future That Is Happening” co-authored by Xia Yanna and Zhao Shenghe.
This article is reprinted from WeChat:Sensor IoT
● Disclaimer ●
This article is a network reprint, and the copyright belongs to the original author. However, due to numerous reprints, it may not be possible to confirm the true original author, so only the source of reprint is indicated. If there are any copyright issues, please contact us, and we will negotiate copyright issues or delete content promptly! The content represents the author’s personal views and does not represent the views of this public account or its authenticity.
12 carefully planned times
About aviation
What you want to know
Aviation is about to happen 2016
The subscription for “Aviation Knowledge” 2016 has begun
↓↓↓
Subscriptions are available at post offices nationwide, postal issue number 2-410
Unit price 12 yuan, annual 144 yuan (12 issues)
Consultation phone 010-82317056
www.2-410.com


Wind and cloud | Cloud stories
WeChat ID: hkzs1958
 Long press the QR code to follow Aviation Knowledge
Long press the QR code to follow Aviation Knowledge