
The human demand for sound, light, and color has given rise to a variety of information carriers, leading to significant advancements in display technology. Plasma TVs, LED TVs, LCD monitors… these are the well-known mature display methods. In addition, there are some futuristic new display technologies gradually entering our lives.
1. Quantum Dot Display Technology
Quantum dots are zero-dimensional, dot-like nanosemiconductor materials that possess many novel electronic and optical properties, making them applicable in various fields, including display technology. The display technologies utilizing quantum dots mainly include two types: Quantum Dot Liquid Crystal Displays (QD-LCD) based on LCD technology and Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode Displays (QLED) based on OLED technology.

QD-LCD mainly utilizes the photoluminescence principle of quantum dots. The blue light emitted by the LED light source in the backlight module passes through the quantum dot film, where part of it is converted into green and red light by the quantum dots. These three colors of light mix to form the white backlight source for the LCD. The green and red light emitted by the quantum dots is purer than that emitted by the LEDs, thus allowing the LCD to display more accurate image colors and more natural color transitions.
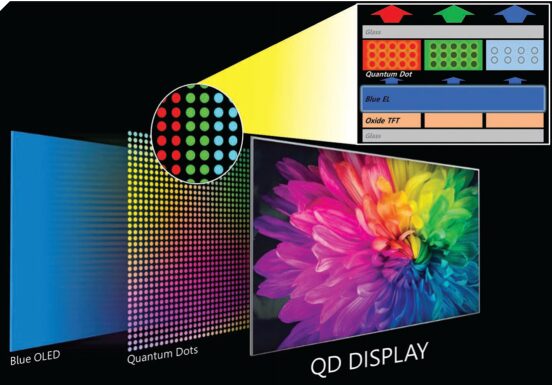
QLED primarily utilizes the electroluminescence principle of quantum dots, where voltage drives the quantum dots to emit red, green, and blue primary colors, which are then mixed spatially to convert these colors into various pixel colors.
The light-emission principle of QLED is very similar to that of the OLED screens we commonly encounter, simply replacing the organic light-emitting materials in OLED with quantum dot materials. This gives QLED almost all the advantages of OLED, along with longer lifespan and brightness compared to OLED. QLED represents a more advanced application of quantum dots in display technology.
2. Laser Display Technology

Laser TVs, as the name suggests, use lasers as the display light source. Due to the excellent monochromaticity of lasers, the color effect of the TV is outstanding. Although called laser TVs, this display technology is more akin to projectors. However, unlike projectors that require a long projection distance, laser TVs adopt ultra-short throw projection to illuminate a light-resistant screen, producing a display effect superior to traditional projectors and TVs.
3. E-Paper Display Technology
E-paper, also known as electronic ink display, is a special type of display screen where the images displayed look like printed pictures on paper. This unique display effect gives it the potential to replace paper.
The display of e-paper primarily derives from the countless ink particles in the middle layer of the screen, which are filled with a transparent base liquid. This base liquid also suspends positively charged white ink and negatively charged black ink, with the size of the ink particles being comparable to the diameter of human hair. When a negative electric field is applied to the ink particles, the white ink moves to the negative electrode of the electric field, while the black ink moves to the positive electrode. The positive electrode is inside the screen, so the black ink is hidden, and the pixel displays white. Similarly, when a positive electric field is applied, the pixel displays black, and countless pixels combine to form an image.
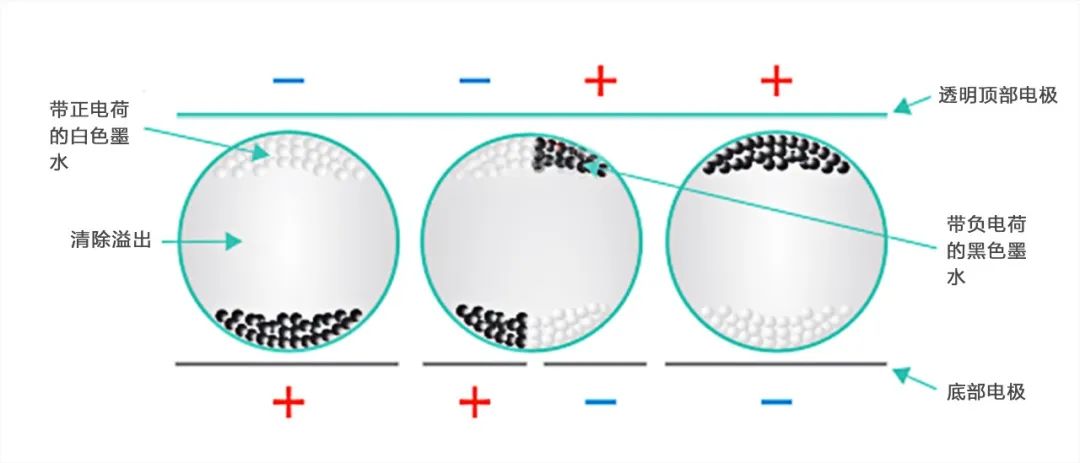
Black and white e-paper principle diagram
E-paper also has a special characteristic: even when the power is turned off, the distribution of the ink on the screen does not disappear. This is a feature not found in other types of screens, and the brightness of the image changes according to the intensity of ambient light.
The most common type on the market is black and white e-paper, while color e-paper is relatively rare. Some color e-papers place a layer of color filters above the ink particles, while others replace them with colored ink particles, using electric fields to change the positions of different colored inks within the particles, which mix to present various colors.
Future Technology – Glasses-Free 3D Display
Currently, many devices can help us present two-dimensional images in a three-dimensional effect. They all utilize the perceptual capabilities of the human visual system.
The human visual system perceives depth from a multitude of external information, most of which are two-dimensional cues, including shadows, perspective direction, relative size, occlusion, and blur. Once these two-dimensional depth cues are processed by the human visual system, we perceive them as existing in three-dimensional space.
Whether it is painting, photography, or video, as long as two-dimensional depth cues are embedded, the human eye will generate a three-dimensional perception effect; otherwise, optical image illusions may occur. Therefore, a 3D display system must first ensure the presence of these two-dimensional depth cues, and then address other three-dimensional perception factors, such as stereoscopic parallax, motion parallax, and visual accommodation conflicts. VR is a device that achieves 3D display based on binocular parallax. However, if we want to achieve glasses-free 3D, holographic three-dimensional display might provide us with this experience.
Compared to binocular parallax, which can cause discomfort like dizziness, holographic 3D displays can record and restore all information of the light waves from an object, and the reproduced image has the same three-dimensional characteristics as the original object, resulting in minimal discomfort for the viewer.
The trend in three-dimensional display methods is towards large depth of field, wide field of view, high resolution, and true color real-time three-dimensional display, approaching or even surpassing the reality perceived by the human eye.