
Click the above Computer Enthusiasts to follow us
As one of the oldest wireless transmission technologies, Bluetooth has now been upgraded to version 5.0. Most new smartphones and Bluetooth headphones have included Bluetooth 5.0 technology as a standard option. So, what changes have occurred with Bluetooth 5.0 compared to the more familiar Bluetooth 4.x? What significant evolution can it bring to Bluetooth peripherals?
The Evolution from Bluetooth 4 to 5
Bluetooth (Bluetooth) is an “ancient” wireless technology that was born in 1998, but it really became widely recognized after the promotion of the Bluetooth 2.0/2.1+EDR standard in 2007. With the update of PC wireless network cards and the entry of smartphones into the 4G era, Bluetooth technology has undergone updates from 4.0 → 4.1 → 4.1 → 5.0. Therefore, before discussing Bluetooth 5.0, we should revisit the features of Bluetooth 4.x.

Tip: During the era of Bluetooth 3.0, the Bluetooth Special Interest Group introduced the HS (High Speed) protocol, allowing mobile devices to achieve a transmission speed of 24Mbps via Wi-Fi channels. Starting from Bluetooth 4.0, most Bluetooth devices we encounter focus on low energy Bluetooth (BLE, such as Bluetooth 4.2LE), and the balance between speed and power consumption has become the future development direction of Bluetooth. In response to the demand for numerous low-power and compact devices, chip manufacturers are gradually integrating main controllers and RF functions into a single chip, forming BLE SoC for customers.
Changes in Bluetooth 4.x
Compared to earlier Bluetooth versions, Bluetooth 4.0 was officially referred to as “Bluetooth Smart”. It introduced the revolutionary BLE protocol and added a low-power physical layer and link layer in highly integrated devices, featuring lower power consumption, reduced costs, lower latency, increased connection distance, and AES-128 encryption. From Bluetooth 4.0 onwards, subsequent Bluetooth versions have aimed to optimize and upgrade for IoT devices.

The Bluetooth 4.1 standard was launched in 2013, addressing the potential interference of Bluetooth technology with 4G signals, while also supporting IPv6, allowing simultaneous transmission/reception of data (i.e., connecting multiple devices at once). The maximum single packet data transmission size was increased from 20 bytes to 23 bytes, enhancing the data transmission rate by 15%.
Released at the end of 2014, the Bluetooth 4.2 standard made significant improvements in transmission speed and security. The maximum single packet data transmission size (which can be understood as bandwidth) increased from 23 bytes during the 4.1 period to 255 bytes, accommodating more than ten times the data volume, leading to an approximate 2.5 times increase in data transmission speed. Additionally, Bluetooth 4.2 implemented stricter key management between devices to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and allowed Bluetooth devices to connect via IPv6, enabling data synchronization and interaction among various wearable and IoT devices.

The Evolution of Bluetooth 5.0
The Bluetooth 5.0 standard was born in 2016, achieving a qualitative leap in speed, distance, and connectivity compared to Bluetooth 4.2 (LE low energy Bluetooth).

According to the official indicators, Bluetooth 5.0 can provide four times the transmission distance (300 meters, but this is just a theoretical value; Bluetooth 4.2’s signal becomes very weak beyond 10 meters), double the transmission speed (from 1Mbps to 2Mbps), and eight times the broadcast data transmission volume (able to output audio signals to multiple Bluetooth audio devices simultaneously, thus facilitating the establishment of surround sound effects). Additionally, Bluetooth 5.0 has added navigation features, which, in conjunction with ubiquitous Wi-Fi and Bluetooth signals, can achieve indoor positioning accuracy close to 1 meter.

Bluetooth 5.0 can also be considered a new generation of wireless standards tailored for IoT devices. Its power consumption is lower than that of Bluetooth 4.2, and it has undergone many underlying optimizations for the IoT, such as the introduction of Bluetooth mesh networking technology, which breaks the traditional “one-to-one” pairing of Bluetooth devices and transforms it into a “many-to-many” signal transmission mode, allowing Bluetooth 5.0 devices to act as signal relay stations (similar to powerline adapters), theoretically transmitting Bluetooth signals indefinitely.
The Challenging Path to Popularization
As a very powerful wireless technology, Bluetooth 5.0 technology had already “entered” the smartphone field in early 2017. However, by the end of 2018, Bluetooth 5.0 had still not become popular in the smartphone market. Why is that?
Many people have misconceptions about smartphone processor platforms (SoC), thinking that SoC integrates all modules including CPU, GPU, ISP, Modem, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and power management on a single chip. In reality, many modules, including Modem, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and power management, coexist on the same PCB motherboard in the form of independent chips. Therefore, the theoretical parameters of an SoC do not represent the actual parameters that a smartphone can achieve.

Tip: Even with Bluetooth 5.0 chips, there may be differences in functionality and performance based on customer needs, such as removing support for dual-mode and high-definition protocols to pursue low power consumption and long standby times.
For instance, Qualcomm has supported Bluetooth 5.0 technology since the Snapdragon 636, but the smartphones equipped with Snapdragon 636 that support Bluetooth 5.0 are limited to a few products like Redmi Note 5. Most other smartphones adopt a combination of Snapdragon 636 and Bluetooth 4.2 chips.

The official parameters of Redmi Note 5 show support for Bluetooth 5.0

Honor 8X Max, also equipped with Snapdragon 636, only supports up to Bluetooth 4.2
The reason is simple: Bluetooth 5.0 technology is not a “must-have” for smartphones, and the cost of Bluetooth 5.0 chips is higher than that of Bluetooth 4.0 chips. Therefore, for a long time, the vast majority of smartphone manufacturers have shown little interest in Bluetooth 5.0.
Huawei/Honor is one of the smartphone manufacturers that is not in a hurry to promote Bluetooth 5.0. Whether it is the previous flagship Mate 10/P20 equipped with Kirin 970 or the new Honor 8X equipped with Kirin 710, even though Kirin 970 and Kirin 710 theoretically support Bluetooth 5.0, the Bluetooth standard of the above smartphones remains at 4.2. Currently, only the Mate 20 series, Honor Magic 2/Honor V20, and other new products equipped with Kirin 980 have just officially introduced Bluetooth 5.0 technology.

52audio compiled a list of smartphones supporting Bluetooth 5.0 as of October 2018. Although it is not particularly comprehensive, it still confirms one point—Bluetooth 5.0 has not become popular in the smartphone field; it remains a patent of a few mid-to-high-end smartphones.
Market Demand Needs Cultivation
The reason Bluetooth 5.0 has not experienced explosive growth, aside from the high cost of Bluetooth 5.0 chips, is primarily due to insufficient market demand. The application fields of Bluetooth technology are still relatively limited for ordinary users.

For example, no matter how fast Bluetooth transmission speed is, it can’t match Wi-Fi. Various sharing apps can build wireless hotspot channels, easily achieving data transmission environments exceeding 20MB/s; no matter how far Bluetooth transmission distance is, some may worry about risks—thieves may have left the subway station, while you are still oblivious, listening to music with your Bluetooth headset; although Bluetooth 5.0 can assist in the development of IoT, many users still have no concept of what IoT is…

Therefore, before Bluetooth 5.0 has a killer application environment, it is reasonable for smartphone manufacturers to maintain a cautious promotion attitude. The good news is that as more manufacturers participate in the development of Bluetooth 5.0 chips (such as Qualcomm, CSR, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, Nordic, Dialog, Toshiba, and Juniper), the threshold for Bluetooth 5.0 hunting is gradually decreasing. Relatively speaking, the new generation of Bluetooth headphones similar to Apple AirPods is the most likely “trigger” to ignite Bluetooth 5.0 technology.
Opportunities from Bluetooth 5.0 Headphones
Due to the “demonstration effect” of the iPhone, more and more high-end Android smartphones are eliminating the 3.5mm headphone jack design. To listen to music, one must either choose wired headphones with USB Type-C connectors (or USB Type-C to 3.5mm adapters) or use Bluetooth headphones. Bluetooth 5.0 technology can enhance the experience of Bluetooth headphones and further stimulate more users to prioritize choosing smartphones and headphones that support Bluetooth 5.0 features.
Improvements in Bluetooth 5.0 Features
Bluetooth standards are backward compatible, so there is no need to worry about not having matching smartphones when purchasing Bluetooth 5.0 headphones. With higher bandwidth, Bluetooth 5.0 can reduce the speed of transmitting voice commands to terminals from 90ms to about 40ms, greatly enhancing the functionality of headphones. For example, many Bluetooth headphones now integrate voice assistants, gesture control, active noise cancellation, health monitoring, etc. Bluetooth 5.0 can make these functions operate more smoothly without any delay. Additionally, the Bluetooth 5.0 module consumes less power, further extending the battery life of Bluetooth headphones.
It is important to note that many Bluetooth 5.0 true wireless earbuds (two earbuds separated, not connected by cables) will prominently feature “dual-ear calling” functionality in their promotions, giving the impression that only Bluetooth 5.0 can enjoy this special feature.

In reality, “dual-ear calling” is not exclusive to Bluetooth 5.0. Many Bluetooth 4.x headphones, including AirPods, already support dual-ear calling functionality, while Bluetooth 5.0 headphones represented by Jabra Elite can only output sound from one side (the right side).
It can be seen that dual-ear calling is not limited by Bluetooth version; it can only be said that the vast majority of Bluetooth 5.0 chips will include dual-ear calling as a standard feature, while Bluetooth 4.x chips need to put in extra effort to achieve this functionality. For example, the W1 chip used in AirPods not only integrates a Bluetooth decoding module but also includes a Wi-Fi chip, allowing AirPods to synchronize without occupying two Bluetooth channels, ultimately achieving dual-ear calling.
Enhancements in Bluetooth 5.0 Audio Quality
Bluetooth headphones do not have a cable connection to smartphones, so their audio quality largely depends on the quality of the headphones themselves. When we use Bluetooth headphones to listen to music, the process is as follows:
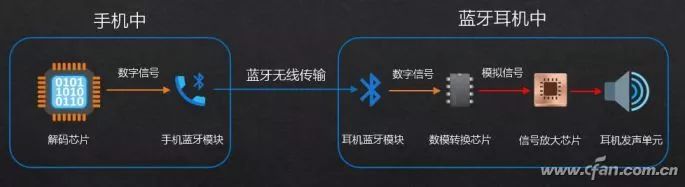
1. The Codec (coder-decoder) or DAC (digital-analog converter) in the smartphone decodes and converts audio files in formats like MP3 into digital signals;
2. The smartphone compresses the digital signal via Bluetooth based on the A2DP protocol and sends it wirelessly to the Bluetooth headphones;
3. The Bluetooth headphones receive the compressed digital signal and decode it into an analog signal using the integrated DAC chip;
4. The signal amplification chip inside the headphones amplifies the analog signal and transmits it to the sound unit in the headphones, ultimately outputting sound suitable for human hearing.
The question arises: Bluetooth’s bandwidth (transmission rate) is limited, making it theoretically difficult to output CD-quality audio signals. To achieve high audio quality, one must focus on “how to utilize existing bandwidth more efficiently”. Therefore, when using Bluetooth headphones to listen to music, audio signals need to be encoded (compressed) first, which is the second step in the listening process.
Currently, common Bluetooth audio transmission formats range from weak to strong: SBC, AAC, aptX/aptX HD (led by Qualcomm), and LDAC (led by Sony), among which only aptX HD and LDAC can achieve true “lossless” quality, providing near Hi-Fi audio quality. The good news is that Qualcomm and Sony have opened sourced their technologies for aptX and LDAC to Google, so as long as the Android system is upgraded to 8.0 or higher, it can be supported (for PCs, Windows 10 is required). However, to use aptX on the mobile side, it also needs to be paired with Qualcomm’s Snapdragon mobile platform (other hardware platforms require Qualcomm’s authorization).

Theoretically, the transmission rate of Bluetooth 4.2 (1Mbps) is sufficient to meet the needs of aptX HD and LDAC encoding because LDAC encoding only supports audio transmission rates of up to 990kbps at 24bit/96kHz. However, based on user feedback, Bluetooth 4.2 headphones supporting LDAC experience certain delays and stuttering issues, which can only be perfectly matched by Bluetooth 5.0. Therefore, although Bluetooth 5.0 itself does not make specific optimizations for audio, its advantages in higher bandwidth and transmission rates can effectively eliminate the physical transmission bottleneck between Bluetooth headphones and wired headphones.

It is important to note that to experience Bluetooth 5.0, both the smartphone and the headphones must support Bluetooth 5.0. To experience the high audio quality of aptX HD or LDAC technology, in addition to the system (Android 8.0) limitations on the mobile side, the music files played on the mobile side must also be in lossless format, and the Bluetooth chip in the headphones must also be authorized for aptX HD or LDAC, which incurs a considerable cost. Therefore, Bluetooth headphones supporting these two technologies are generally not cheap. When both the smartphone and the headphones meet the above conditions, users can select the required version of the Bluetooth audio codec in the system settings. If the codec option is grayed out, it indicates that at least one side (smartphone or headphone) does not support these codecs.

Whether you need it or not, Bluetooth 5.0 has become a development trend, and in 2019, more smartphones and headphones will incorporate it as a standard feature. Although Bluetooth 5.0 has excellent theoretical specifications, its most intuitive benefits at this stage are signal stability, low energy consumption, and low latency, which enhance the audio performance of Bluetooth headphones. However, as mentioned earlier, Bluetooth 5.0 does not guarantee good audio quality; it also requires the Bluetooth chip on the headphone side to support more advanced aptX HD and LDAC decoding, along with better speaker units. Expecting a hundred-dollar Bluetooth 5.0 headphone to challenge a thousand-dollar Bluetooth 4.2 headphone is still a joke.

Click “Read Original” for more exciting content