AboutSTM32
Do You Know The Five Major Embedded Operating Systems?
Today, Hua Mei will popularize some knowledge for everyone.
Here are
Some characteristics and shortcomings of these five embedded systems
Are you ready???
(There is a surprise at the end of the article~)

Before the formal explanation,
Hua Mei will first reveal some news!
👇👇👇
Countdown to the 2024 Hua Qing Yuan Jian Course Product Launch Conference4 Days

Learning STM32 embedded development, understanding the following five commonly used embedded operating systems (RTOS) is very important:
① FreeRTOS:
FreeRTOS is a powerful and widely used open-source embedded real-time operating system. It provides basic task scheduling, synchronization, communication, and timing functions, and features high portability and low resource consumption, making it suitable for small to medium-sized embedded systems.
② μC/OS-II and μC/OS-III:
μC/OS-II and μC/OS-III are two popular commercial embedded real-time operating systems developed by Micrium. They feature customizability and high configurability, supporting multitasking scheduling, interrupt handling, synchronization, and communication functions.
③ RT-Thread:
RT-Thread is an open-source, highly customizable real-time operating system suitable for various embedded platforms. It provides a lightweight kernel and rich components, supporting multitasking, semaphores, message queues, and memory management functions.
④ eCos:
eCos is an open-source real-time embedded operating system that is configurable and customizable.
⑤ uClinux:
uClinux is a Linux kernel designed for embedded systems and microcontrollers. Compared to traditional Linux kernels, uClinux optimizes memory management and task scheduling to suit resource-constrained embedded environments.
Understanding and mastering the characteristics, usage methods, and related development tools of these five embedded operating systems can help you better perform task scheduling, resource management, and multithreaded programming in STM32 development, thereby improving system stability and scalability.
Choosing the right embedded operating system for project needs is also determined by specific applications and system complexity.Next, let’s understand the characteristics and shortcomings of these five major embedded operating systems!
① FreeRTOS:
System Characteristics:
-
FreeRTOS is an open-source, event-driven real-time operating system designed for resource-constrained embedded systems;
-
It is compact and lightweight, suitable for embedded systems and applications;
-
It provides task management, memory management, queues, semaphores, and other real-time operating system functions;
-
It has extensive hardware support and portability.
System Shortcomings:
-
Functionality is relatively basic and may not meet the requirements of complex embedded systems;
-
Requires self-expansion and addition of any advanced features;
-
Limited by open-source community support; users may need to rely on their own capabilities to solve problems.
② uC/OS-II:
System Characteristics:
-
uC/OS-II is a very popular commercial embedded real-time operating system, known for its portability and configurability;
-
It is compact and customizable, suitable for embedded systems and applications;
-
Supports multitasking management, semaphores, message queues, memory management, and other real-time operating system functions.
System Shortcomings:
-
Over time, the development of uC/OS-II has stagnated, and its features are relatively outdated;
-
No open-source version, and commercial license fees are relatively high;
-
Relatively weak in concurrent performance, not suitable for applications requiring high concurrency.
③ RT-Thread:
System Characteristics:
-
RT-Thread is an open-source real-time operating system for embedded systems;
-
It is small, flexible, and customizable, suitable for resource-limited embedded devices;
-
Provides rich real-time functions and components, such as task management, thread communication, memory management, etc.;
-
Has strong community support, with an active developer community and support for various hardware platforms.
System Shortcomings:
-
Compared to other commercial real-time operating systems, RT-Thread’s maturity and industry recognition still need development;
-
Some advanced features may require additional configuration and customization.
④ eCos:
System Characteristics:
-
eCos (Embedded Configurable Operating System) is an open-source, customizable real-time operating system;
-
Provides rich features and configurability, supporting multitasking, soft real-time, and hard real-time applications;
-
Has portability and extensive hardware support, suitable for a range from low-power microcontrollers to embedded processors.
System Shortcomings:
-
Not as popular as other operating systems, development is relatively slow, and community support is limited;
-
Requires a certain level of capability to configure and customize the operating system;
-
May lack some advanced features, such as multi-core processor support and dynamic module loading.
⑤ uClinux:
System Characteristics:
-
uClinux is an open-source operating system for embedded systems that can run on processors without an MMU (Memory Management Unit);
-
Supports various processor architectures, including ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, etc.;
-
Has lower memory and processor resource requirements, suitable for resource-constrained systems;
-
Provides core functions and tools of the Linux operating system, including process management, memory management, file systems, etc.
System Shortcomings:
-
Due to the lack of an MMU, it cannot provide all the features of traditional Linux operating systems, such as virtual memory management and process isolation;
-
Lacks full support for applications with high real-time requirements;
-
Community support is relatively limited, and updates and maintenance are not timely.
The above is a detailed interpretation of the five major embedded operating systems for STM32. Did you get it?! Additionally, Hua Mei has prepared a surprise benefit for everyone! Participate in the activity as required for a chance to win a grand prize~
Reply with the keyword in the background of the public account 【Lucky Draw】
And follow the requirements (the content in the red box in the picture below)Share to Moments
Take a screenshot and send it to the background
Then you will have a chance to participate in the mini-program lucky draw~
The specific steps are as follows~
👇👇👇
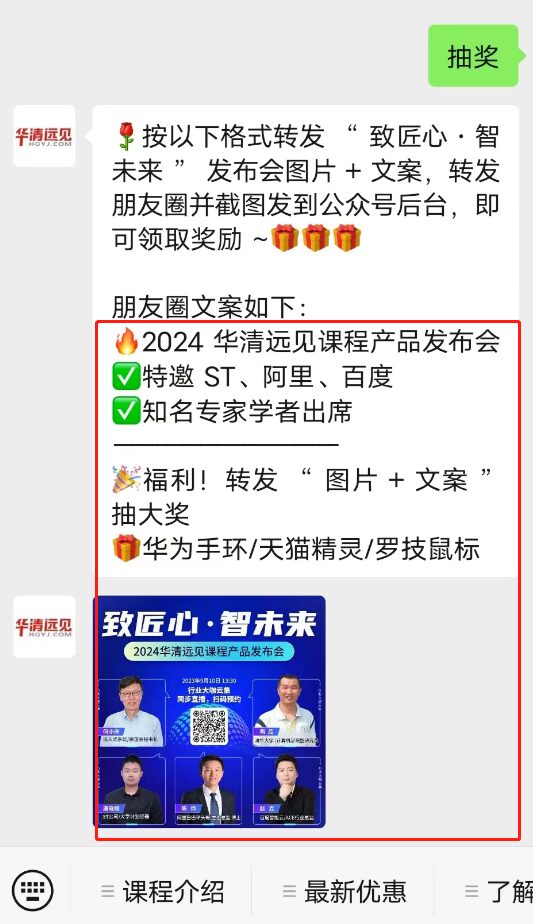
Activity participation format illustration
And have a chance to win the following prizes~
👇👇👇

Additionally, Hua Mei has prepared a 【Back to School】 gift package for everyone, allowing your September to set sail!


Previous Recommendations
July “Fengshen” season, 20K+ high salary offers are really winning!
Back to school gifts! 100% profit guaranteed~
Heavy debut! 2024 Hua Qing Yuan Jian Course Product Launch Preview!
So loud! Huawei’s strong return with “Kirin + 5G” hits back at the US!