Source: Sensor Alliance
Organized and published by Sinan IoT
Every piece of equipment in a factory generates data. From the perspective of equipment data, one can mine and analyze the reasons for unexpected downtime, ways to improve yield rates, and find better maintenance methods, thereby enhancing the overall production efficiency of the factory. This is the value of big data in the industrial field. Therefore, the collection, transmission, and monitoring of equipment data become critical steps. With the continuous evolution of market demand and technological advancement, the IoT intelligent gateway has emerged. To better understand its value and the opportunities for its emergence, one must start from the development history of data collection, transmission, and monitoring of equipment machines.
In the early stages of industrial development, the awareness of data collection was just beginning to emerge. Due to a lack of sensors and outdated transmission technology, most data collection relied on manual measurement. The drawbacks of manual measurement are self-evident: it is time-consuming and labor-intensive, and the detectable range is very narrow. Thus, the manual measurement method was quickly eliminated by the demands of factory production.
Initial Local Monitoring: The First Attempt at Data Collection

True data monitoring should begin with local monitoring. By connecting the device’s main control unit to the PLC or HMI through a wired network, human-machine interaction and information exchange can occur locally. Data from the equipment, such as bearing temperature and rotational speed, is displayed directly on a PC or HMI.

Displays need to be installed close to the equipment overview, and personnel must monitor and provide feedback 24 hours a day. At this time, human power still dominates. If workers rely on the naked eye to monitor the terminal display data and provide timely feedback, it requires a shift system, and the data feedback is still very delayed and inaccurate. Management personnel cannot timely understand the factory’s data and provide corresponding decision-making judgments.
This shows that the actual significance of local monitoring is minimal; it merely stays at simple data statistics.
The Emergence of Ethernet: Extending Physical Transmission Distance

Due to the limitations of local monitoring, people began to apply wired broadband technologies such as Ethernet to data collection and transmission, extending the range of data transmission. When industrial equipment nodes connect to sensors and reach Ethernet through certain conversions, they arrive at the terminal display. In terms of transmission range, it has been extended to a certain extent based on the original range.

However, the differences in protocol standards in between lead to communication not being smooth, and the inherent limitations of wired networks are that remote monitoring is not possible, which again creates a huge demand in the industrial data market. How to expand the transmission range? How to support more protocols to meet different industrial production scenarios? Ethernet data transmission clearly cannot satisfy the demand for remote monitoring of data in real production environments.
The Emergence of Gateways: Adapting to More Protocol Standards

The actual production environment is complex, and with physical distance limitations, remote data transmission has become a pressing pain point in industrial data. How to transmit data to the cloud or remote terminals at low cost and high efficiency has become a key research focus in the industry.
With the emergence of wireless transmission technologies such as 2G/3G/4G networks, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, the issue of remote data transmission has seen a breakthrough, but the multiple protocol standards of various communication protocols hinder the “dialogue” between devices. At this time, to adapt to more protocol standards, the emergence of gateways is timely. Unlike bridges that simply convey information, gateways act as translators between communication protocols and data, repackaging received information to meet system requirements.

The gateway’s conversion ability, combined with wireless communication protocol technology, greatly extends the distance of IoT. However, IoT technology also faces unique challenges. One challenge is that many IoT nodes cannot directly connect to IP-based networks due to limitations in system memory, data storage capacity, and computing power, making it difficult to achieve the interconnection of all things. The IoT gateway can fill this gap, bridging the public IP-based network and the local IoT, using different communication protocols, data formats, or languages, and even completely different system architectures.
Simply put, with industrial gateways, the so-called M2M is no longer narrowly defined as communication between machines, but rather a barrier-free communication between devices, systems, and people.
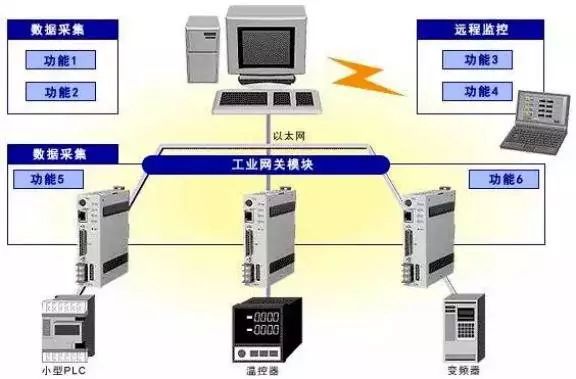
However, if communication is barrier-free, how efficient is the communication? How much valid information is there? Besides data collection and transmission, can it undertake more functions? Since data is converted through the gateway and then uploaded to the cloud for computation and analysis, the time lag in between leads to the inability to timely feedback real-time data… These are all areas where traditional gateways have not performed well, and naturally, they become key breakthrough points in the design of industrial gateways.
Modern IoT Intelligent Gateways: Driving Predictive Maintenance of Devices

Modern IoT intelligent gateways play a very important role in the IoT era. They are not only the link between sensing networks and traditional communication networks. As gateway devices, IoT intelligent gateways can achieve protocol conversion between sensing networks and communication networks, as well as between different types of sensing networks, enabling both wide-area and local interconnections. Furthermore, IoT intelligent gateways also need to have device management capabilities. Operators can manage various sensing nodes at the bottom through IoT intelligent gateways, understand the relevant information of each node, and achieve remote control. The unique edge computing capability of IoT allows traditional factories to achieve faster and more precise data collection and transmission during the digital transformation process.
Edge Computing Capabilities Bring Two Major Benefits to Factory Equipment:
First, the data analysis and computing capabilities of the gateway itself allow data to be aggregated, optimized, and filtered at the gateway level. By conducting local pre-analysis of collected data, the equipment can respond directly, while simultaneously uploading results and high-value data to the cloud, allowing managers to receive feedback with almost zero delay.
Secondly, at the gateway level, a large amount of status data from the equipment is filtered and optimized, reducing the network pressure of massive data uploads. Thus, industrial gateways are no longer narrowly defined as translators but also fulfill the role of filtering.
Combining data collection, efficient transmission, and rapid analysis capabilities, it truly achieves real-time status monitoring of equipment and uses big data analysis to detect potential issues, thereby predicting equipment development trends and possible fault patterns, and formulating predictive maintenance plans in advance.
Characteristics of IoT Intelligent Gateways

Support for remote updates and maintenance is achieved based on software development of industrial gateways. For example, IoT intelligent gateways can add supported protocols based on software upgrades at any time, providing development interfaces based on JS language. Modifications to hardware product functionality can be completed simply by downloading the corresponding configuration application. If issues arise during the use of the gateway, there is no need to go on-site for repairs; modifications can be made at the software level using the Ruff Explorer remote management tool, allowing for early detection and resolution of potential issues, making maintenance smarter and equipment operation more stable and reliable.
Secondly, in terms of compatibility, modern IoT intelligent gateways also have strong compatibility, adopting a plug-and-play design concept that is compatible with mainstream manufacturers’ devices and protocols. Providing protocol downloads and secondary development interfaces makes compatibility easier. Since hardware gateways are controlled at the software level, factories do not need to incur high costs to replace compatible gateway devices during the transformation process; simple modifications to the software logic will suffice.
Currently, some companies in China, such as Huawei and Ruff (Nanchao), have successfully practiced edge computing gateways and IoT intelligent gateways in real production environments multiple times. They have helped customers in the engineered wood industry, automotive manufacturing, and wood processing industries quickly and efficiently connect devices, collect and transmit data, and through their edge computing capabilities, provide nearby edge intelligent services, meeting critical industry digitalization needs in agile connectivity, real-time business, data optimization, application intelligence, and security and privacy protection. The reduction of labor costs, equipment maintenance costs, and time costs is very valuable, and this will be a core competitiveness for many small and medium-sized factories in the industrial 4.0 transformation battle.
Of course, the technical capabilities of gateways and industrial demand have not reached their endpoint. As market demand continues to rise and IoT technology continues to improve, it is believed that more comprehensive industrial gateways will continue to emerge, providing better services for the future development of IoT.
Key Takeaways
1、IoT Gateways: Important Support Points for Smart Home Development
2、Solution | Overall Solution for Smart Home Multifunctional Gateway
3、Things to Know About Smart Home Gateways




Click “Read Original” for more information!