Introduction
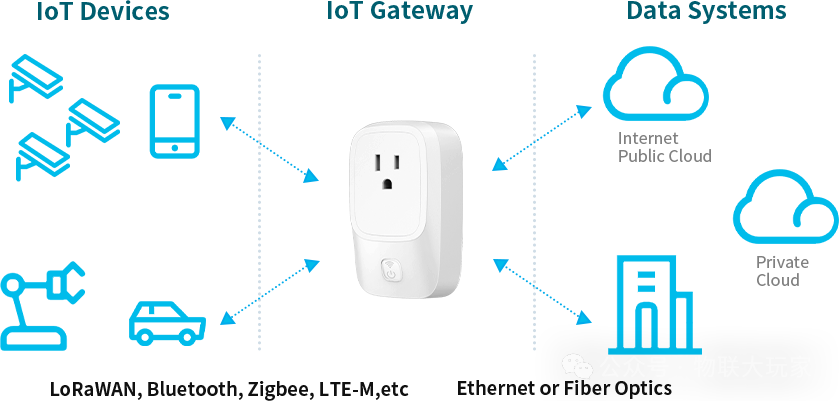
The IoT Gateway is a core component that connects physical devices and digital networks. It acts as a bridge between edge devices and cloud platforms, facilitating interconnectivity and communication between devices through data collection, protocol conversion, and security management.
Core Functions
-
Protocol Conversion: Unifies communication protocols used by different devices (such as Modbus, MQTT, HTTP, etc.) into a format that can be understood by the cloud.
-
Data Processing: Processes and filters data at the edge to reduce bandwidth pressure.
-
Security Management: Provides encryption and authentication features to ensure the security of data transmission.
-
Remote Management: Supports device firmware upgrades, configuration management, and remote control.
Applications
IoT Gateways are widely used across various vertical industries, promoting the widespread adoption of the Internet of Things.
-
Industrial IoT (IIoT): Sensors and controllers in factories connect to cloud platforms via gateways, achieving production automation and intelligent decision-making.
-
Smart Home: Gateways connect home devices from different brands, allowing users to control lighting, security, and temperature devices with a single application.
-
Smart City: Gateways transmit data from traffic monitoring, environmental sensors, and public facilities to city management platforms, aiding in resource optimization and real-time monitoring.
-
Agricultural IoT: In precision agriculture, gateways collect information such as soil moisture and weather data, providing data support for crop management.
Technical Features
-
Edge Computing Capabilities: Many modern gateways have edge computing capabilities, allowing for analysis and processing of data before it is transmitted to the cloud, thereby reducing latency and improving efficiency.
-
Support for Multiple Protocols: Supports protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, LoRaWAN, etc., ensuring compatibility.
-
High Scalability: IoT gateways typically have a modular design, allowing for the addition of features as needed (such as adding 5G, Wi-Fi modules).
-
Security: Provides multiple layers of security mechanisms, including data encryption, firewalls, and endpoint authentication, to prevent network attacks.
Scenarios
Factory Automation
A manufacturing company uses gateways to connect hundreds of factory devices, collecting data through Modbus protocol and converting it to MQTT for transmission to the cloud. The gateway analyzes data at the edge, detects abnormal vibrations, and provides early warnings of equipment failures.
Smart Agriculture
A farm connects soil sensors, weather stations, and irrigation systems through gateways. The gateway sends data to the cloud and automatically controls irrigation based on instructions from the cloud platform.
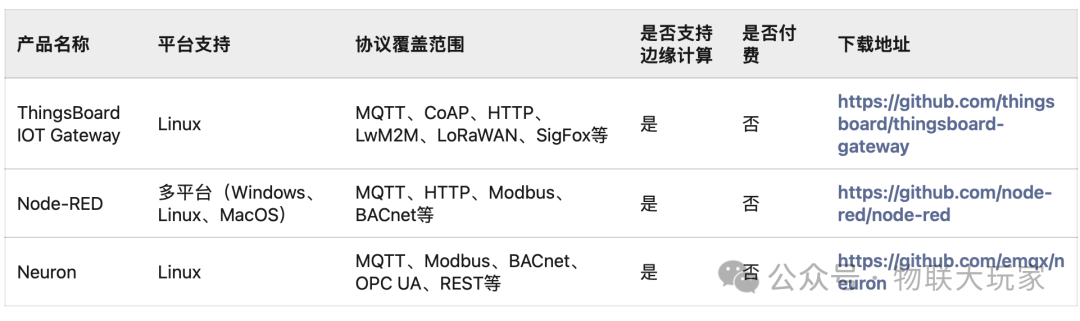
Open Source Products
The following popular open-source products can serve as gateways.
Development Trends
As a core component of the IoT ecosystem, the development of gateways directly impacts the maturity of the entire IoT industry. Whether in industrial automation or smart city construction, their role is indispensable and may develop in the following trends:
-
Edge AI: Future gateways will combine AI technology for intelligent analysis and decision-making at the edge.
-
Multi-Protocol Integration: As the variety of IoT devices increases, gateways will need to support more protocols and simplify device interoperability.
-
Green Gateways: High energy-efficient designs will become a trend, helping companies reduce carbon emissions.
-
Zero Trust Security Model: Enhancing the security of IoT gateways to address complex network threats.