▎According to GGII statistics, the sales of humanoid robots in China are expected to reach approximately 2,400 units in 2024, and 7,300 units in 2025, with the market size expected to approach 2.4 billion yuan; by 2035, domestic sales of humanoid robots are expected to reach around 2 million units, with a market size close to 140 billion yuan.
Author|Lin Zhijia
Editor|Hu Runfeng
This article was first published on the Titan Media APP
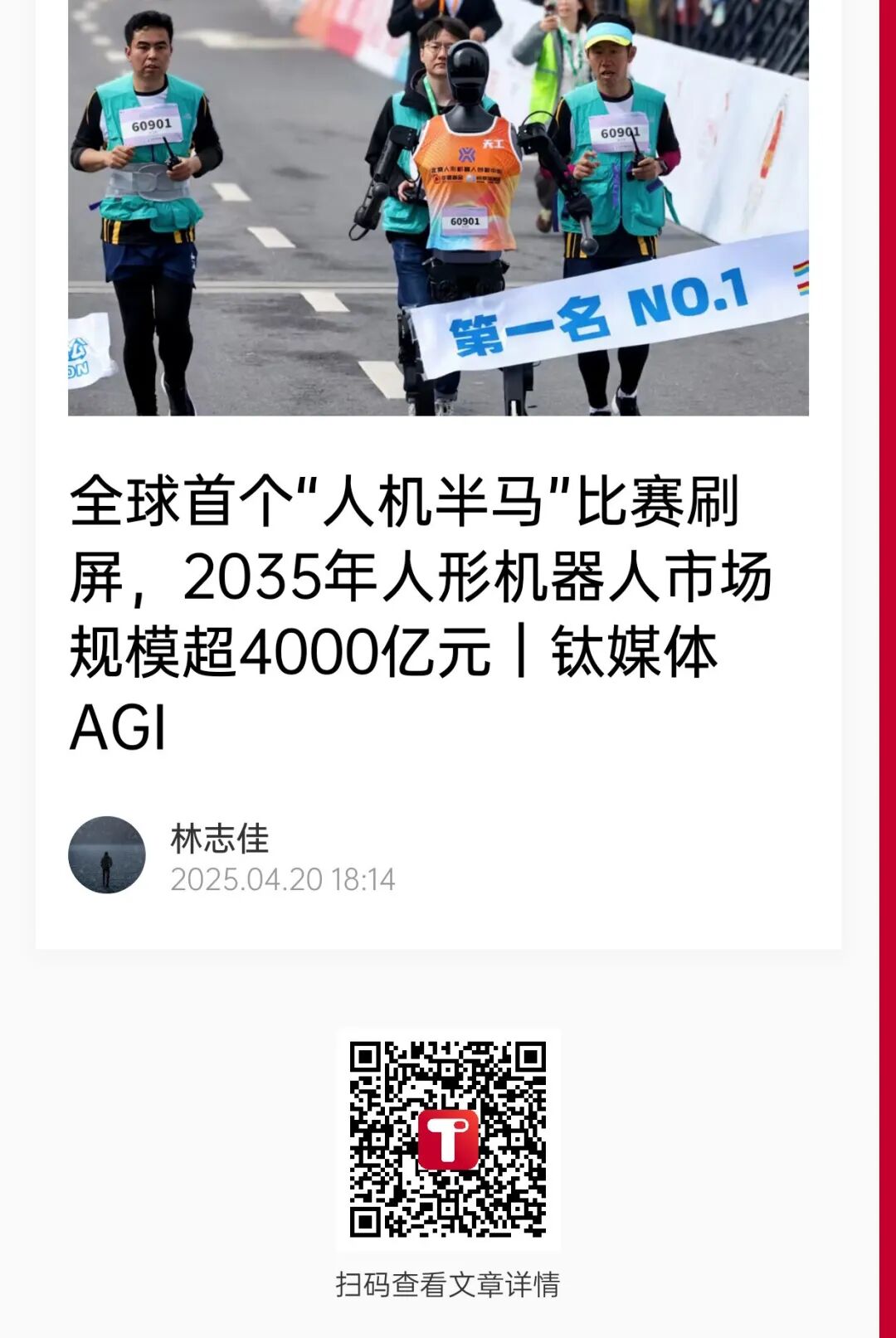
The world’s first humanoid robot half marathon held on April 19 has been trending, with over 23 related topics on Weibo and a reading volume exceeding 2.3 billion.
According to the latest data released by the organizers on the evening of the 19th, on the 21.0975-kilometer track, the “Tiangong Ultra” developed by the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center crossed the finish line first, winning the championship with a total time of 2 hours, 40 minutes, and 42 seconds; the second place (runner-up) was the “Songyan Power N2” robot from the Little Rascal team, finishing in 3 hours, 37 minutes, and 50 seconds; the third place (bronze) was the “Walker No. 2” robot from Shanghai Zhuoyide Robot Co., Ltd. (DroidUp), finishing in 4 hours, 25 minutes, and 56 seconds.
This event is the world’s first “human-robot co-running” activity, attracting 20 robot teams and 12,000 human participants to compete together. However, the results show that current robot technology is still far from that of humans, as the fastest human marathon runner completed the race in just 1 hour and 2 minutes.
However, the “human-robot marathon” craze continues to grow. According to the official website of Chinese marathons, on April 20, a total of 43 marathon events were held nationwide, marking the highest number of marathons held in a single day in China, distributed across 40 cities in 18 provinces, including Zhejiang, Hunan, Shandong, Beijing, and Guangxi, with a total scale exceeding 410,000 participants. Among them, humanoid robots from institutions such as Fourier and the National Local Joint Humanoid Robot Innovation Center appeared at the Shanghai Pudong half marathon.

Animation of the robot’s brain and body separating after falling
In fact, the reason these types of competitions attract so much attention is that through the “human-robot half marathon,” they comprehensively test the real walking, running, full-body coordination, and embodied intelligence capabilities of Chinese humanoid robots, while exposing issues such as joint precision, energy efficiency, heat dissipation, control algorithms, communication interference, and battery management, highlighting both the progress and limitations of such robots, as well as demonstrating how far robots are from human walking and running.
Of course, during the competition, both the robots and their developers faced significant risks. If a robot falls, freezes, or gets lost on the road, it would be a huge embarrassment for the developers.
Therefore, behind every humanoid robot on the field, dozens of people are needed to push it forward.
Clearly, concerns about robots taking jobs are premature; instead, they have created new positions.
Li Yan, Senior Director of Intel’s Edge Computing Division in China, stated on April 18 to Titan Media AGI that “embodied intelligence” as an emerging market is expected to bring new growth points to the domestic industry. According to data from third-party research institutions, currently, 70% of newly deployed robots are in Asia, with 50% in China, driven by the enormous demand in the Chinese market. China is already at the forefront of the global embodied intelligence industry and needs to continue to focus on ecosystem development and the integration of large and small brains to accelerate the deployment of embodied intelligence and humanoid robots.
Champion of the Robot Marathon Emerges
Who Are the Stakeholders Behind It?

On April 19, the “Tiangong Ultra” from Beijing Yizhuang successfully won the championship of the world’s first humanoid robot half marathon with a time of 2 hours, 40 minutes, and 42 seconds.
It is reported that “Tiangong Ultra” was developed by the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center (referred to as the “Innovation Center”), which is backed by two publicly listed companies in Hong Kong: UBTECH, which went public in 2023, and Xiaomi Group, which went public in 2018.
According to Qichacha, the Innovation Center was established in November 2023, jointly held by Beijing Xiaomi Robot Technology Co., Ltd. (referred to as “Xiaomi Robot”), Beijing UBTECH Intelligent Robot Co., Ltd. (referred to as “UBTECH”), Beijing Jingcheng Electromechanical Industry Investment Co., Ltd. (referred to as “Jingcheng Electromechanical”), and Beijing Yizhuang Robot Technology Industry Development Co., Ltd. (referred to as “Yizhuang Robot”). Among them, Xiaomi Robot, UBTECH, and Jingcheng Electromechanical each hold 28.57%, while Yizhuang Robot holds 14.29%.
UBTECH is the initiating and managing unit of the Innovation Center. At the end of 2023, UBTECH, along with Jingcheng Electromechanical, Xiaomi Robot, Yizhuang Robot, and 10 other enterprises and institutions, jointly funded the establishment of the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center, with Dr. Xiong Youjun, CTO (Chief Technology Officer) and Executive Director of UBTECH, serving as the legal representative and general manager of the Innovation Center.
“This is a historic moment; the robot has completed the half marathon course,” Dr. Xiong stated after the race. He expressed hope that in the future, robots could truly enter daily life and assist humans in performing tasks in dangerous environments unsuitable for human work.
Humanoid robots refer to autonomous machines that resemble humans in form and can “exhibit human-like shapes and behaviors.” Compared to ordinary robots, humanoid robots emphasize interaction with humans, and their environmental perception and decision-making capabilities have rapidly developed alongside AI advancements. Therefore, the evolution and development of AI technology are key factors in promoting the intelligent development of humanoid robots.
Currently, humanoid robots generally consist of nine parts, covering the entire industrial chain system of components, body design and manufacturing, secondary development and system integration, and terminal applications: 1. Servo actuators, which are the “joints” of the robot; 2. Motion control research and development; 3. Position control and force control; 4. Whole-body flexible control; 5. The robot’s working capabilities, such as hand-eye coordination, grasping, force-position hybrid control, precision control, and coordination; 6. Navigation algorithms; 7. Biometric recognition; 8. Multimodal interaction; 9. Robot operating systems.
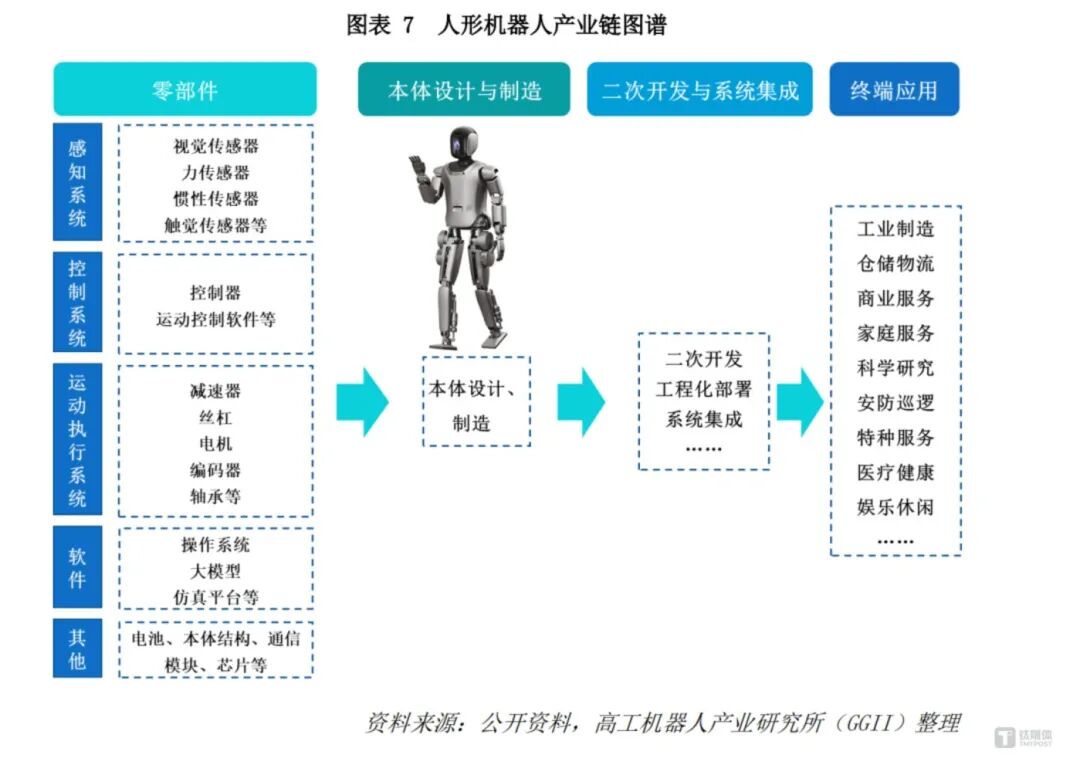
Currently, there are over hundreds of thousands of enterprises in China entering the robot and embodied intelligence sector.
Statistics show that in 2024, a total of 188,800 new robot-related enterprises were registered in China, a slight increase compared to 2023, marking a new high in registration volume in nearly a decade. As of now, there are over 808,400 existing robot-related enterprises in China, among which the number of humanoid robot body enterprises has exceeded 100, and there are thousands of core component enterprises in the industrial chain.
As early as the 2024 Zhongguancun Forum, the Innovation Center released its independently developed general humanoid robot mother platform “Tiangong,” which stands 163 cm tall, weighs 43 kg, supports 550 trillion operations per second, and can run steadily at a speed of 6 km/h; in March 2024, “Tiangong 2.0” was unveiled, achieving the first adaptive walking capability for complex terrains in the country, realizing the first industrial-grade robot’s sustainable operation capability, and with multi-condition energy consumption control technology, it will have far superior endurance compared to previous generations, with comprehensive energy efficiency indicators reaching an internationally leading level.
In March 2025, UBTECH and the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center jointly launched the research and education embodied robot “Tiangong Walker” for market sales, priced from 299,000 yuan, attracting market attention.
Dr. Xiong Youjun once told Titan Media AGI that the biggest advantage of “Tiangong” lies in its powerful body and its expandable, more technical general mother platform, which can be opened to the entire industry for secondary development and iteration, reducing redundant investments.
In his view, the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center aims to be like Apple Inc. (Apple). Whether in terms of research funding, social resources, or R&D teams, “I hope we become the ‘vanguard’ in the global humanoid robot technology field, just as Apple pushed the world into the smartphone era,” Dr. Xiong stated, adding that the Innovation Center has already established dozens of joint laboratories with leading companies in the industry.
CTO Tang Jian of the Beijing Humanoid Robot Innovation Center stated that the “Tiangong 2.0” robot will soon be released, achieving small-batch production and application. In the future, as humanoid robots are deployed on a large scale, their prices will be comparable to those of entry-level sedans.
According to Titan Media AGI, the Innovation Center is developing two major parts: two major tasks— the “Tiangong” general robot mother platform and the “Kaiwu” multi-functional embodied intelligent body mother platform; three coordinations— industry resource organizer, industrial development cultivator, and application promoter, aiming to create a globally influential source of innovation and application demonstration for embodied intelligence. According to an early public plan, by 2025-2027, the organization will focus on industrial ecosystem construction, building an open-source OS and developer community, completing the construction of an open-source OS for humanoid robots and establishing an open-source community.

In Dr. Xiong’s view, the development of humanoid robot technology requires step-by-step, phased development, including aspects such as joints, structures, safety, and data. Humanoid robots need to form a system and standards, requiring top-level design.
“Our next step will be to create a foundational technology open-source community for humanoid robots and develop it into a self-controllable domestic humanoid robot operating system, similar to Android and iOS systems, to develop various tools and applications, not just repeating the development trajectory of personal computers and smartphones. It is expected to become a massive, trillion-level industrial platform, capable of entering factories to assemble cars, microwaves, or entering homes to accompany the elderly and entertain children,” Dr. Xiong stated, emphasizing that in the future, humanity will welcome a world of “human-robot integration,” where humanoid robots will change the world.
On April 18, Dr. Xiong emphasized, “China’s robot industry is already in the first tier globally, and our iteration speed, application scenarios, data volume, and talent level are all top-notch worldwide. I am confident in the development of China’s computational intelligence and humanoid robot industry.”
Global Humanoid Robot Market to Exceed 400 Billion in 10 Years

During the 2025 CCTV Spring Festival Gala, the humanoid robot “Fu Xi”‘s spectacular performance not only made it a hot topic but also sparked widespread attention in the humanoid robot industry.
On April 18, Titan Media AGI learned from the 2025 Intel Embodied Intelligence Solutions Promotion Conference that data from the High-tech Robot Industry Research Institute (GGII) indicates that in 2024, the estimated sales volume of humanoid robots in China will reach 2,400 units (referring to robots with two arms, a head, and two legs), while the market sales in 2025 will reach 7,300 units, with the market size expected to approach 2.4 billion yuan; by 2035, humanoid robots will enter a rapid growth phase, expected to reach around 2 million units, with the market size expected to approach 140 billion yuan.
Globally, the sales volume of humanoid robots is expected to reach 12,400 units in 2025, with a market size of 6.339 billion yuan, and by 2035, the global humanoid robot market sales will exceed 5 million units, with a market size exceeding 400 billion yuan.
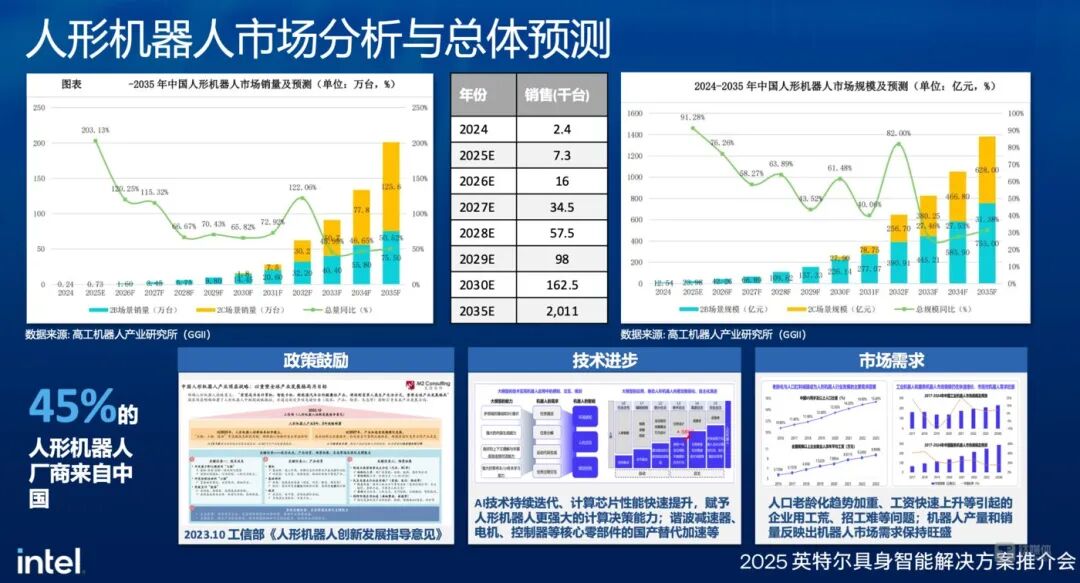
Additionally, according to Goldman Sachs, by 2035, the global market size for humanoid robots is expected to reach 38 billion USD (approximately 272.236 billion yuan), potentially entering household scenarios.
Currently, humanoid robots are performing actively in the Chinese market, with 45% of humanoid robot products coming from China, mainly due to China’s complete supply chain and strong market demand.
However, the humanoid robot industry is still in its early stages and faces many challenges, including the low accuracy of dual-arm robots mimicking human actions, significant disparities between robot manufacturers, a lack of robot data, and the weak integration of AI and hardware, as well as the weak market deployment of robots. Therefore, how to quickly solve issues such as data scarcity and the integration of large and small brains has become crucial.
On April 18, Intel released its embodied intelligence solution, highlighting the integration of large and small brains, enabling efficient integration of perception, interaction, task planning, and motion control within a unified system. As the computational core, Intel’s Core Ultra processor operates in collaboration with the integrated Intel Iris GPU and NPU, providing high-performance heterogeneous computing power and high-precision real-time performance, supporting the stable operation of diverse loads in embodied intelligence systems, while significantly enhancing the overall efficiency and responsiveness of the embodied intelligence system.

Xiong Rong, Chief Scientist of the Zhejiang Humanoid Robot Innovation Center and a distinguished professor at Zhejiang University, told Titan Media AGI that the separation of large and small brains from a hardware perspective makes it difficult for teams to integrate multiple sensors. Currently, the small brain is not just for execution and control; it is hoped that it can also perform tasks such as visual servoing and vision servoing.
It is reported that the Zhejiang Humanoid Robot Innovation Center has also developed the “Navigator 2.0 NAVIAI” humanoid robot based on Intel’s Core processor, achieving breakthroughs in generalized high-precision visual servoing, multi-behavior joint learning for long-sequence behavior planning, and vision fusion operational behavior learning, enabling it to perform complex tasks in industrial scenarios and complete human-robot interaction and assistance tasks in service scenarios, aiding the deep evolution of robot intelligence and promoting its development towards higher levels of wisdom.
Regarding the topic of humanoid robot endurance, Xiong Rong stated that there is no direct correlation between data demand and robot endurance; a large amount of data is mainly used for training, while actual execution requires deploying models to computing devices. A good model should ideally be compressible, distilled, and pruned to reduce computational requirements. Computing devices need to be miniaturized, lightweight, and heat-dissipating to lower battery demands. Therefore, enhancing endurance mainly relies on three aspects: battery technology, reduced device power consumption, and lowered algorithmic demands on computing power.
“Humanoid robots are the most eye-catching representatives in the field of ’embodied intelligence,’ but they are not the only ones. Embodied intelligence does not equal humanoid robots. Humanoid robots are often considered the best carriers of embodied intelligence, but in reality, humanoid robots also represent the greatest demand and challenge for embodied intelligence,” Xiong Rong stated.

Currently, the embodied intelligence and humanoid robot industry is on the eve of an explosion, and how to leverage the current global situation to promote China’s self-controllable robot industry and achieve large-scale deployment is of great significance.
“For ordinary people, a half marathon is a highly challenging sport, and everyone will be exhausted, but robots can continue running by changing batteries. In the future, there may be robots participating in cooking, rock climbing, or swimming competitions. I look forward to all of them,” said a participant in this half marathon.
It is worth noting that after the competition, Hangzhou Yushu Technology issued a statement saying that Yushu has recently been busy preparing for humanoid robot combat live broadcasts and did not participate in any competitions. Several independent teams used Yushu’s robots in this marathon. Customers used their own algorithms to participate in the competition, and the performance of the robots varied greatly under different operators or developers.
Liu Li, Deputy Director of the Beijing Economic and Technological Development Zone Management Committee, stated that this competition should have a good driving and leading effect on the entire robot industry, promoting robots to enter factories, schools, and homes, using these demands to drive innovation, research, and manufacturing, thereby forming a complete industrial ecosystem.

In November 2023, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China released the “Guiding Opinions on the Innovative Development of Humanoid Robots,” which first planned the development of the humanoid robot industry in China for the next 10 years, believing that humanoid robots are expected to become disruptive products following computers, smartphones, and new energy vehicles, profoundly transforming human production and lifestyle.
The guiding opinions propose that by 2025, a preliminary humanoid robot innovation system will be established in China, with breakthroughs in a number of key technologies, ensuring the safe and effective supply of core components, achieving international advanced levels in complete products, and realizing mass production; by 2027, China’s technological innovation capabilities in humanoid robots will be significantly enhanced, forming a safe and reliable industrial chain supply chain system, and building an internationally competitive industrial ecosystem, with comprehensive strength reaching world advanced levels.
“The marathon of humanoid robot industry development has just begun,” stated an article in the WeChat account of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, indicating that mainstream humanoid robot products have already achieved “standing firm, walking steadily, and running fast,” and are accelerating the transition from “moving on stage” to “being used in factories.”
(This article was first published on the Titan Media App)

Recommended Hot Video
Yushu Technology responds to its robot falling during the half marathon: Yushu did not participate, and the robot’s performance is closely related to the user.
Like and FollowTitan MediaVideo account, watch more exciting videos