The intelligent logistics and warehousing system is represented by the three-dimensional warehouse and distribution sorting center, composed of three-dimensional shelves, rail-guided stacker cranes, inbound and outbound pallet conveyor systems, detection reading systems, communication systems, automatic control systems, computer monitoring management, etc. It integrates automated control, automatic conveying, front-end automatic sorting, and in-house automatic conveying, achieving automation and intelligence in the physical movement of goods and information management within the warehouse through a software platform that automatically records, manages, and verifies goods information.
Intelligent logistics is a core component of Industry 4.0, with intelligent logistics warehousing located at the backend, serving as a critical link between manufacturing and end-users. With the application of new technologies such as the Internet of Things, machine vision, warehouse robots, and drones, logistics warehousing automation technology is undergoing rapid transformation, becoming one of the most stable growth areas with the greatest potential in the entire automation sector.
Speaking of intelligent logistics and warehousing systems, one cannot fail to mention Amazon’s eighth-generation logistics center, which has become a model of intelligent logistics and warehousing due to its pervasive black technology that it has opened to the media.
Kiva Technology of Intelligent Robots
In 2012, Amazon acquired the robotic warehousing business of automation logistics provider Kiva for $775 million. Currently, there are over 15,000 Kiva robots working in Amazon’s distribution centers in the United States.
Normal distribution centers typically set up dedicated storage locations for products, but Amazon randomly places goods after they are stored. After a user places an order, the system issues picking instructions to the Kiva robots, with an algorithm planning the shortest route to retrieve the required goods, and then you can see thousands of robots shuttle back and forth in tens of thousands of square meters of warehouse!
The accuracy of Kiva robots reaches 99.99%, significantly relieving manual labor. The “eyes” of Kiva robots are located at the top center, allowing them to recognize shelves, after which a black plane aligned with the “eyes” will rise, lifting the shelf and delivering it to the staff.

Ship First, Order Later
In 2013, Amazon applied for a patent for “predictive shipping,” which predicts user consumption behavior based on big data to ship goods before users place their orders, greatly enhancing delivery speed, particularly for best-selling products.
The conditions for predictive shipping include: order records, search records, wish lists, shopping carts, and even the time the mouse hovers over a product.
Amazon Drone Delivery
Amazon’s drone delivery project is undoubtedly one of the biggest innovations in global logistics. The U.S. FAA has finally given it the “green light” to conduct related experiments.
Despite strict regulations and numerous challenges, Amazon remains committed to its “drone dream.”
Shortly after Amazon announced its drone news, drones from UPS and FedEx followed suit. Domestic companies such as JD.com and SF Express have also showcased drone delivery.

Taxi Delivery
Amazon collaborates with the mobile taxi app Flywheel to use taxis for delivering packages to users. Amazon uses the Flywheel app to call taxis near small distribution centers, handing over up to 10 packages with the same postal code to the taxi for delivery, paying $5 per package, with a delivery requirement of within 1 hour.
Delivering Packages to Car Trunks
Amazon collaborates with DHL and Audi in Germany to deliver packages to the recipient’s car trunk, where the courier will obtain a one-time access code for the trunk and the car’s GPS location, and users will receive email notifications upon successful delivery.

The automated warehousing system is a layered distributed computer control system, generally divided into management level, monitoring level, control level, and equipment level. The main components of the system are high-level shelves, aisle stackers, and computers.
Each system design is divided into several main stages, each with its objectives:
· Demand Analysis
· Confirm the form and specifications of goods units
· Confirm the form, operation methods, and mechanical equipment parameters of the automated warehouse
· Establish a model, mainly referring to determining the overall size of the shelves and the internal layout of the warehouse based on unit goods specifications
· Determine the process flow and calculate the warehouse’s working capacity
· Put forward actual requirements for civil construction and public works
· Select control methods and warehouse management methods
During the operation of the automated warehouse, there are generally several control methods to facilitate operators and debugging personnel to flexibly handle various situations in the warehouse as needed. Control methods can be divided into manual control, semi-automatic control, remote control, and fully automatic control.
· Manual Control
Manual control refers to the handling and storage operations of goods being completed by human labor or manually operating simple machinery. This method is mostly used during debugging or accident handling.
· Semi-Automatic Control
Semi-automatic control refers to the handling and storage operations of goods being partially completed by human labor. The entire warehouse operation can be controlled via PLC or microcomputer.
· Remote Control
Remote control centralizes the control of all operational machinery in the warehouse to one control room, where operators control warehouse operations remotely via electronic computers.
· Fully Automatic Control
Fully automatic control means that loading and storage operations are conducted automatically through various control devices, with electronic computers controlling all operational activities in the warehouse. This is the control method used under normal operating conditions.
· Centralized Control Method
In the early 1980s, with the rise of single-board computers in industrial applications, most automated warehouse equipment was controlled by single-board computers. A large-capacity, multi-I/O interface single-board computer system can be selected for control.
To improve system reliability, several measures can be taken: one is hardware redundancy measures, and the other is to use high-function, high-reliability PLCs, while also implementing various software design measures to enhance reliability.
· Layered Distributed Control Method
The advantage of a layered distributed control system is that all system functions are not concentrated on one or a few devices. Therefore, even if certain devices fail, it will not significantly affect other devices, and the control method is also hierarchical. The system can operate at high levels as well as at lower levels. For this reason, this type of control system structure is widely used abroad and is suitable for large-scale control scenarios.
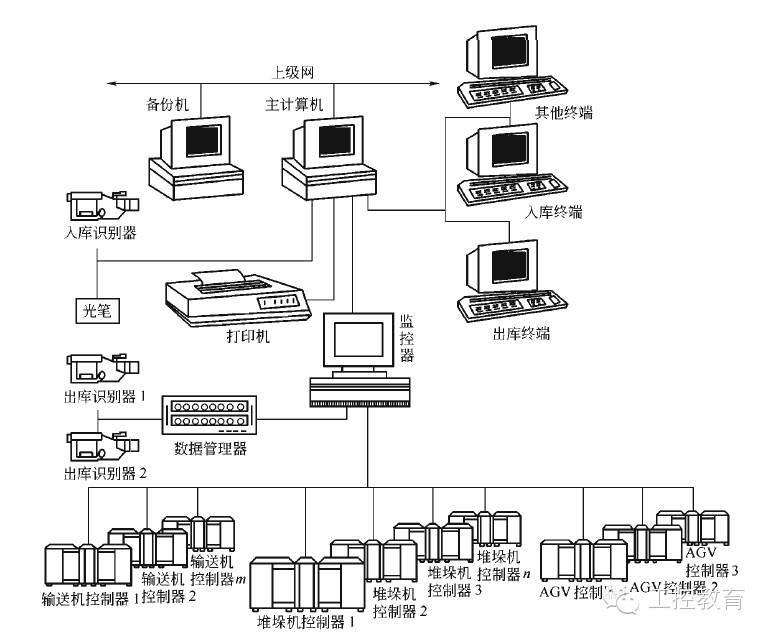
With the development of logistics industrial production, flexible manufacturing systems, computer-integrated manufacturing systems, and engineering automation have raised higher demands for automated warehouses. Handling and storage technologies must provide more reliable and real-time information, and logistics in factories and warehouses must be accompanied by parallel information flows. Radio frequency data communication, barcode technology, scanning technology, and data collection are increasingly applied to warehouse stackers, automated guided vehicles, conveyor belts, and other transport equipment, while mobile robots are also playing an increasingly important role as flexible logistics tools in flexible production, warehousing, and product delivery. Achieving system flexibility and adopting flexible transport equipment and logistics routes is the trend in achieving logistics and warehousing automation.
Below is an application plan for real-time logistics in a certain enterprise in the automotive industry, which integrates advanced wireless networks, RF terminals, and voice picking terminal devices to achieve real-time demand-driven pulling of raw materials, more efficient real-time replenishment at all levels of the supply chain, online acquisition of real-time coordinates of vehicles, and intelligent entry logistics operations.
 With the widespread application of new-generation RFID, sensors, GPS, cloud computing, and other information technologies in logistics transportation, warehousing, packaging, loading and unloading, processing, distribution, and information services, logistics systems will become more intelligent, networked, automated, visualized, and systematic. China’s logistics and warehousing automation will have even greater development space in the coming years.
With the widespread application of new-generation RFID, sensors, GPS, cloud computing, and other information technologies in logistics transportation, warehousing, packaging, loading and unloading, processing, distribution, and information services, logistics systems will become more intelligent, networked, automated, visualized, and systematic. China’s logistics and warehousing automation will have even greater development space in the coming years.
This article is an original piece by the user “开舒克飞机的贝塔” on Gongkong, and the images are sourced from the internet. Please indicate the source when reprinting.

-
Gongkong Education WeChat ID: Gongkong Education
-
Gongkong Education QQ ID: 3173802991
-
IAAT Project WeChat ID: IAAT
Contact Us
Phone: 400-1010-875, 010-58930031
Fax: 010-58931038
Email: [email protected]
Website: http://www.gongkongedu.com
Address: 8th Floor, Block B, Jiahao International, No. 116, Zizhuyuan Road, Haidian District, Beijing
About Gongkong Education
Gongkong Education (www.gongkongEDU.com) is an online learning platform provided by Gongkong Network for professionals in industrial automation and related fields, as well as students in various higher education institutions.
Gongkong Education platform provides users with online course learning in the automation field, download of learning materials, online examinations, online certifications, on-site training registration, and other services.
About the IAAT Project
The National Industrial Automation Training Project (Industry Automation Accreditation Training, abbreviated as IAAT Project) is a training program aimed at cultivating skilled and innovative industrial automation talents, promoting employment and career choices for automation engineers, jointly launched by Gongkong Network and several excellent enterprises in the industrial automation field. In 2010, this project received support from the Ministry of Education’s Educational Management Information Center and has been implemented nationwide.
The IAAT Project Office is located at Gongkong Network (Beijing) Educational Technology Co., Ltd., providing a series of collaborations such as teacher training, online learning, examination certification, recruitment and employment, competition exchange, and school-enterprise cooperation for schools. By integrating social educational resources and adhering to application-oriented principles, a standardized curriculum system is established, targeting students in various higher education institutions and professionals in society, aiming to enhance the employment and career competitiveness of participants, and conducting training and certification work nationwide to provide professional automation talents for factories and automation enterprises. The project aims to cultivate, assess, and certify high-tech automation talents based on the job requirements in the industrial automation industry, ultimately achieving targeted employment delivery for talents.
The official websites of the IAAT Project Office are: China Education Resource Network (http://www.cern.net.cn), IAAT Project Official Website (http://www.iaat.org.cn), Gongkong Network (http://www.gongkong.com), which will fully participate in the publicity and reporting of the IAAT Project.