 Follow「Raymond Operations」 WeChat official account, and set it as「Starred」, you can also scan the QR code at the bottom to join the group chat, to get the latest content in real time and never miss exciting content.
Follow「Raymond Operations」 WeChat official account, and set it as「Starred」, you can also scan the QR code at the bottom to join the group chat, to get the latest content in real time and never miss exciting content.
Introduction to DNS
DNS (Domain Name System): is a system that uses a client/server mechanism to convert computer names to IP addresses. As an important network service, DNS is the foundation of the international internet and is widely used in internal corporate networks.
Functions of DNS Servers
Forward Resolution: Finding the corresponding IP address based on the host name (domain name)Reverse Resolution: Finding the corresponding host domain name based on the IP address
Distributed Data Structure of DNS System
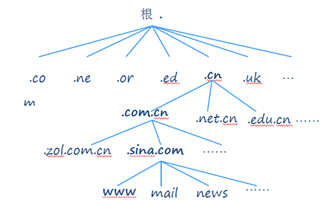
DNS Query Methods
Recursive Query: Most clients resolve domain names through DNS servers
Iterative Query: Most DNS servers resolve domain names through other DNS servers
Types of DNS Servers
Cache Name Server
Cache Name Server: Also known as a high-speed cache server, it queries other name servers to obtain domain name->IP address records and caches the results locally to improve speed for repeated queries.
Primary Name Server
Primary Name Server: The official server for a specific DNS zone, unique, responsible for maintaining all domain name->IP address mapping records within that zone.
Secondary Name Server
Secondary Name Server: Also known as an auxiliary name server, its domain name->IP address records are sourced from the primary name server.
BIND Domain Service Basics
BIND (Berkeley Internet Name Daemon) Berkeley Internet Domain Service.
Official site: https://www.isc.org/
BIND server-side program
Main execution program: /usr/sbin/named
Service script: /etc/init.d/named
Default listening port: 53
Main configuration file: /etc/named.conf
Data file storing DNS resolution records located at: /var/named/chroot/var/named/
Configuration File Analysis
/etc/named.conf
options { #Options
listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; }; #Service listening port is 53
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; }; #Service listening port is 53 (ipv6)
directory "/var/named"; #Directory where configuration files are stored
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db"; #Cache of resolved contents
statistics-file"/var/named/data/named_stats.txt"; #Static cache (generally not used)
memstatistics-file"/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt"; #Static cache (in-memory, generally not used)
allow-query { localhost; }; #Allowed connecting clients
recursion yes; #Recursive lookup
dnssec-enable yes; #DNS encryption
dnssec-validation yes; #DNS encryption advanced algorithms
dnssec-lookaside auto; #DNS encryption related items
/* Path to ISC DLV key */
bindkeys-file"/etc/named.iscdlv.key"; #Key for encryption (private/public key encryption, very strong)
};
logging { #Log
channel default_debug {
file"data/named.run"; #Running status file
severity dynamic; #Static server address (root domain)
};
};
zone "." IN { #Root domain resolution
type hint; master slave
file"named.ca"; #Root domain configuration file
};
include"/etc/named.rfc1912.zones"; #Extended configuration file (for new domain names)
/etc/named.rfc1912.zones
zone "localhost.localdomain" IN { #Local host full name resolution
type master; #Type is master domain
file "named.localhost"; #Domain configuration file (stored in /var/named directory)
allow-update { none; }; #Clients are not allowed to update
};
zone "localhost" IN { #Local host name resolution
type master;
file "named.localhost";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone ".0.ip4.arpa" IN { #IPv6 local address reverse resolution
type master;
file "named.loopback";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa" IN { #Local address reverse resolution
type master;
file "named.loopback";
allow-update { none; };
};
zone "0.in-addr.arpa" IN { #Local network address reverse resolution (used for / domain updates)
type master;
file "named.empty";
allow-update { none; };
};
/var/named/named.localhost
$TTL 1D #Update to a maximum of 1 day
@ (domain name used) IN SOA (authoritative DNS server) @ (authoritative DNS server name) rname.invalid. (rname@invalid email) (
0 ; serial # (change number) ten-digit serial number
1D ; update frequency
1H ; failure retry time
1W ; expiration time
3H ) ; cache time
NS (domain name server) @ (domain server name)
A (forward resolution record) 127.0.0.1 (IP for forward resolution)
AAAA (ipv6 forward resolution) ::1 (IP for ipv6 forward resolution)
Setting Up a DNS Server
Installing the DNS Server
Install the bind package
yum install bind
Start the service
systemctl start named.service
Set to auto-start
systemctl enable named.service
Configuration Files
Configure the main configuration file
vim /etc/named.conf
Change to
listen-on-v6 port 53 { any; };
allow-query { any; };
Configure zones file
Forward resolution configuration
Add forward resolution
zone "lzy.com." IN {
type master;
file "lzy.com.zone";
allow-update { none; };
};
Reverse resolution configuration
Add reverse resolution
zone "134.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN {
type master;
file "134.168.192.zone";
allow-update { none; };
};
Configure the zone configuration files
Copy files
cp /var/named/named.empty /var/named/lzy.com.zone
cp /var/named/named.empty /var/named/134.192.168.zone
Change permissions
chown :named zlt.com.zone
Forward resolution configuration
Design forward resolution for excesoft.com domain, copy /var/named/named.empty, rename it to excesoft.com.zone,
change the file group to named, and modify its contents
$TTL 3H
@IN SOA lzy.com. root.lzy.com. (
0; serial
1D; refresh
1H; retry
1W; expire
3H); minimum
NS dns.lzy.com.
dns A192.168.134.139
www A192.168.134.139
Reverse resolution configuration
Design reverse resolution for excesoft.com domain, copy /var/named/named.empty, rename it to 137.168.192.zone, change the file group to named, and modify its contents.
Configure network card
vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR1=192.168.134.139
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.134.2
DNS1=192.168.134.139
Start the DNS server
systemctl start named.service
Check the configuration file
named-checkconf
Configure the Client
Modify the configuration file
Modify the configuration file: #vim /etc/resolv.conf.
Write the following content:
excesoft.
nameserver 192.168.137.22
Test the DNS server
Test the DNS server
Use the command nslookup on the client computer to test.Link: https://www.cnblogs.com/yanlzy/p/11918018.html
Copyright belongs to the original author, infringement will be deleted
WeChat Group
Group
WeChat group

To facilitate better communication on operations and related technical issues, a WeChat group has been created. Those who want to join can scan the QR code below to add me as a friend (note: join the group).

Blog
Guest
Blog

CSDN Blog: https://raymond.blog.csdn.net

Juejin Blog: https://juejin.cn/user/4262187909781751

Long press to identify the QR code to visit the blog website and see more high-quality original content.