Digital output primarily includes three forms: RS232, RS485, and wireless transmission. The specific digital output type is chosen based on the actual communication distance and the complexity of the terrain.
RS232 output is generally suitable for short-distance transmission within 15 meters and has weak electromagnetic interference resistance; RS485 output is suitable for longer distances, generally not exceeding 1200 meters, and has strong electromagnetic interference resistance; wireless transmission is suitable for complex terrain situations.
The analog product outputs are: analog current 4mA-20mA or analog voltage 0-10V. The output current or voltage changes in real-time with distance, with analog values corresponding directly to distance values.
Radar level gauge (taking a range of 0-10 meters as an example)
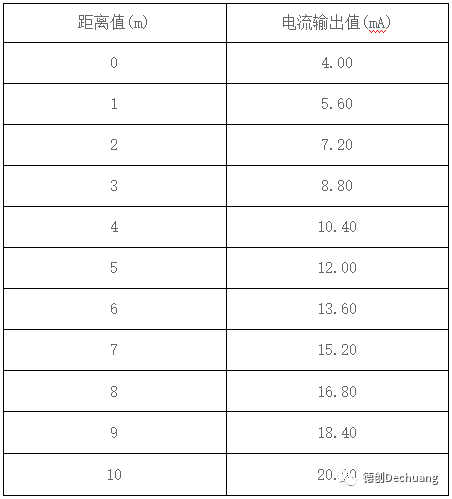
Online gas analyzer (taking a range of 0-100% as an example)
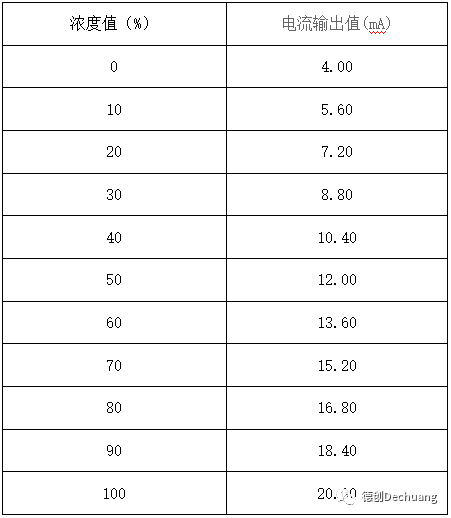
The HART protocol output product is a popular digital protocol that combines characteristics of both analog systems and digital control systems. The HART protocol uses frequency-shift keying (FSK) based on the Bell 202 standard to superimpose digital information onto the traditional 4-20mA analog signal. It is an industrial standard used to define the communication protocol between smart field devices and control systems.
Switch quantity products can support relay output, corresponding to two preset values. When the measured distance reaches the preset upper limit, the corresponding output terminal opens. The preset values can be set according to user requirements.
Click to learn about industrial sensor transmission methods.
A sensor is a type of semiconductor device that converts natural signals from the environment into electrical signals to meet the requirements for information transmission, processing, storage, display, recording, and control.
Generally composed of a sensitive element, a conversion element, a transformation circuit, and a power supply.
Directly senses the measurement and outputs a physical quantity that has a definite relationship with the measurement.
The core component of the sensor, which takes the output from the sensitive element as input and converts the sensed non-electric quantity into an electrical signal output. The conversion element can also be used as an independent sensor, known as a component sensor.
Involves the relevant circuits that convert the electrical signals output by the sensing element into useful electrical signals that are easy to process, control, record, and display.
Sensors can be classified based on their measurement objects, including sensors for detecting light, radiation, sound signals, magnetic signals, pressure, displacement information, distance, temperature and humidity, solution flow rate, and more.
The application fields of sensors are the data collection entry points for the Internet of Things, smart industry, smart devices, and autonomous driving. The industrial intelligent sensor market applies products in life sciences and health, mechanical processing and manufacturing, automotive, semiconductors and electronics, industrial automation, transportation and logistics, energy and electricity, food, oil and gas, aerospace, etc.
Before detailing what a sensor is, what different types of sensors exist, and the applications of these different types, let’s first look at a simple example of an automation system, which may be due to sensors (and many other components).
Application of sensors in the automotive industry: automotive sensors can be divided into body perception sensors and environmental perception sensors based on their usage purposes. Body perception sensors enhance the information level of a single vehicle, allowing it to perceive itself; based on the input measurement, they can be categorized into pressure sensors, position sensors, temperature sensors, linear acceleration sensors, angular acceleration sensors, airflow sensors, and gas sensors, most of which adopt MEMS solutions from a working principle perspective. Environmental perception sensors enable a single vehicle to perceive external environments, helping the vehicle’s computer obtain environmental information and make planning decisions, supporting intelligent driving; environmental perception sensors are mainly classified into onboard cameras, ultrasonic radar, millimeter-wave radar, laser radar, and infrared radar.
The temperature sensor first appeared in mobile phones, capable of monitoring the temperature changes of the battery, processor, etc., especially in today’s smartphones where it is used more to control hardware monitoring, environmental temperature, and humidity detection, etc.
Many mid-to-high-end mobile devices are now equipped with this barometric sensor, which mainly consists of external and internal pressure sensors, used to detect atmospheric pressure in daily life and can calculate the altitude of one’s location based on atmospheric pressure changes, suitable for outdoor sports altitude measurement, and detecting the sealing degree of three-proof equipment.
The gravity sensor is used in Apple’s iPhone, allowing users to easily switch between horizontal and vertical screens, and can also be used in games and 3D applications. It can physically measure the rotation angular velocity when tilted, which is also helpful for photography and inertial navigation applications.
A position sensor, or GPS, can provide us with navigational services for location information, which is configured in mobile phones, suitable for map positioning, finding lost devices, and monitoring.
The proximity sensor is also a basic feature in mobile phones. For example, when we receive a call, the phone’s screen automatically turns off when brought close to the face, which not only saves battery but also prevents accidental disconnection. Its characteristic is that the distance is very short, usually only a few centimeters.
The light sensor is actually a brightness sensing processor, which is quite common in tablets and mobile phones. For example, mobile phones have adaptive brightness operations that can automatically adjust the screen brightness based on the ambient light, providing the most comfortable visual effect.
Magnetic sensors are present in both phones and tablets, but they are different. They can determine orientation, assist positioning devices, and when viewing the mobile map, the movement on the screen is determined by the magnetic sensor’s orientation.
The super sensitive touch sensor can assist capacitive screen touch usage, and is a common feature in today’s smartphones and tablets. It can detect the position of a finger’s operation based on voltage changes, allowing operation even while wearing gloves.

