Introduction to Galileo AI
LogRocket’s Galileo AI can monitor every session, revealing important user experience issues and key behavior patterns. Comparing programming languages is not a new topic in the technical ecosystem. Developers continuously evaluate languages, frameworks, and tools.
Rust and Nim: A Comparison of Programming Languages
Rust and Nim share many similarities and differences in design, syntax, and use cases, making them interchangeable in many situations. This article provides an overview of the Rust and Nim programming languages and explores their advantages, disadvantages, and features.
What is Rust?
Rust is a multi-paradigm, statically typed, general-purpose programming language. It is known for its performance, type safety, memory safety, and concurrency. Developed by the Mozilla Foundation, Rust has seen its developer ecosystem grow since its release, becoming one of the most popular languages in various surveys, including the annual Stack Overflow Developer Survey.
Rust Features
-
Efficient C Bindings: Rust was designed with compatibility with C in mind, allowing for interaction with C code.
fn main() { println!("Hello World!"); }Every Rust program must have a
<span>main</span>function as the entry point. The<span>println!</span>macro is used to output text parameters to the console at runtime. -
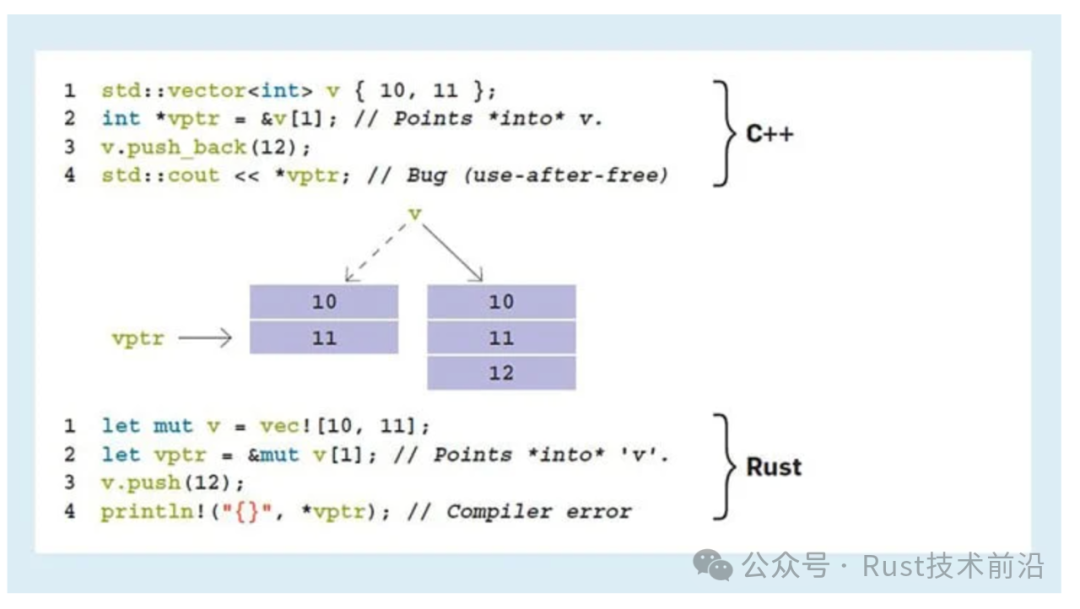
Memory Safety: Unlike Nim, which uses a garbage collector, Rust ensures memory safety through a borrow checker and ownership model.
-
Expressiveness: As a multi-paradigm programming language, Rust provides easy-to-use error handling, various data types, and a pattern matching system to enhance developer productivity.
Rust Use Cases
-
System Programming: Rust is competitive in the field of system programming, with low-level expressiveness giving it a unique advantage in embedded systems.
-
Web Development: An increasing number of projects are choosing Rust as a server-side programming language to leverage its safety and performance advantages. Frontend frameworks like Yew and Moonzoon, and backend frameworks like Actix, Rocket, Warp, or Tide all support Rust.
-
Building Tools and Services: Rust is suitable for building libraries and tools for other languages, as well as for browsers, operating systems, and network services that require low-level resource interaction.
Advantages of Rust:
-
Provides type safety and memory safety, reducing errors in production environments.
-
A versatile, general-purpose programming language suitable for various environments and use cases.
-
Supports most features of modern programming languages, with high expressiveness.
Disadvantages of Rust:
-
Compiled binaries are relatively large, and the compiler is comparatively slow.
-
The learning curve for new concepts is steep, and the developer community is relatively small.
What is Nim?
Nim is a dynamically typed yet statically typed compiled system programming language with a concise syntax. The design philosophy of Nim is inspired by Ada, Python, and Modula, incorporating many features favored by developers. The Nim community is active and well-governed.
Nim Features
-
Cross-Language Interoperability: Nim can interact with C and C++ through FFI, and code can be compiled to C, C++, and JavaScript.
-
Memory Management: Nim provides both manual and automatic memory management features, with an efficient garbage collector that offers flexibility and control based on different use cases.
-
Expressiveness: Nim’s syntax is influenced by popular languages and supports functional and object-oriented programming paradigms.
Nim Use Cases:
Nim’s versatility and good interoperability with other languages have led to its success in various application domains. Whether pursuing high performance or flexible memory management strategies, Nim can provide solutions.
Despite being a relatively new programming language, developers and companies are already using Nim for development and investing in it. Here are some broad application scenarios where Nim excels:
Game Development: Game developers are adopting Nim at an astonishing rate, primarily because Nim’s foundational features are well-suited for game development. Nim offers performance, ease of abstraction, and resource management. To build fully functional games, developers can utilize game development engine packages, frameworks, and simulator packages within the Nim ecosystem.
Web Development: Considering various factors such as performance and ease of use, Nim is an excellent server-side programming language. In the Nim ecosystem, you can find frameworks, routers, ORMs, SQL, and NoSQL database packages that help accelerate your web application development. Additionally, since Nim code can be transpiled to JavaScript, you can explore using Nim on the frontend of web applications.
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Development: Nim is widely used for developing graphical user interfaces, with toolkits similar to GUI packages in other languages. Packages inspired by the GTK toolkit can be used to build cross-platform GUI applications, web applications, and interactive command-line interfaces.
Advantages of Using Nim: Choosing Nim as the language for project development allows you to enjoy the convenience of its interoperability. If there is a need to switch languages, as long as Nim supports it, you can easily transpile the code to the target language. This means you can write code in Nim for a wider range of purposes and environments. Nim is a fully open-source general-purpose programming language, with many production-ready libraries in its ecosystem, and as the ecosystem rapidly develops, it will soon support any applications backed by the community.
Disadvantages of Using Nim: Nim is new, and while it is a modern programming language with much to offer, it is not as popular. This means finding developers and support within the Nim ecosystem can be a challenge, and using Nim in production for critical applications may not be the best solution. Compared to Rust, Nim’s support for concurrent programming and threads is less robust, which is a limitation for many application scenarios.
Getting Started with Nim: Nim is simple and elegant, with syntax inspired by other successful languages. Printing output in Nim is very similar to printing in bash. Here is a simple “Hello World” program:
echo "Hello World"
<span>echo</span> keyword prints text to the console.
Comparing Rust and Nim Programming Languages: Rust and Nim are both modern programming languages designed to solve similar problems, sharing similar advantages and disadvantages, as well as design principles. Rust is more popular than Nim, thanks to Mozilla’s support, while Nim lacks backing from large companies and has few well-known tech figures acknowledging its use in production.Both Rust and Nim are statically typed, highly expressive, and support multiple programming paradigms, making them suitable for the same purposes.
| Metric | Rust | Nim |
|---|---|---|
| Popularity | Very Popular | Less Popular |
| Level of Abstraction | Low-Level Abstraction | Low-Level Abstraction |
| Programming Paradigms | Object-Oriented; Functional; Procedural | Object-Oriented; Functional; Procedural |
| Developer Experience | Highly Expressive, with Generic Support | Very Highly Expressive |
| Type System | Statically Typed | Statically Typed |
| Use Cases | General Purpose (Web, Systems, Applications, Networking) | Multi-Purpose (Applications, Web Development, Scripting, Systems) |
It is recommended to use Rust wherever possible, and only choose Nim when necessary. This is because Rust has a larger pool of developers and a more extensive ecosystem, providing more software support needed during development. While Nim is a promising language, Rust is currently the better choice for achieving broader resonance.
Assuming Rust and Nim are of equal maturity, one might lean towards choosing Nim, as it allows for performance gains without the need to worry about the borrow checker and other troublesome concepts to write safe code like in Rust.
Debugging Rust applications can be challenging, especially when users encounter hard-to-reproduce issues. If you want to monitor and trace the performance of Rust applications, automatically surface error messages, and track slow network requests and loading times, consider using LogRocket. LogRocket acts like a DVR for web and mobile applications, recording almost everything that happens in the application instead of guessing the cause of issues. LogRocket also monitors application performance, reporting metrics such as client CPU load and memory usage.
「Click 👇 to Follow」
Like + Share + View to Quickly Improve Your Programming Skills👇
Reference Link: https://blog.logrocket.com/comparing-rust-nim/