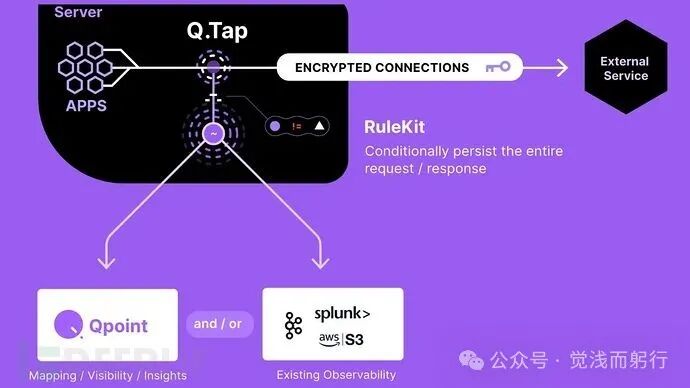
Qpoint recently released Qtap, an open-source network traffic monitoring tool based on eBPF technology, specifically designed for Linux systems. This tool hooks into TLS/SSL encryption functions, allowing it to capture traffic information before and after data encryption, and presents detailed network data in plaintext, including processes, containers, hosts, users, and protocols.
Qtap operates in an out-of-band mode, with extremely low overhead, ensuring that it does not increase network latency or interfere with the normal operation of applications. This lightweight tool can run securely without complex configurations, making it particularly suitable for monitoring network activities of complex applications, third-party services, or legacy systems.
Core Features
Qtap provides developers, security experts, and system administrators with deep insights into outbound traffic without the need to modify applications, deploy agents, or manage certificates. Whether auditing sensitive data, diagnosing network issues, or analyzing legacy systems, Qtap offers a clear view of network activities.

Key Features and Use Cases
As a foundational component of observability pipelines, Qtap’s versatility makes it suitable for the following scenarios:
- Security Auditing: Verifying whether sensitive data is leaked during network communication
- Network Debugging: Diagnosing API errors, parameter configuration issues, or abnormal responses through real-time traffic analysis
- API Development: Ensuring that applications send requests in the correct format and handle responses properly
- Third-Party Integration: Checking whether data exchanges with external services comply with documentation standards
- Learning and Research: Studying protocol behavior characteristics by observing real-time traffic
- Legacy Systems: Analyzing undocumented systems when source code is unavailable
- Validation Testing: Confirming that application changes do not disrupt existing network communication patterns
Quick Start
Demo Mode Experience
Execute the following command in the terminal to experience Qtap’s traffic monitoring capabilities:
$ curl -s https://get.qpoint.io/demo | sudo sh
Installation and Running
Complete installation steps:
# Install Qtap
$ curl -s https://get.qpoint.io/install | sudo sh
# Run with default configuration
$ sudo qtap
System Requirements:
- Linux kernel version 5.10 or higher
- BTF and eBPF support must be enabled (check if /sys/kernel/btf/vmlinux file exists)
- Elevated permissions required: sudo permissions in host environment, CAP_BPF capability and privileged mode in Docker environment
Development Guide
The Qtap project is open-sourced on GitHub, and developers can contribute in the following environments:
- Operating System: Linux (kernel 5.10+), MacOS users can create a Linux virtual machine using Lima
- Development Tools: Go 1.24+, make toolchain, clang 14 (required), clang-tidy (optional)
Source Compilation
$ git clone https://github.com/qpoint-io/qtap.git
$ make build
Common Make Commands
<span>build</span>: Compile eBPF binaries and Go applications<span>generate</span>: Generate eBPF binaries<span>run</span>: Start a debug instance<span>ci</span>: Perform continuous integration checks
Project Status Note: Qtap is currently in the early development stage, and API interfaces may change, with documentation potentially being incomplete. Feedback can be submitted via GitHub Issues or Discussions. All contributors must sign a Contributor License Agreement (CLA), which applies to both open-source and commercial use.
References:
Qtap – An Open-Source Tool to See Through Encrypted Traffic in Linux systems