Power Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC) is the Chinese term for 电源管理集成电路, which is characterized by high integration, encapsulating traditional multi-output power supplies into a single chip, making multi-power applications more efficient and compact.
PMIC is an indispensable key component in today’s electronic devices, providing power for various devices from mobile phones and smartwatches to cars and industrial equipment with its excellent performance and multifunctionality.PMIC not only supplies power to electronic devices but also leads new trends in power management to meet the growing demand in the electronic market.
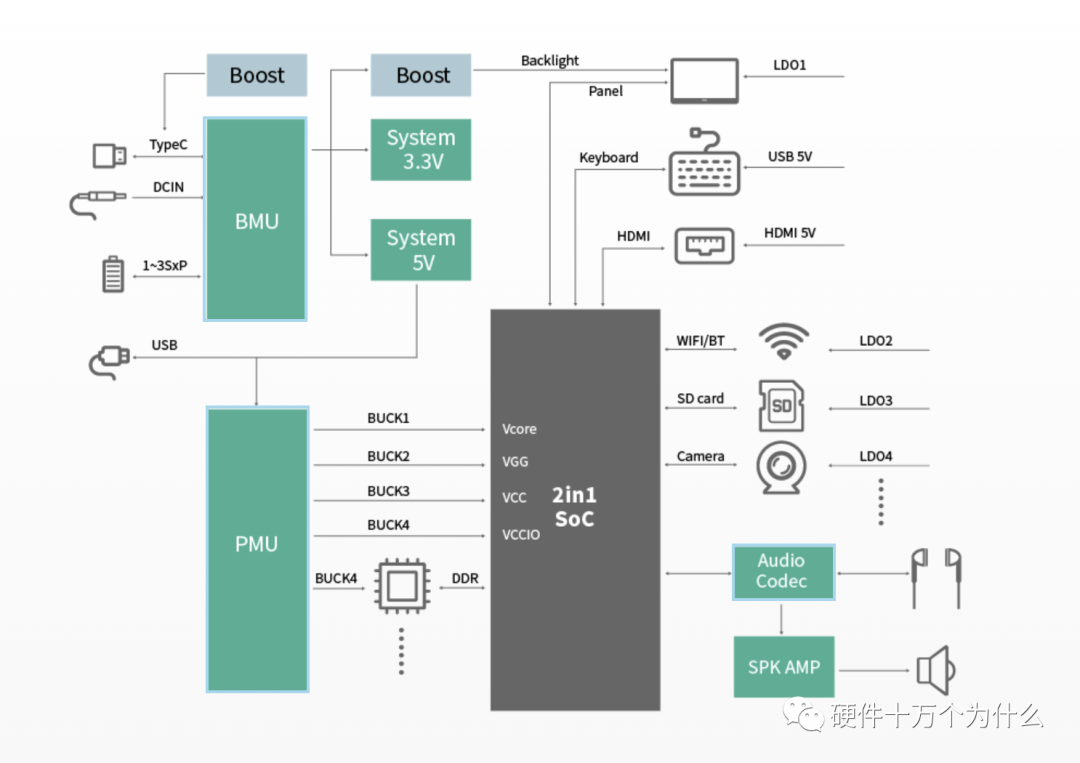
In CPU systems, we often use PMICs. For instance, in set-top box design, smart voice speaker design, large industrial control equipment design, etc.
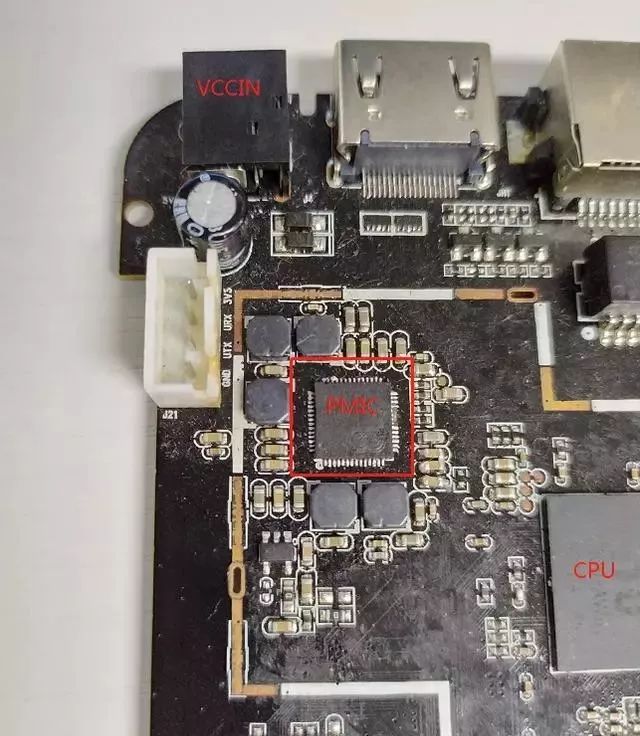

PMIC in Set-Top Boxes
Modern electronic devices often require multiple voltage and current levels to meet the needs of various electronic components. These components may operate at different voltages within the same device, necessitating an effective power management system to coordinate and distribute electrical energy. Additionally, electronic devices often need to dynamically adjust power voltage and current across different operational modes (such as standby, active, sleep, etc.) to enhance efficiency and extend battery life.
Some basic functions of PMIC include:
Power Management: PMIC is responsible for distributing electrical energy to different parts of the device to meet the power requirements of various modules.
Voltage Regulation: PMIC can adjust output voltage to accommodate different loads and operational modes.
Current Regulation: PMIC can also adjust output current to satisfy different load requirements.
Battery Management: For devices powered by batteries, PMIC is responsible for battery charging, protection, and status monitoring.
Clock Generation: PMIC can also provide the clock signals required by the device to synchronize the operations of various modules.
2. Examples of PMIC Chips
The power management chips mainly include the AXP series, which consists of AXP152, AXP155, AXP192, AXP228, AXP288, AXP2402, AXP2585, AXP2601, and AXP15060. The AXP series chips are widely used in tablet computers, 2-in-1 tablets, TV boxes, dash cams, action DV, wireless storage devices, smart hardware, handheld payment terminals, e-readers, and micro projectors.
Chipone has specialized multi-power solutions for tablet computers.
AXP15060 supports 23-channel power output, including 6 switching power supplies and numerous LDOs.
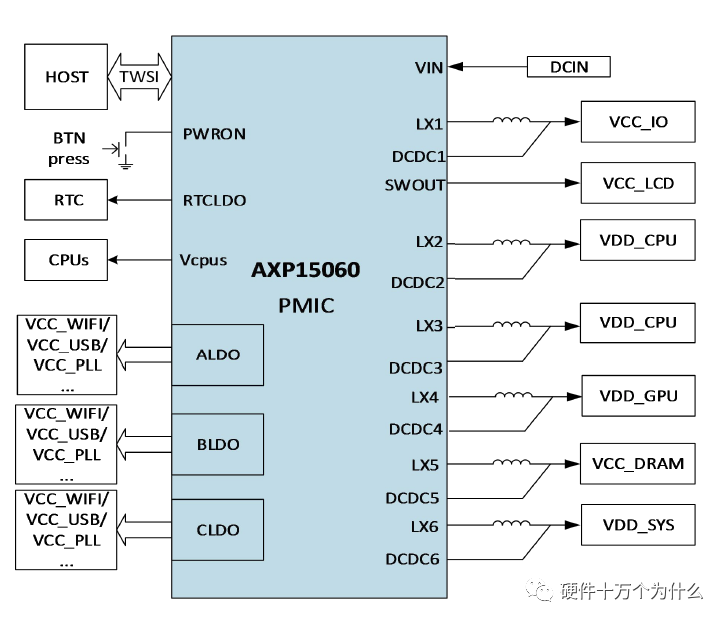
A chip that solves multiple problems, through such a product combination, is highly cost-effective and integrated:
-
High Integration: AXP15060 integrates various functional modules, including battery charging management, power management, battery protection, and system monitoring, achieving a highly integrated design in a compact space, which helps simplify circuit board layout and reduce system size.
-
Efficient Battery Charging: Supports various battery charging modes, including constant current charging and constant voltage charging, allowing selection of the appropriate charging mode based on battery type and requirements, improving charging efficiency and extending battery life.
-
Multiple Power Outputs: AXP15060 provides multiple independent power output channels, including fixed voltage outputs and programmable voltage outputs, meeting the power needs of different devices and providing flexible power supply solutions.
-
Battery Protection Features: Integrates various battery protection features, such as overcurrent protection, overtemperature protection, and over-discharge protection, effectively ensuring battery safety and prolonging battery life.
-
System Monitoring: Built-in system monitoring functions can monitor battery status, input voltage, output voltage, and other key parameters in real-time, providing feedback and ensuring system stability.
-
Low Power Design: AXP15060 adopts advanced low-power design, helping to reduce overall system power consumption and improve battery life, suitable for portable devices with high power consumption requirements.
Overall, AXP15060, as a highly integrated and feature-rich PMIC, provides reliable power management solutions for portable electronic devices, characterized by efficient charging, multiple power outputs, battery protection, and system monitoring, suitable for the design and application of various mobile devices.
Hard Ten has developed an evaluation board based on AXP15060, and will provide a review later.
AXP152 is a highly integrated PMIC from Chipone, primarily used in digital cameras, set-top boxes, network devices, monitoring equipment, and other products.AXP152 integrates an adaptive and USB-compatible PWM charger, four buck converters (Buck DC-DC converters), and seven LDOs.It also features protection circuits such as overvoltage/undervoltage protection (OVP/UVP), overtemperature protection, and overcurrent protection (OCP), ensuring the safety and stability of the power system.
The package of AXP152 is a 5×5 40-pin QFN package. As shown below.
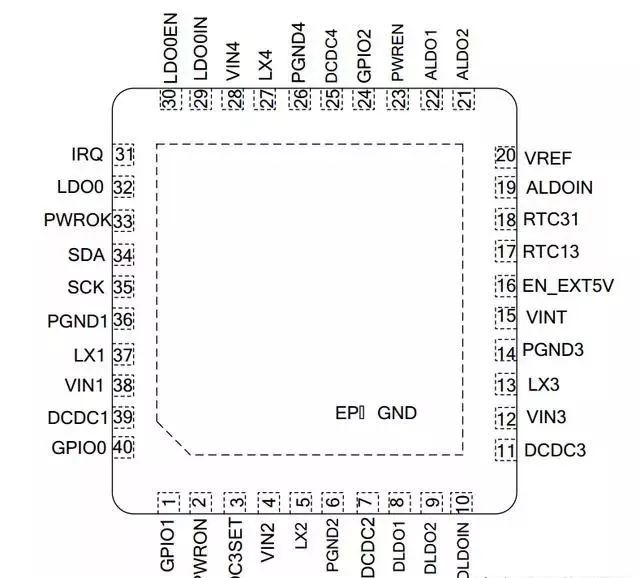
Additionally, AXP152 includes a two-wire serial interface (TWSI), allowing the CPU to enable/disable certain power outputs and program voltages to reduce power consumption, thereby providing more comprehensive power management.
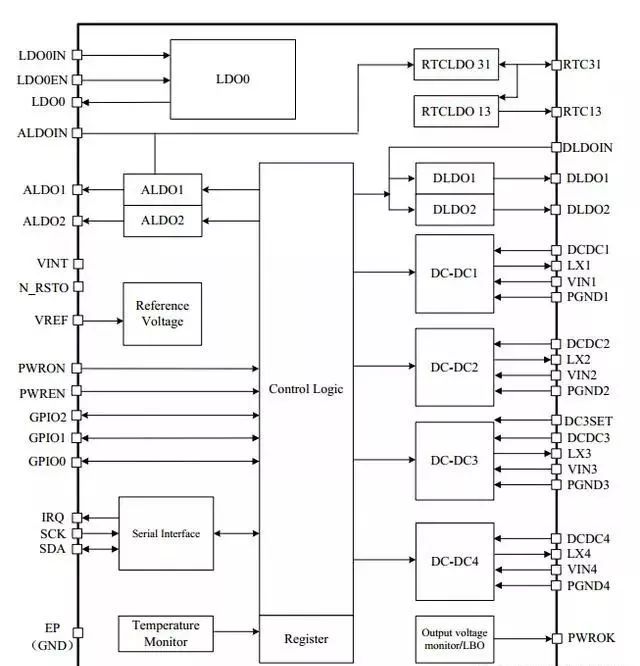
Internal Block Diagram of AXP152
From the structure diagram above, we can see that PMIC has a large logic control unit, with all DC-DC and most LDOs controlled by the logic module, and can control the output of DC-DC and LDOs by configuring the TWSI interface and changing the corresponding configuration registers. The configuration manual for the registers can be referenced in the datasheet.
Additionally, the SCK/SDA pins of the TWSI interface in AXP152 are already pulled up internally, allowing the master device (CPU) to flexibly monitor and configure through this interface.
The following diagram compares the outputs of four DC-DC converters.
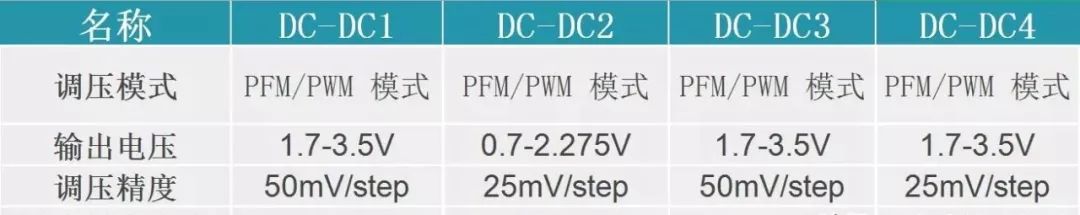
Four DC-DC Outputs
It can be seen that the output voltages of the four DC-DC converters are adjustable, with an adjustable range from 0.7 to 3.5V, meeting the power supply requirements of most minimal systems. For example, the CPU power supply is 3.3V, EMMC requires 3.3V or 1.8V, and DDR requires 1.25 to 1.35V. All these DC-DC converters can meet these requirements.
The voltage adjustment accuracy of DC-DC1 and 3 is 50mV/step, while that of DC-DC2 and 4 is 25mV/step. If the system requires higher voltage precision adjustment, the DC-DC with 25mV/step precision can be used.
The following diagram compares the outputs of seven LDOs.
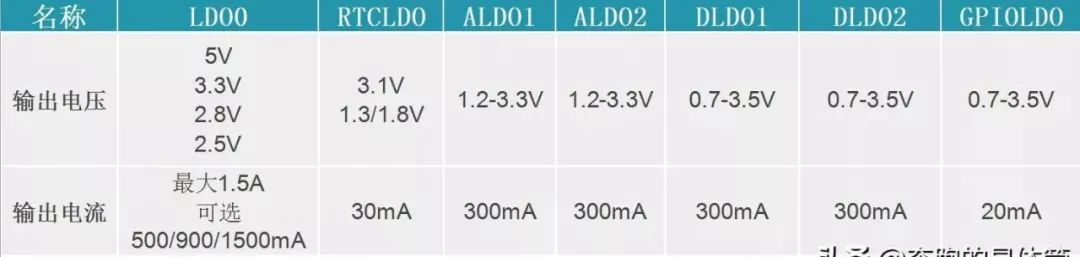
Seven LDO Outputs
These seven LDOs generally supply power to the system’s peripherals, such as powering SRAM or PLL, WiFi and Bluetooth modules, control circuits, driving circuits, sensors, and peripheral interfaces. The output voltage ranges from 0.7V to 5V, and when using them, the output current capacity should be considered. If the PMIC’s LDO cannot meet the power requirements of peripherals with relatively high power consumption, an external DC-DC or LDO should be connected to provide power.
Among these LDOs, ALDO1/2 and GPIOLDO are low-noise LDOs, and the analog circuits should be powered by these low-noise LDOs.
All DC-DC and LDOs support self-monitoring and current limiting functions. When the load current exceeds the driving capacity, to protect the internal circuits, all output voltages will be reduced. When the DC-DC output voltage drops below 85% of the set voltage, the PMIC will automatically shut down.
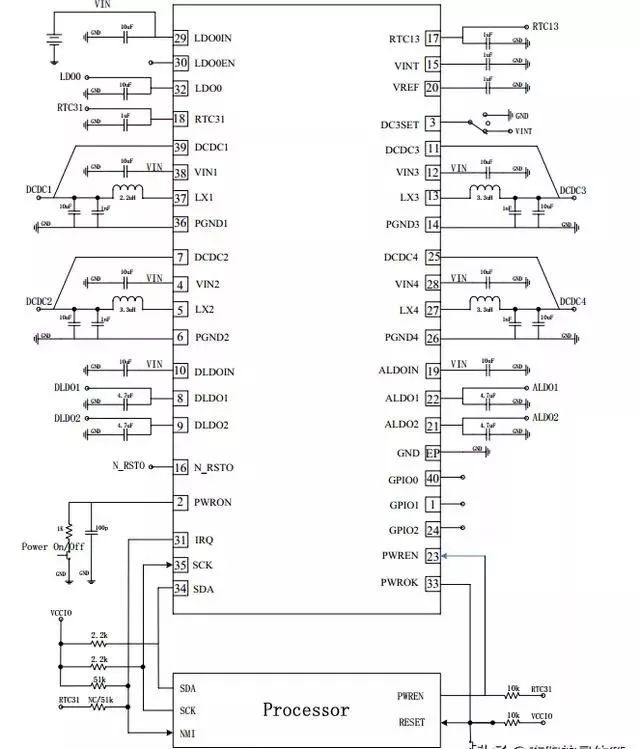
Application Block Diagram
In applications, we connect the TWSI interface of AXP152 to the CPU’s I2C interface, and also need to provide enable and reset signals. It can be seen that for each DC-DC converter, it only needs to be treated as discrete DC-DC converters for configuration.
It is recommended to use a 10uF X7R low ESR ceramic capacitor for output capacitance. When the output voltage exceeds 2.5V, it is recommended to use a 3.3uH power inductor. Additionally, the saturation current of the inductor should be more than 50% greater than the maximum current demand of the circuit.
3. Future Trends of PMIC
PMIC technology is continuously evolving and innovating to meet the growing demands of the electronic market. Here are some future trends in the PMIC field:
1. Higher Integration
Future PMICs will further enhance integration, incorporating more functions into a single chip to reduce size, improve efficiency, and simplify design.
2. Higher Efficiency
As the importance of energy efficiency continues to grow, PMICs will continue to provide higher efficiency power management, reducing energy waste.
3. Increased Power Density
PMICs will provide higher power density without increasing size to meet the demands of high-performance devices.
4. Smarter Power Management
Future PMICs will leverage advanced digital signal processing and algorithms for smarter power management.
For procurement needs, technical support, or business inquiries related to Chipone PMICs,
please contact Manager Deng from Shenzhen Hard Ten.
