Special Review: Mobile Edge Computing
[Preface] According to statistics from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, China has built the world’s largest and technologically advanced 5G network. By the end of 2023, the number of mobile phone users in China reached 1.727 billion, with 5G mobile phone users numbering 800 million. The total number of 5G base stations in China reached 3.377 million, further consolidating the network foundation and continuously enriching network applications. The large-scale commercial use of 5G has not only enhanced user communication capabilities and service quality but has also further promoted rapid growth in network traffic. According to the “Ericsson Mobile Market Report” prediction, global mobile data traffic is expected to increase from 33 EB per month at the end of 2019 to 164 EB per month by 2025. In response to the global trend of 5G development, academia and industry have begun exploring next-generation mobile communication systems. Against this backdrop, Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) is particularly important. It is not only a key technology to address future mobile communication challenges but also a core pillar for building intelligent and efficient network environments. As an extension of centralized cloud computing, MEC servers are typically deployed near resource-constrained nodes, possessing powerful storage and processing capabilities. They can bridge applications and services between cloud computing and end users, transferring the computing and storage resources needed by users to the network edge, thereby maximizing resource utilization and optimizing resource allocation for services. This addresses the challenges posed by the explosive growth of network transmission demands that traditional data processing models cannot meet. However, despite the significant advantages of MEC in terms of latency, energy consumption, security, and user experience quality, it still faces many challenges during implementation. The article “Research Review of Mobile Edge Computing for Future Mobile Communications” reviews the development history and basic concepts of MEC, summarizing the current domestic and international research progress from four aspects: computation offloading, resource allocation, cache management, and security protection. It introduces potential application scenarios of MEC in next-generation mobile communications and discusses the challenges and future development trends it faces in future mobile communication research.
Research Review of Mobile Edge Computing for Future Mobile Communications
Yang Shouyi1, Chen Yihang1, Zhang Shuangling2, Han Haojin1, Li Guangyuan3, Hao Wanming1
1. Zhengzhou University, School of Electrical and Information Engineering; 2. Henan University of Light Industry, Department of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering; 3. Yellow River Science and Technology College, Faculty of Engineering
Click “Read Original” at the end of the article to view the references!
Table of Contents
01
Abstract
02
Chart Appreciation
03
Cite This Article
04
Author Introduction
Abstract
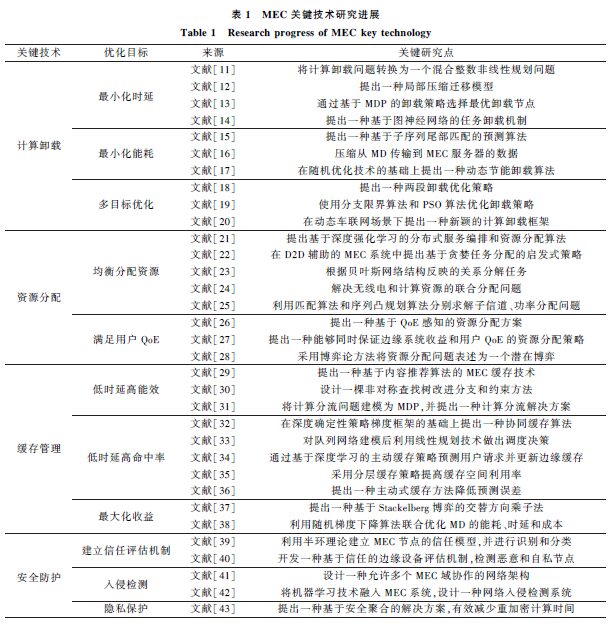
As an emerging computing paradigm, Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) can offload computing and storage tasks generated by mobile devices from centralized data centers to the network edge. It features low latency and high security, meeting the diverse service needs of complex communication scenarios, and has become one of the key technologies for future communications. As an extension of centralized cloud computing, as shown in Figure 1, MEC servers are typically deployed near resource-constrained nodes, possessing strong storage and processing capabilities. They can bridge applications and services between cloud computing and end users, transferring the computing and storage resources needed by users to the network edge, thereby maximizing resource utilization and optimizing resource allocation for services. This addresses the challenges posed by the explosive growth of network transmission demands that traditional data processing models cannot meet.
This article discusses the development history from cloud computing, fog computing to mobile edge computing, introduces the basic concepts and frameworks of MEC technology; based on this, it discusses the research progress of MEC from four aspects: computation offloading, resource allocation, cache management, and security protection, providing a detailed review of relevant research results. Furthermore, as shown in Figure 2, typical application scenarios of edge computing, such as the combination of the Internet of Things, blockchain with MEC, AI-assisted MEC systems, integrated sensing and computing, and cloud-edge collaboration, are summarized to illustrate the potential benefits of mobile edge computing in creating intelligent, efficient, and secure communication networks, as well as its advantages and development trends in ultra-reliable low-latency communication, integrated sensing and computing, and satellite-ground integrated mobile communication. Finally, challenges faced by MEC research in terms of interoperability, security risks, mobility management, and scalability are pointed out, and the future development trends of MEC in mobile communications are summarized and forecasted.
Chart Appreciation
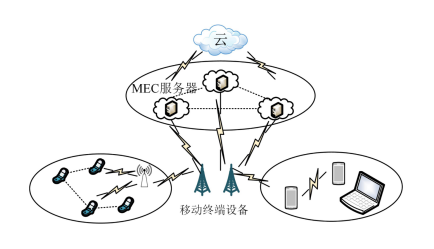
Figure 1: Basic Three-Layer Architecture of MEC
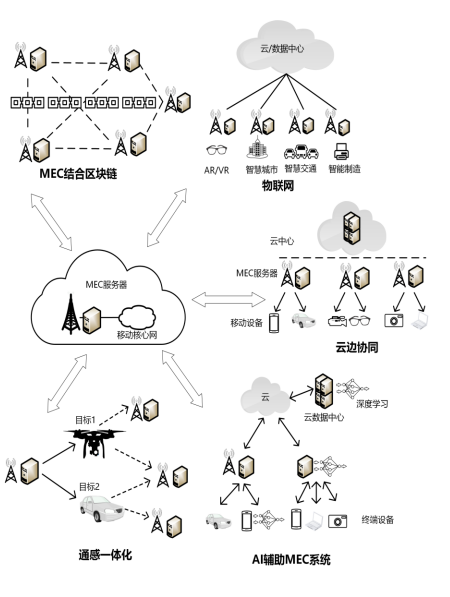
Figure 2: Application Scenarios of MEC
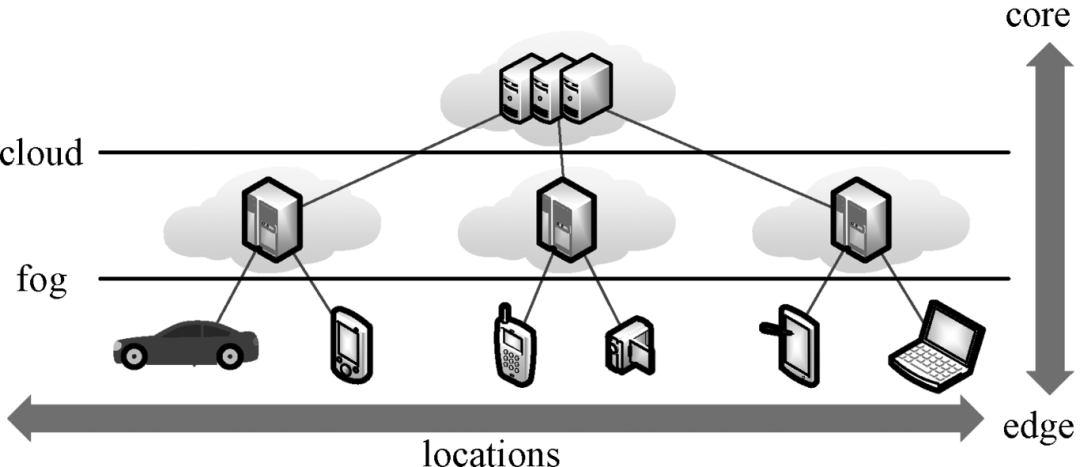
Figure 3: Fog Computing between Cloud and Edge Devices
Figure 1: Fog Computing between Cloud and Edge Devices
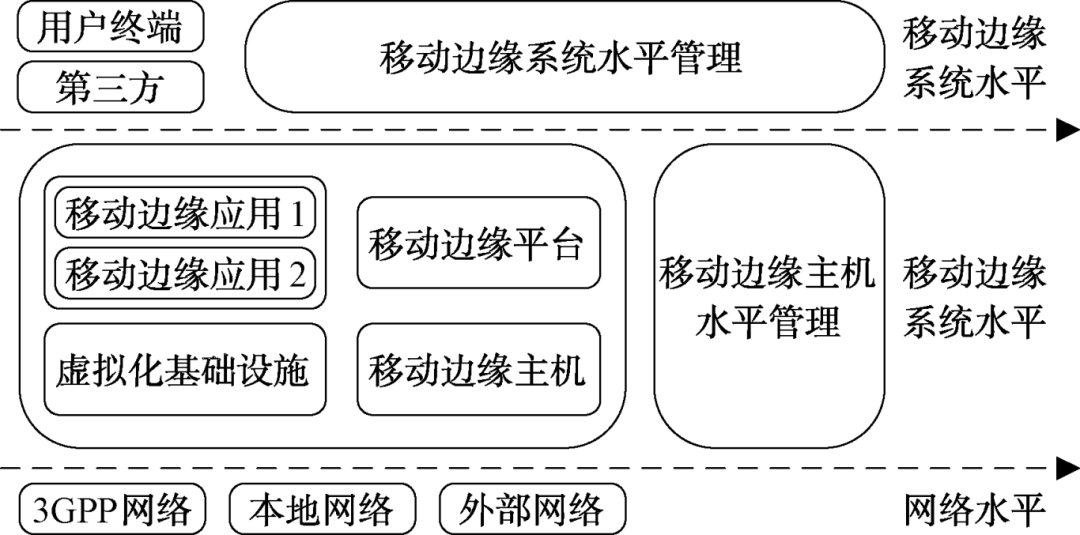
Figure 4: Basic Architecture of MEC
Figure 2: Basic Architecture of MEC
Cite This Article
Yang Shouyi, Chen Yihang, Zhang Shuangling, et al. Research of mobile edge computing for future mobile communications: a review [J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), 2024, 45(4):1-10, 29.
YANG S Y, CHEN Y H, ZHANG S L, et al. Research of mobile edge computing for future communications: a review [J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), 2024, 45(4):1-10, 29.
Author Introduction
Professor and doctoral supervisor at the School of Electrical and Information Engineering, Zhengzhou University; Director of the Communication Engineering Department; Academic and Technical Leader of Henan Province.
Main Research and Teaching Experience: Obtained a Ph.D. from Beijing Institute of Technology in 2003, visiting scholar at Mie University, Japan. Engaged in scientific research and teaching in wireless mobile communications and mobile cloud computing for a long time. Representative articles: “Green Communication for NOMA-Based CRAN”, “Small Cell Cluster-Based Resource Allocation for Wireless Backhaul in Two-Tier Heterogeneous Networks with Massive MIMO”, etc.
Research Projects: National Natural Science Foundation General Project, No. 20476044, Research on Fractional Fourier Transform Multi-Component Image Digital Watermarking; National Natural Science Foundation Henan Provincial Joint Fund, No. U1604159, Research on Multi-Master User Cognitive Access Multi-Objective Optimization and Intelligent Cloud Offloading; National Key Research and Development Program “Intergovernmental National Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation” Key Special Project, No. 2016YFE0118400, Research on High-Performance Deep Ultraviolet Lasers Based on Nitride Semiconductors.
✦
Contact Information for Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science):
Submission Website:http://gxb.zzu.edu.cn
WeChat Official Account: zdxbgxb
Contact Email: [email protected]
Contact Number: 0371-67781276
Contact Number: 0371-67781277
For more exciting content, please follow us

Copyright Statement:
This article is an original content of the editorial department of the Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science), and reproduction is welcome!
