Mijia BLE Mesh devices are divided into version 1.0, which is based on the MHCB05P module, and version 2.0, which is based on the MHCB12G module. The main differences are that Mijia BLE Mesh 2.0 supports gateway remote upgrades, consistent scenes, second-level network configuration, ultra-low power consumption, and other capabilities, providing a better experience. However, these capabilities require a central gateway to be used and are backward compatible with version 1.0.This article mainly introduces the development of Mijia BLE Mesh 1.0, and subsequent articles will cover the development and considerations related to version 2.0.1. Developer Platform DevelopmentThe platform development section skips the basic configuration and focuses on function definition and plugin development.1.1 Function DefinitionAfter creating a Mesh product, you need to select a solution related to the product definition. If no solution is available, it indicates that the current category does not support BLE Mesh access, and a work order must be submitted to request the addition of the Mesh category.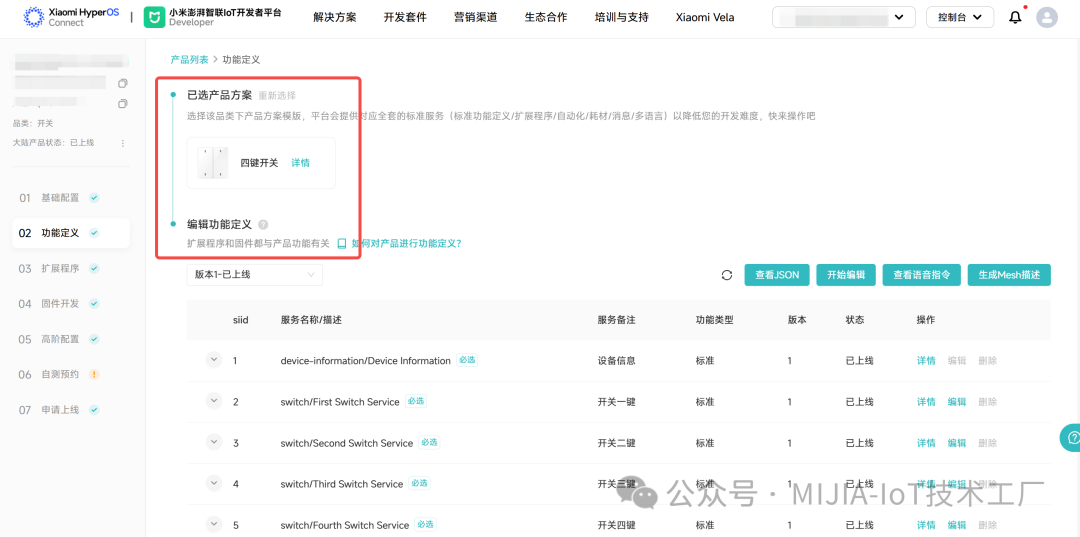 Clicking “Generate Mesh Description” allows you to see the mapping relationship between function definitions and Mesh. If model_id only contains038F0000, it indicates that the current device’s function definition supports the cloud template. The firmware side must enable the correct template macro; otherwise, the device will be uncontrollable after network configuration.
Clicking “Generate Mesh Description” allows you to see the mapping relationship between function definitions and Mesh. If model_id only contains038F0000, it indicates that the current device’s function definition supports the cloud template. The firmware side must enable the correct template macro; otherwise, the device will be uncontrollable after network configuration.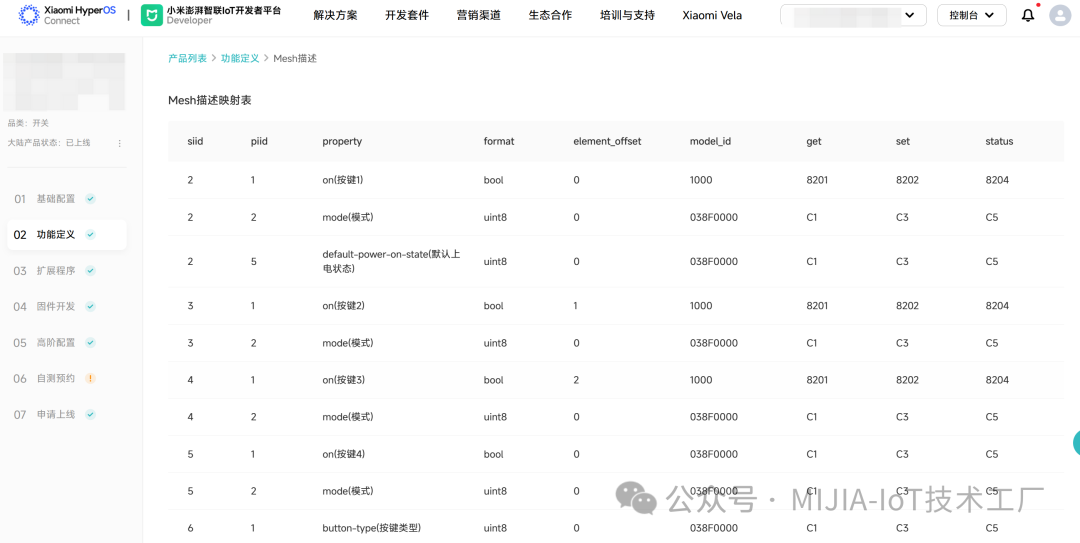 1.2 Extension Program DevelopmentThere are two modes for extension program development: standard development and custom development.
1.2 Extension Program DevelopmentThere are two modes for extension program development: standard development and custom development.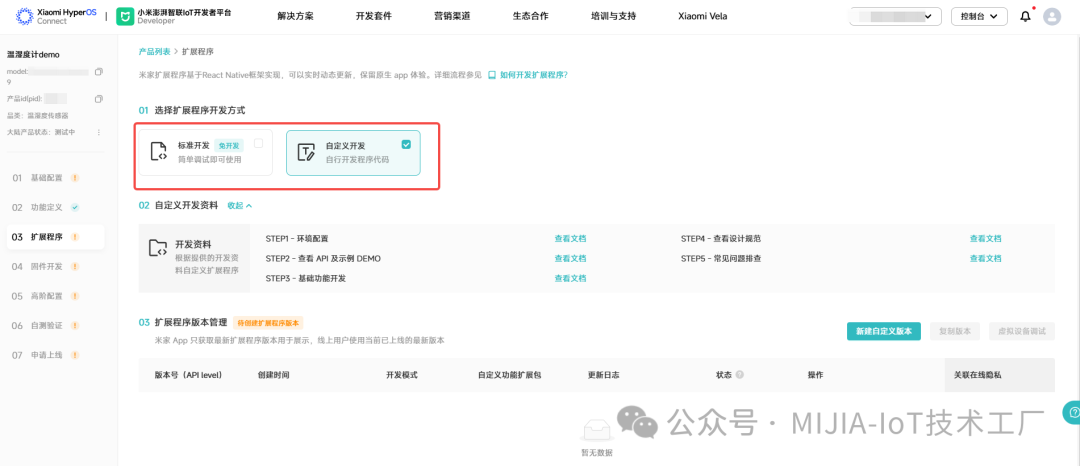 Standard development refers to the programs developed by Xiaomi for product categories, which can be loaded through the Mijia App after selection. The extension program will automatically load related functions based on the standard function definition. Custom development refers to freely developing related UI and functions based on the Xiaomi extension program SDK, which offers higher flexibility but requires certain technical capabilities from enterprise developers. Currently, Mijia BLE Mesh supports many standard plugins for various categories, and most of them support both GATT direct communication and BLE Mesh communication, significantly reducing development workload.2. Embedded Software Development2.1 Basic ConfigurationDefine firmware version and other information in the custom_mi_config.h file:
Standard development refers to the programs developed by Xiaomi for product categories, which can be loaded through the Mijia App after selection. The extension program will automatically load related functions based on the standard function definition. Custom development refers to freely developing related UI and functions based on the Xiaomi extension program SDK, which offers higher flexibility but requires certain technical capabilities from enterprise developers. Currently, Mijia BLE Mesh supports many standard plugins for various categories, and most of them support both GATT direct communication and BLE Mesh communication, significantly reducing development workload.2. Embedded Software Development2.1 Basic ConfigurationDefine firmware version and other information in the custom_mi_config.h file:
#define DEVELOPER_VERSION 0160 //Version number#define MI_MESH_ENABLED 1//Enable mesh#define MI_MANU_TEST_ENABLE 0//Enable module production testing capability, usually needs to be enabled when the module firmware is burned by Xiaomi factory2.2 Network Configuration Binding2.2.1 Macro DefinitionsDefine device pid, model, and template in the product_info.h file. The template macro must refer to the device function definition for correct selection; incorrect configuration may lead to communication anomalies, such as some attributes being communicable while others are not.
//Product pid, a unique id for a product on the platform, can be viewed in the device page at the bottom left under "Basic Information"#define PRODUCT_ID 2716 // xiaomi BLE devboard#define MODEL_NAME "isa.switch.kg02hl"//#define MI_MESH_TEMPLATE_LIGHTNESS//#define MI_MESH_TEMPLATE_LIGHTCTL//#define MI_MESH_TEMPLATE_ONE_KEY_SWITCH#define MI_MESH_TEMPLATE_TWO_KEY_SWITCH //Dual-key switch template//#define MI_MESH_TEMPLATE_THREE_KEY_SWITCH//#define MI_MESH_TEMPLATE_FAN//#define MI_MESH_TEMPLATE_CLOUD2.2.2 Callback Events
The device network status switch will ultimately call back in the user_state_process function:
void user_state_process(schd_evt_t *p_event){ switch(event){ case MIBLE_USER_PROV_CB_TYPE_UNPROV:// Device unconfigured break; case MIBLE_USER_PROV_CB_TYPE_PROVED:// Device configured break; case MIBLE_USER_PROV_CB_TYPE_START:// Device starts configuration break; case MIBLE_USER_PROV_CB_TYPE_COMPLETE:// Device configuration complete break; case MIBLE_USER_PROV_CB_TYPE_FAIL:// Device configuration failed break; case MIBLE_USER_PROV_CB_TYPE_RESET:// Device reset remotely (app-gateway-device) break; case MIBLE_USER_GAP_CB_CONNECTED: // Device direct connection successful break; case MIBLE_USER_GAP_CB_DISCONNECTED:// Device disconnected break; default:break; }}2.2.3 API
Network configuration-related interfaces are declared in the miio_user_api.h file:
// Set broadcast timeout, after timeout, it will broadcast, parameter 0 will immediately close broadcaststatic inline int miio_ble_set_adv_timeout(uint32_t timeout)// Reset device and restore static inline int miio_system_restore(void)The Mijia App discovers devices based on the broadcast content of the device, so when a device is not found, it is necessary to confirm whether the device is sending broadcasts normally.
2.3 Communication Control
2.3.1 Gateway Mesh Communication
Reported through the gateway interface declared in the miio_user_api.h file:
//Property periodic pub table initialization, maximum 10 (including template properties), unnecessary properties are not recommended to add to the periodic tablestatic inline int miio_mesh_properties_period_publish_init(uint16_t siid, uint16_t piid, uint32_t period)// Property report, usually this interface limits 25 calls every 10 minutes, but properties added to the periodic pub table are not limitedstatic inline int miio_mesh_properties_changed(uint16_t siid, uint16_t piid, property_value_t *newValue)// Event reportstatic inline int miio_mesh_event_occurred(uint16_t siid, uint16_t eiid, arguments_t *newArgs)// Request server information: includes timezone, weather, UTC timestatic inline int miio_mesh_request_property(uint8_t type)// Mesh message receiving registration function issued by the gateway, including set_properties, get_properties, actionstatic inline int miio_mesh_user_callback_register(property_operation_callback_t set_cb, property_operation_callback_t get_cb, action_operation_callback_t action_cb, mible_user_event_cb_t user_event_cb)Data reporting interfaces can only be called after the device network configuration binding. It is important to note that Mesh devices should not send data indiscriminately; keep it concise to prevent network storms.
2.3.2 GATT Direct Connection Spec Communication
The direct connection communication interface is declared in the miio_user_api.h file:
// Direct connection spec communication initialization. set_cb, get_cb, action_cb are direct connection spec operation callback functions. The buflen represents the buffer length required by the firmware side when the plugin gets multiple attributes at once. Assuming the plugin retrieves a maximum of 5 attributes at once, it is recommended that buflen ≥6 (header consumption) + 5*12 (attribute content) + 6 (encryption header) = 72. If there are string type attributes, the length of the string attribute value should be added to this base, for example, if the numeric string length is 10, then buflen ≥82static inline int miio_gatt_spec_init(property_operation_callback_t set_cb, property_operation_callback_t get_cb, action_operation_callback_t action_cb, uint16_t buflen)// During direct connection, the device actively reports properties to the mobile pluginstatic inline int miio_gatt_properties_changed(uint16_t siid, uint16_t piid, property_value_t *newValue)// During direct connection, the device actively reports properties to the mobile pluginstatic inline int miio_gatt_properties_changed(uint16_t siid, uint16_t piid, property_value_t *newValue)The direct connection status between the device and the mobile will call back to the user_state_process function:
void user_state_process(schd_evt_t *p_event){ switch(event){ case MIBLE_USER_GAP_CB_CONNECTED: // Device direct connection successful break; case MIBLE_USER_GAP_CB_DISCONNECTED:// Device disconnected break; default:break; }}Before the device and mobile perform direct connection communication, login authentication must be completed, and the authentication callback is the mi_schd_event_handler function:
void mi_schd_event_handler(schd_evt_t *p_event){ switch (p_event->id) { case SCHD_EVT_ADMIN_LOGIN_SUCCESS : // Direct connection login successful break; case SCHD_EVT_ADMIN_LOGIN_FAILED : // Direct connection login failed break; default:break; }}2.3.3 Direct Connection Spec Communication
The direct connection communication interface is declared in the miio_user_api.h file:
// Direct connection spec communication initialization. set_cb, get_cb, action_cb are direct connection spec operation callback functions. The buflen represents the buffer length required by the firmware side when the plugin gets multiple attributes at once. Assuming the plugin retrieves a maximum of 5 attributes at once, it is recommended that buflen ≥6 (header consumption) + 5*12 (attribute content) + 6 (encryption header) = 72. If there are string type attributes, the length of the string attribute value should be added to this base, for example, if the numeric string length is 10, then buflen ≥82static inline int miio_gatt_spec_init(property_operation_callback_t set_cb, property_operation_callback_t get_cb, action_operation_callback_t action_cb, uint16_t buflen)// During direct connection, the device actively reports properties to the mobile pluginstatic inline int miio_gatt_property_changed(uint16_t siid, uint16_t piid, property_value_t *newValue)// During direct connection, the device actively reports multiple properties to the mobile pluginstatic inline int miio_gatt_properties_changed(uint8_t nums, properties_t *newProps)// During direct connection, the device actively reports events to the mobile pluginstatic inline int miio_gatt_event_occurred(uint16_t siid, uint16_t eiid, arguments_t *newArgs)2.4 OTA
The module’s own upgrade function SDK has integrated support, and the firmware side can enable the USE_MIBLE_OTA macro (which is enabled by default). The corresponding upgrade status callback function is app_dfu_callback.
static void app_dfu_callback(mible_dfu_state_t state, mible_dfu_param_t *param){ switch (state) { case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_START: MI_LOG_INFO("fragment size is %d\n", param->start.fragment_size); break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_UPGRADE_STATUS: MI_LOG_INFO("upgrade status is %x\n", param->upgrade_status.req); param->upgrade_status.rsp = param->upgrade_status.req; break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_TRANSFER: MI_LOG_INFO("last fragment index is %d\n", param->trans.last_index); break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_VERIFY: MI_LOG_INFO("verify result is %d\n", param->verify.value); break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_SWITCH: MI_LOG_INFO("switch to new firmware\n"); break; case MIBLE_DFU_STATE_CANCEL: MI_LOG_INFO("the sequence is canceled\n"); break; default: MI_LOG_INFO("state of DFU is unknown %d\n", state); break; }}When uploading firmware to the developer platform, it is essential to strictly follow the platform documentation for each step to ensure everything is normal. If the chip/module log shows <span>Not found TAG HEAD(MAGIC NUM)</span>, it indicates that there is a problem with the firmware upload/configuration. Common reasons include: wild versions (the current firmware version of the device has not been uploaded to the platform firmware list), version disorder, and not configuring the minimum version that supports signature and https.
3. Extension Program Development
3.1 Direct Connection Communication
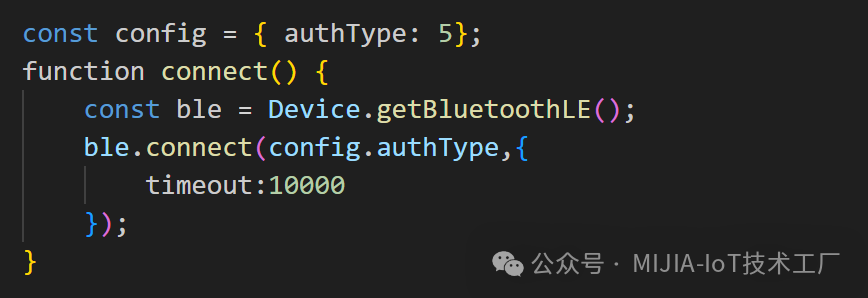
Direct connection communication can refer to the extension program development section in the “Mijia BLE Device Development Guide”. It is important to change authType to 5.
| type | Description |
| -1 | Automatic judgment, Android does not support |
| 0 |
Ordinary Xiaomi Bluetooth protocol device |
| 1 |
Xiaomi Bluetooth device with security chip (e.g., lock products) |
| 2 | Shared security chip Xiaomi Bluetooth device |
| 3 |
Ordinary BLE Bluetooth device (no mibeacon, no Xiaomi FE95 service) |
| 4 | Standard Auth standard Bluetooth authentication protocol |
| 5 | Mesh device |
| 6 | Shared lock device |
3.2 Mesh Communication
The extension program can remotely control BLE Mesh devices through downlink commands issued by the gateway, and the usage method is exactly the same as that of Wi-Fi devices. It can also obtain attribute value caches and historical records of attribute/event reports.
3.2.1 Bluetooth Gateway Connection
After the device successfully connects to the gateway, the extension program can obtain the attribute values of the BLE Mesh device and execute methods. BLE/BLE Mesh devices can actively report attribute values and events. The “successful connection” mentioned here does not refer to the successful direct Bluetooth connection between the device and the gateway, but rather that the gateway has scanned the broadcasts emitted by the device.
The following code can be used to determine whether the device has been scanned by the Bluetooth gateway:
import React, { Component } from 'react';import { Device, DeviceEvent, Bluetooth } from 'miot';import { View } from 'react-native';import logger from '../../logger.js';class GatewayComponent extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { connected: false }; } async isGatewayConnected() { const { isOwner, isOnline, mac } = Device; if (!isOwner) { return Promise.resolve(isOnline); } try { const gatewayStatus = await Bluetooth.isBleOrMeshGatewayConnected( mac, true ); const gatewayConnected = gatewayStatus?.code === 0 && gatewayStatus?.data?.connected; return Promise.resolve(!!gatewayConnected); } catch (err) { logger.e('Update gateway connection status err: ', err); return Promise.resolve(false); } } updateStatus() { this.isGatewayConnected().then((connected) => { this.setState({ connected }); }); } componentDidMount() { this.updateStatus(); this.listener = DeviceEvent.deviceStatusChanged.addListener(() => { this.updateStatus(); }); } componentWillUnmount() { this.listener && this.listener.remove && this.listener.remove(); } render() { return <View />; }}3.2.2 Signal Strength Scanned by the Gateway
export function getRssi() { Bluetooth.getBtGateWaySubDeviceRSSI(Device.mac).then((res) => { logger.i('RSSI : ', res?.data?.RSSI); }).catch((err) => { // Device offline or mobile without network connection logger.e('getBtGateWaySubDeviceRSSI error: ', err); }); }3.3 Firmware Upgrade
Since the firmware version of BLE Mesh (1.0) devices depends on the mobile connection to read and report to the cloud, the SDK’s firmware upgrade detection behavior occurs after the extension program and device direct connection is successful. Therefore, it is necessary to attempt to connect to the device every time the extension program enters the device upgrade page to ensure that the SDK’s firmware upgrade detection can be triggered.
Code should be added to the index.js in the project root directory:
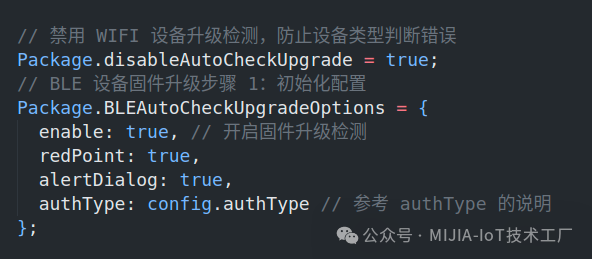
Configure the extraOptions property of the CommonSetting component:
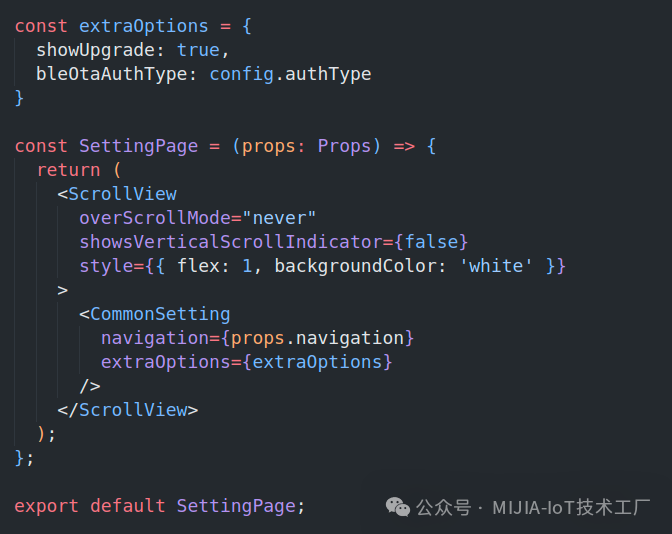 4. ConclusionAlthough Mijia BLE Mesh 1.0 has provided a relatively complete development system and interface support, attention must still be paid to details during actual development, such as the correct selection of function templates, reasonable simplification of communication data, and accuracy in firmware upload configuration, to ensure the stability and reliability of device development. Future developments related to Mijia BLE Mesh 2.0 will also bring more features and challenges for developers, and we look forward to further exploration and sharing. If you have any questions about this article, feel free to leave a comment for discussion!!!
4. ConclusionAlthough Mijia BLE Mesh 1.0 has provided a relatively complete development system and interface support, attention must still be paid to details during actual development, such as the correct selection of function templates, reasonable simplification of communication data, and accuracy in firmware upload configuration, to ensure the stability and reliability of device development. Future developments related to Mijia BLE Mesh 2.0 will also bring more features and challenges for developers, and we look forward to further exploration and sharing. If you have any questions about this article, feel free to leave a comment for discussion!!!




