
Recently graduated friends, do you find hardware and programming daunting? However, with the right approach, these can be easily mastered. Today, I will share how university graduates from non-electronic information majors can easily understand hardware and quickly learn Arduino programming to engage in IoT in the future.
Easy Learning of Hardware Basics
Many people are intimidated by hardware, thinking that electronic components and circuit knowledge are complex and difficult to understand. In fact, as long as you grasp the basics, you can open the door to the world of hardware.
Understanding Common Electronic Components

Start by getting to know common electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which are the basic building blocks of hardware. You don’t need to delve into their complex principles right away; just understand their general functions. For example, resistors can adjust current levels, and capacitors can store and release charge. There are many interesting educational videos online, such as those from hardware science creators on Bilibili, which use vivid animations to demonstrate the working principles of electronic components, making them easy to understand.
Learning Basic Circuit Knowledge
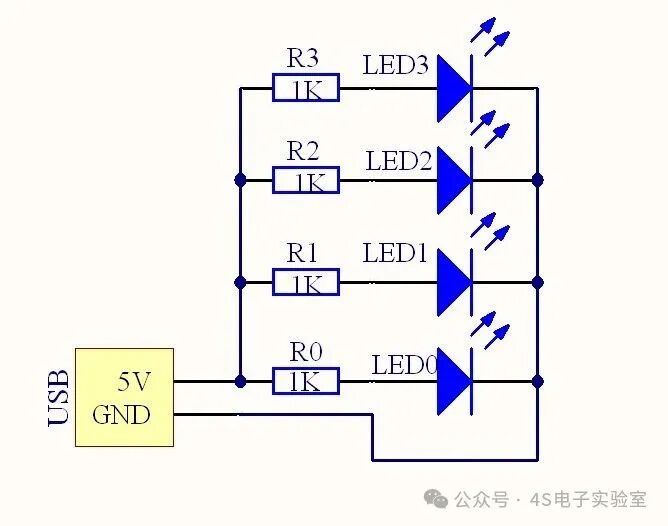
Series and parallel circuits are the fundamentals. Understand the direction of current flow in circuits and how different circuit connections affect voltage and current. You can use a breadboard and some simple electronic components to build circuits yourself. For example, create a simple series circuit to light up several LEDs, experiencing the mysteries of circuits through practice. This not only deepens your understanding of the knowledge but also provides a sense of accomplishment. Websites like “Circuit Kid” offer many basic circuit experiment tutorials and online simulators, allowing you to familiarize yourself with circuit building in a virtual environment before hands-on practice.
Familiarizing with Hardware Development Tools

Tools like multimeters and oscilloscopes may seem professional, but they are not difficult to operate. A multimeter can measure voltage, current, and resistance, while an oscilloscope can display the waveform of electrical signals. Find some related operation tutorials, and after a few practical attempts, you will master the basic functions. Many university laboratories have these tools, so if you have the opportunity, you can attend lab classes to learn hands-on under the guidance of instructors.
Quickly Getting Started with Arduino Programming
Arduino, as an open-source electronics platform, is very beginner-friendly, allowing even those without programming backgrounds to quickly get started.
Understanding Arduino Development Boards

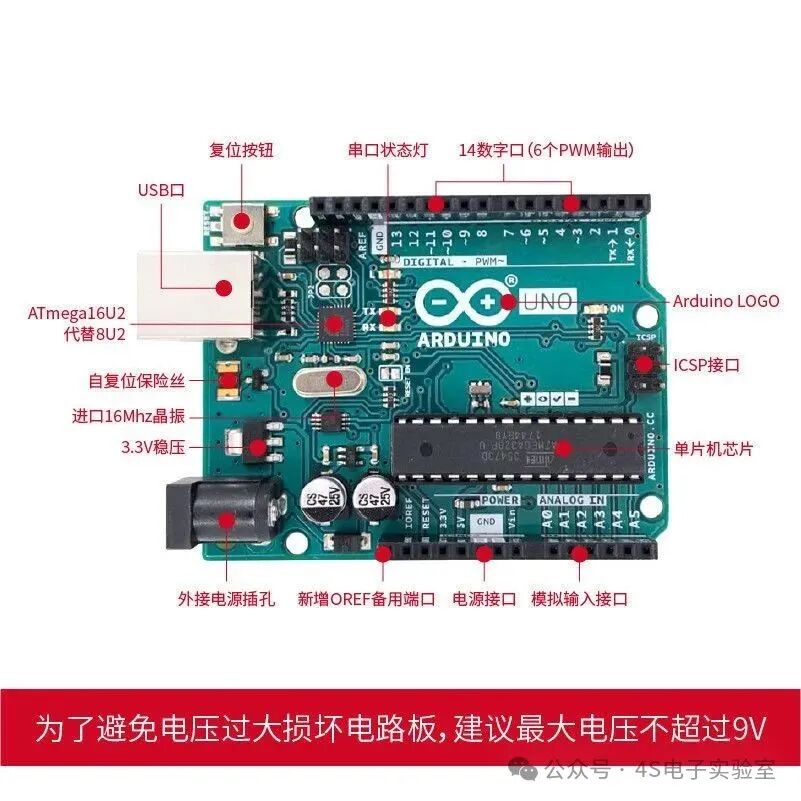
Arduino has various development boards, such as Arduino Uno and Arduino Nano. Each board has its characteristics and suitable scenarios; for instance, Uno is suitable for beginners, while Nano is more compact, suitable for projects with size constraints. Visit the official Arduino website for detailed introductions to understand their hardware parameters and interface functions. You can also purchase development board kits on platforms like Taobao, which usually come with basic tutorials and experimental materials for easier learning.
Installing Arduino IDE

Arduino IDE is the main tool for writing and uploading code, and the installation process is straightforward. Download the installation package for your system version from the Arduino Chinese community and follow the prompts to install it step by step. After installation, open the IDE and familiarize yourself with the interface layout, including the code editing area, compile button, upload button, etc.
Learning Basic Programming Syntax
Arduino uses C++ language, so start by mastering some basic syntax, such as variable definitions, control structures (if – else, for loops, while loops), and functions. There is no need to memorize everything; understanding through practical examples will be faster. For instance, the code to control an LED to blink:

int led = 13; // Define the pin connected to the LED
void setup() {
pinMode(led, OUTPUT); // Set the pin to output mode
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(led, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
delay(1000); // Delay for 1 second
digitalWrite(led, LOW); // Turn off the LED
delay(1000); // Delay for 1 second
}
This code is easy to understand; by setting the pin mode and controlling the pin output high and low, it achieves the periodic blinking of the LED. Doing more similar small experiments will gradually familiarize you with the syntax.
Practice Projects to Gain Experience

Start with simple projects, such as using a button to control the LED’s on and off, or creating a simple temperature alarm (using a temperature sensor). When you encounter problems in practice, don’t panic; this is a great learning opportunity. Search for solutions on Arduino forums or technical communities, and exchange experiences with other enthusiasts; you will find yourself progressing rapidly.
Learning Tips
1. Set a Learning Plan: Arrange your time reasonably, dedicating 1-2 hours each day to study, maintaining continuity in learning. You can start with hardware basics, then move on to Arduino programming, gradually deepening your knowledge. For example, focus on electronic components and basic circuits in the first week, and start exploring Arduino development boards and IDE in the second week.
2. Join a Study Group: Find like-minded friends on social media to form a study group. Everyone can supervise each other, share learning insights, and discuss solutions to problems together, creating a strong learning atmosphere and improving efficiency.
3. Participate in Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer many high-quality hardware and Arduino programming courses, some of which are free. Learning at the pace of professional instructors can help you avoid many detours.

Recently graduated friends, do not be intimidated by the “high-end” nature of hardware and programming. As long as you have interest and patience, and follow these methods step by step, you will find that you can easily master hardware and Arduino programming, opening a new door to the world of technology, and perhaps even uncovering your hidden skills, providing more options for your future career development!