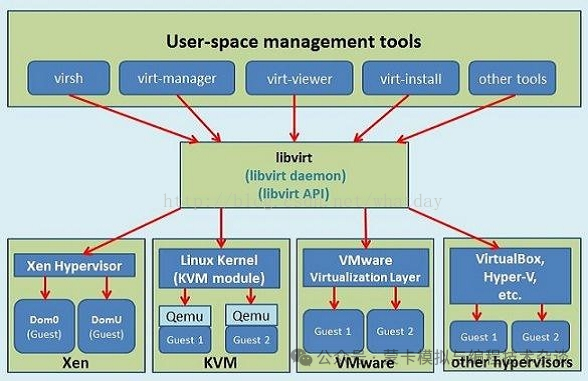
1. KVM + QEMU + libvirt Stack
- KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine)
- is a Linux kernel module that allows user-space programs to access hardware virtualization features of various processors.
- It enables the kernel to function as a hypervisor.
- KVM itself does not simulate hardware but delegates these tasks to higher-level client applications like QEMU.
- QEMU (Quick Emulator)
- provides various hardware and device models, supporting emulation for multiple architectures.
- It can boot various guest operating systems.
- libvirt
- is a library for managing virtualization technologies such as KVM, Xen, VMware ESXi, QEMU, etc.
- virt-manager
- is a tool built using libvirt, included in many Linux distributions.
- kubevirt
- brings virtual machines into Kubernetes (k8s).
- It is based on libvirt + QEMU + KVM.
2. Managing Virtual Machines from the Command Line
(1) Listing Virtual Machines
- Each virtual machine started by
<span>qemu-system-x86_64</span>corresponds to a process on the host machine. - Therefore, listing the
<span>qemu-system-x86_64</span>processes will provide the list of currently running virtual machines on the host. - Use the command:
$ ps -ef | grep qemu-system-x86_64 - Or:
$ ps -ef | grep qemu-kvm - These commands will display detailed information about the
<span>qemu-system-x86_64</span>processes, including the process ID (pid) and the parameters used to start the virtual machine.
(2) Creating a Virtual Machine
- Use the
<span>qemu-system-x86_64</span>command to emulate the Intel x86 64-bit architecture. - Command format:
$ qemu-system-x86_64
3. Checking if KVM is Enabled
- Use the
<span>kvm-ok</span>command to check if KVM is enabled. - For Intel CPUs:
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep vmx - For AMD CPUs:
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep svm <span>vmx</span>indicates Virtual Machine Extensions.<span>svm</span>indicates Secure Virtual Machine.- Check if the
<span>/dev/kvm</span>device exists:$ ls /dev/kvm - Check if KVM-related modules are loaded in the kernel:
$ lsmod | grep kvm - If
<span>kvm-ok</span>is not installed, it can be obtained by installing<span>cpu-checker</span>:$ sudo apt install cpu-checker - If the
<span>kvm-ok</span>command is not available, you can check in the following ways: - Check if the CPU supports virtualization:
4. Enabling KVM
- If KVM is not running, ensure that virtualization is enabled in the BIOS:
- AMD: SVM (Secure Virtual Machine)
- Intel: Virtualization Technology
- IOMMU (Input–Output Memory Management Unit)
5. Installing QEMU
- On Debian/Ubuntu systems:
- Install the packages related to QEMU:
$ sudo apt install qemu-utils qemu-system-x86 qemu-system-gui
Web link:https://www.hackingnote.com/en/virtualization/kvm/