


Introduction to Python

1. Variable Assignment
(1) Single Variable Assignment
Use the equal sign (=) to assign a value to a variable, where the left side is the variable name and the right side is the variable’s value.
(2) Multiple Variable Assignment
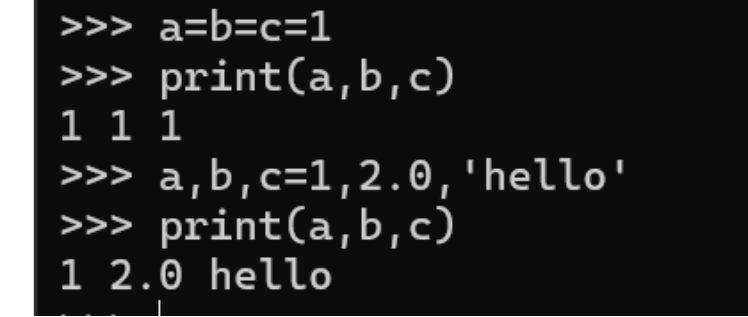

2. Numeric Types
1. Types
(1) Integer (int): whole numbers.
(2) Float (float): decimal numbers.
(3) Boolean (bool): has only two values, 1 for True and 0 for False.
2. Calculations with Numeric Types
(1) Operators
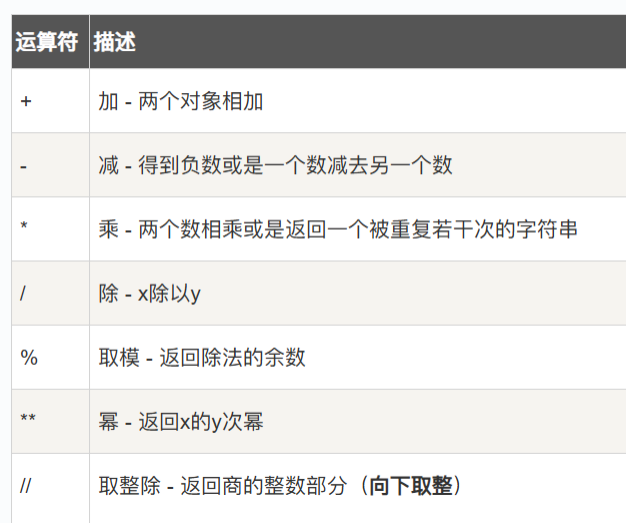
For example:

Note: In Python, Boolean values True and False can directly participate in calculations as 1 and 0.

3. Strings
(1) Definition: In Python, a string (String) is a basic data type used to store and represent text information. A string is composed of a series of characters, which can be letters, numbers, punctuation, or other symbols.
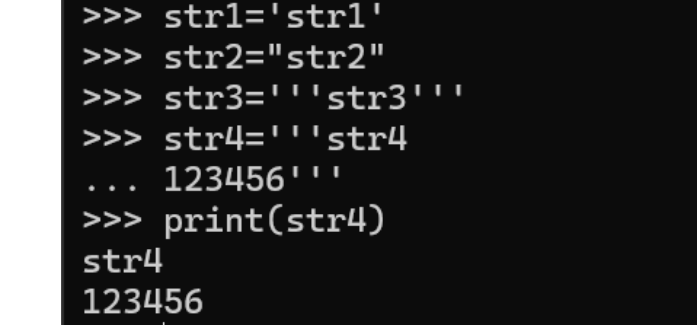
Note: In Python, strings can be defined using single quotes (”), double quotes (“”), or triple quotes (”’ or “””), but only triple quotes can span multiple lines.
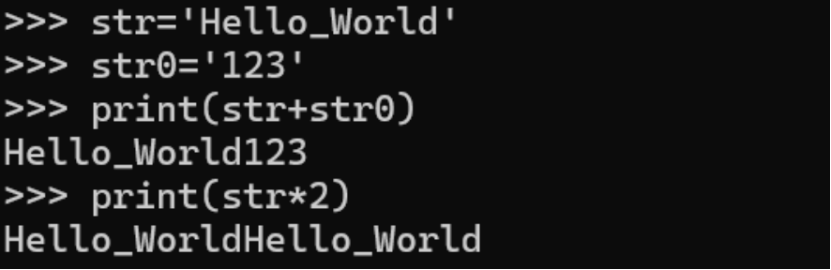
(2) String Addition and Multiplication
Addition: concatenation of strings;
Multiplication: repetition of strings.
END

Mission Statement——To share cutting-edge knowledge in medical artificial intelligence, build a platform for interdisciplinary research, collaboration, and application transformation. Committed to medical artificial intelligence technology, research and development, and providing comprehensive services in medical artificial intelligence.
Text and Images | Chen Haoxiang
Layout | Li Yufei
Final Review | Teacher Yang Chenglin