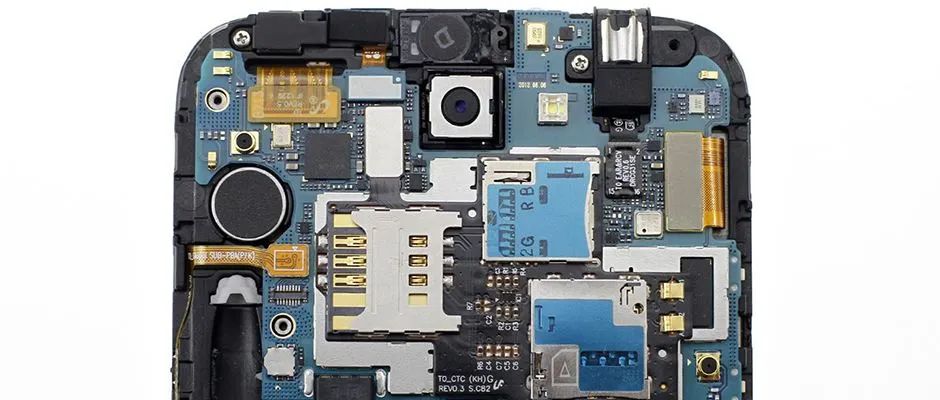
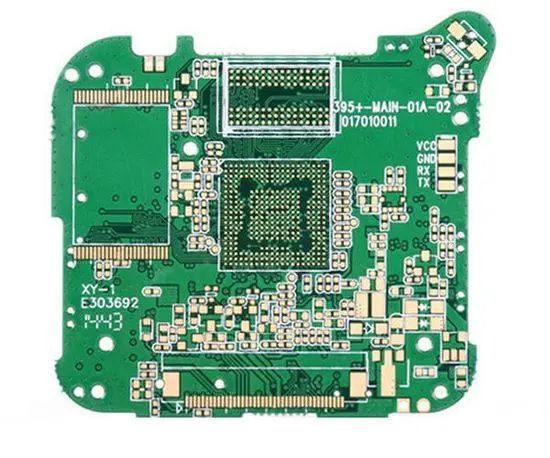
Printed circuit boards, also known as printed circuit boards, printed wiring boards, or PCBs, provide assembly support and electrical connection functions for various electronic systems, earning the title of “Mother of Electronic Products.” Currently, PCBs are widely used in the electronic product manufacturing field and are an important part of the electronic information industry.
Using electronic printing technology, copper foil covered on an insulating substrate is etched to form conductive lines that meet the connection requirements of components, thus creating a circuit board that can install and connect electronic components. Circuit boards are mainly divided into the following types:
1. Communication Boards
Communication boards refer to circuit boards used in the communication field. Communication is the most significant downstream application area for PCBs, with demand in the communication sector divided into communication equipment and communication terminals. Communication equipment includes communication base stations, transmission devices, routers, switches, fiber-to-the-home devices, etc., while communication terminals primarily refer to smartphones. The PCB demand for communication equipment focuses on multilayer boards and high-frequency high-speed boards, while the demand for communication terminals is mainly for HDI boards, flexible boards, and packaging substrates.
2. Automotive Boards
Automotive boards refer to circuit boards used in automotive electronics. Automotive electronics encompass the electronic control devices of the vehicle body and onboard electronic control devices, including engine control systems, chassis control systems, and body electronic control systems. With the development trends of electric vehicles and smart vehicles under the Internet of Things, the penetration rate of automotive electronics will further increase, and the usage of automotive PCBs will also rise. As vehicles evolve towards lightweight, miniaturization, electrification, and intelligence, the demand for automotive PCBs will gradually shift from single/double-sided boards and multilayer boards to flexible boards and HDI boards.
3. Flexible Boards
FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) refers to flexible circuit boards, which are made of PI (polyimide) or PET (polyester) film as the substrate, with lines formed by etching on copper foil, resulting in a printed circuit board that has high reliability and excellent flexibility. Due to their product characteristics, they are widely used in various electronic products.
4. Packaging Boards
Refers to IC packaging boards, which are directly used to mount chips, providing electrical connections, protection, support, heat dissipation, and assembly functions for the chips. Packaging boards act as bridges connecting chips and motherboards, playing a supporting and protective role for the chips. The manufacturing process of packaging boards requires extremely high standards, making them the gem of PCB manufacturing. As electronic products develop towards thinner, faster, and lower energy consumption, new demands are also placed on packaging boards. The main application area is chip packaging for various electronic devices.
5. HDI Boards
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) boards, also known as micro-hole boards or laminated boards, are commonly used to create high-precision circuit boards, achieving characteristics such as high density, fine wiring, and small aperture. The main application areas include smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, wearable devices, etc.