
Since the National Health Commission released the “National Standards and Specifications for Hospital Information Construction (Trial)” in 2018, a relatively complete system framework has been established for hospital information construction and the application standards of IoT technology. In 2022, the Planning Department of the National Health Commission further pointed out in the draft of the revised “Design Specification for Comprehensive Hospital Buildings” that “different types of wireless networks such as WIFI, IoT, and 5G medical private networks should be integrated and deployed” and “the basic network should have scalability to meet future system expansion needs.” The emphasis on “integration” and focus on “expansion” have further standardized the direction of smart hospital IoT construction.
Influenced by the development wave of smart hospital construction and guided by national policies, Yancheng First People’s Hospital (Children’s Hospital) has proposed the need for a medical IoT platform project. The hospital plans to achieve a smart hospital network layout through the construction of an intelligent IoT data management platform, realizing “integration” + “expansion”.
1
“Integration + Expansion”, Full-Frequency Integrated Multi-Network Medical IoT Architecture
Before starting the project, Yancheng First People’s Hospital (Children’s Hospital) conducted extensive research on domestic smart hospital projects, thus proposing clear standards for smart hospital construction. After benchmarking and evaluating different cases, they ultimately chose the “integration + expansion” design scheme for the medical IoT.
As is well known, there are currently issues with multiple protocols and non-unified standards in the IoT, with common communication protocols such as WiFi, LoRa, Bluetooth, RFID, and 5G differing in configuration parameters and usage scenarios. Different device manufacturers have varying choices for their product technologies, leading to incompatibility issues among most products. Therefore, how to achieve data interconnectivity and realize data “integration” is a key issue that needs to be addressed on the path of information construction in hospitals.

For the construction of smart hospital gateways, not only the current business needs must be considered, but also reasonable planning for future additional requirements must be made. Therefore, building the platform requires not only high compatibility and openness but also modular characteristics, where each functional module can operate independently or work together to meet the project requirements for “expansion”.
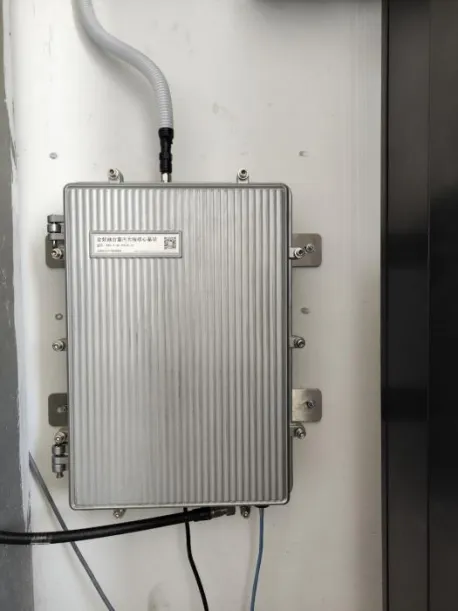
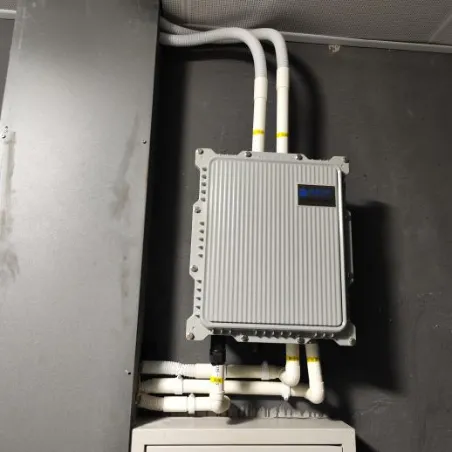



Core Base Station for Full-Frequency Integration
The full-frequency integrated multi-network solution from Jiangsu Maodu Cloud Medical Technology Co., Ltd. perfectly fits the construction needs of the aforementioned project. This platform has a wide range of applicable scenarios and supports full-frequency operation from 400MHz to 7GHz, while also possessing the access capabilities for internal networks, external networks, IoT, positioning networks, 5G private networks, and security intercom networks, truly achieving “integration”. Furthermore, full-frequency integration also supports third-party system access, allowing hospitals to connect to third-party application systems as needed. The modular design not only meets current needs but also reserves upgrade space for future planning, aligning with the project’s expected goals for “expansion”.
2
What is the Full-Frequency Integrated Multi-Network Medical IoT Platform?
Maodu Cloud Full-Frequency Integrated Medical IoT Platform consists of three core components for smart hospital construction solutions: the medical IoT integration middle platform, the full-frequency integrated antenna system architecture platform, and the medical IoT monitoring center. These provide core functions such as data collection, data integration, data governance, data services, and data asset management.
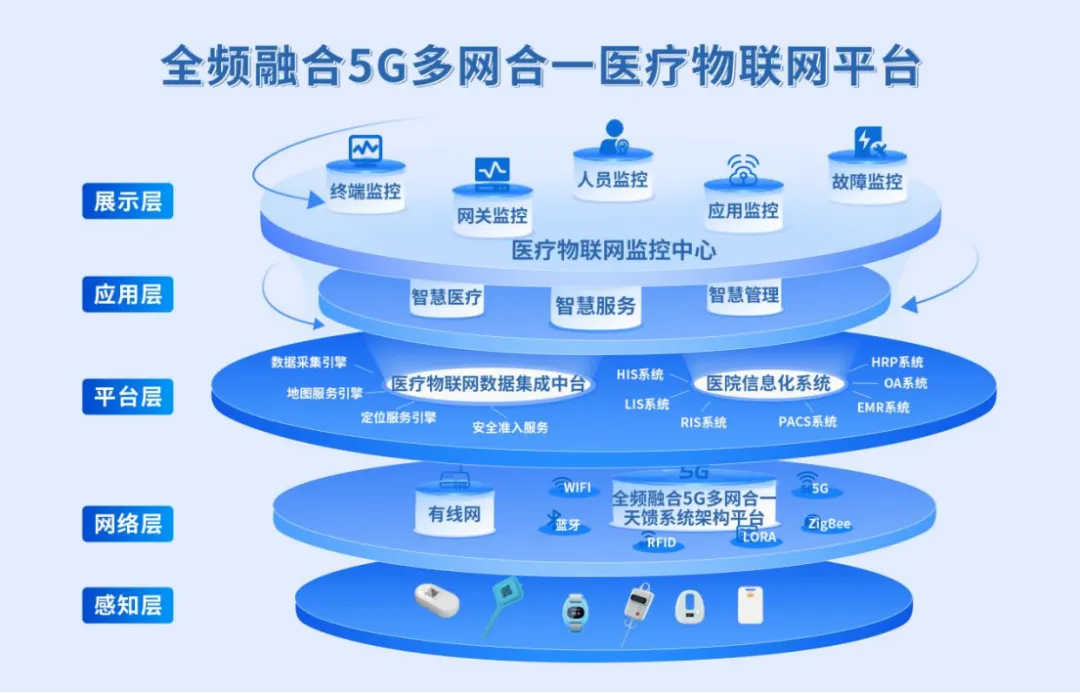
Architecture of the Full-Frequency Integrated Medical IoT Platform
The medical IoT integration middle platform includes systems such as data collection engines, map service engines, positioning service engines, and security access services, using platform adapters to achieve data access from different protocol system terminals. Through algorithm services, data is calculated, processed, stored, and forwarded, providing different data services according to the needs of various users, scenarios, and business logic, ultimately achieving interconnectivity of IoT data.
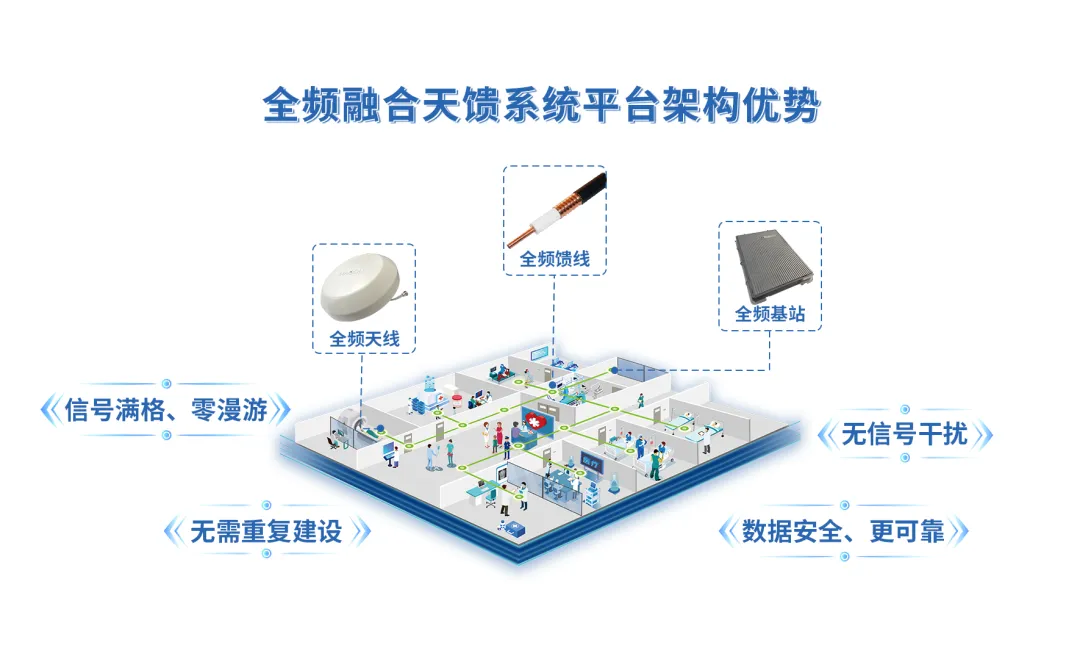
Advantages of the Full-Frequency Integrated Antenna System Platform Architecture
Compared to traditional IoT solutions, the advantage of the full-frequency integrated antenna system platform architecture lies in its ability to extend the signal of a communication module to all areas of the ward, fundamentally solving the switching problems of traditional APs, achieving full signal coverage and zero roaming. Additionally, it isolates data without signal interference through frequency and bandwidth separation; to ensure data security and reliability, it is also equipped with a dedicated security gateway to safeguard data security. Furthermore, full-frequency integration features high scalability and development potential, allowing for upgrades in the RF module without being restricted by communication protocols, supporting multiple application systems, and enabling continuous expansion, truly achieving the goal of a one-time investment without the need for repeated construction.

Full-Frequency Integrated Medical IoT Application Center
On the application layer, the full-frequency integrated medical IoT platform integrates various subsystems into the application center, focusing on “smart healthcare, smart services, and smart management,” and achieves IoT data integration through the medical IoT monitoring center, making the deployment status of each application visualized, with centralized abnormal alarms, meeting the diverse needs of hospitals, improving operational efficiency, and providing higher quality medical services for patients.
END
Source: China Digital Medicine
