FMEA is applied in hardware, and various industries have accumulated considerable practical experience and classic cases. Currently, more and more functions in complete products are implemented by software. So, how should software FMEA be conducted?
This article will explore methods to improve software quality and reliability from the perspective of software development, using the special method of software FMEA as a starting point.
01
What is FMEA?
 FMEA (Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a systematic activity that analyzes potential failure modes of subsystems and components that constitute a product, process, or service during the planning and design phase. It identifies potential failure modes, analyzes their possible consequences, assesses their risks, and takes preventive measures to reduce the severity of failure modes and lower their probability of occurrence, thereby effectively improving quality and reliability and ensuring customer satisfaction.
FMEA (Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a systematic activity that analyzes potential failure modes of subsystems and components that constitute a product, process, or service during the planning and design phase. It identifies potential failure modes, analyzes their possible consequences, assesses their risks, and takes preventive measures to reduce the severity of failure modes and lower their probability of occurrence, thereby effectively improving quality and reliability and ensuring customer satisfaction.

Types of FMEA:
Common types of FMEA based on their application fields include Design FMEA (DFMEA) and Process FMEA (PFMEA), as well as Equipment FMEA, Application FMEA, Procurement FMEA, and Service FMEA.
The AIAG & VDA FMEA Handbook released in June 2019 clearly defines it as a technical risk analysis tool, based on a risk management process (ISO 31000 defines it as risk identification, risk analysis, risk evaluation, and risk control). It employs a preventive mindset (before design begins) to systematically analyze the risks present in product and process control and to evaluate and control them systematically.
From the above, it is clear that the application of FMEA is to apply the results of FMEA development to design and design control activities to enhance the reliability of design outcomes.
To truly realize the value of FMEA, it must be understood as a complete process, which includes initiation (I), development (D), application (A), and dynamic management (A).
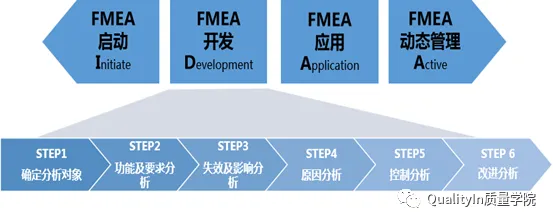
Note: The IDAA model is a practical methodology summarized by QualityIn based on years of FMEA practice and was officially proposed in 2015. Please do not plagiarize or use it for commercial purposes. For specific content about IDAA, please follow our online or offline FMEA-related courses (www.quality-in.com).
-
Initiation
This is the preparation before officially developing FMEA. The 5T (Purpose, Time, Team, Task, Tools) proposed in the AIAG & VDA FMEA Handbook is part of the preparation work for FMEA, and the first step of the seven-step method, “Planning Preparation,” is the initiation.
Of course, I believe that the planning preparation in the seven-step method is not complete, as important tasks such as collecting historical data, lessons learned, and previous FMEA results are not significantly mentioned;
-
Development
This is the critical phase of FMEA and the one that everyone is most concerned about. According to the second to sixth steps of the seven-step method, we will output an FMEA document;
-
Application
In the IDAA model, every phase is very important, but the most crucial aspect is not the development of FMEA, but its application. This means applying the results of FMEA development to the design and design control processes, whether for product design or process design.
-
Dynamic Management
This involves updating the FMEA with the analysis results of issues that occur after mass production, including failure modes, causes, and control measures, etc. This can also be understood as the reverse FMEA we often refer to, which should strictly be considered a form of FMEA application and is an important means of continuously accumulating organizational knowledge and experience.
Complete video course “PFMEA Process Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis“
Course duration: 2 hours and 40 minutes
Course price: 169 yuan (PLUS members 50% off)
180 days course validity
▼▼▼

02
Software Development Quality Control Toolbox!

When it comes to software development quality control, it is easy to associate it with concepts like Agile Development, ASPICE, etc. If we broaden our thinking and do not limit ourselves to existing frameworks like CMMI, there are various tools for quality control and improvement in software development, such as:
-
Expert Experience: Relying on the experience of core experts to comprehensively control the rationality of design schemes and testing processes, thereby controlling the entire design.
-
System Promotion: This is often discussed and encompasses various standardized methodologies, such as various levels of reviews, testing systems, and the establishment and analysis of failure databases. FMEA is also one of them.
-
Management Supervision: From a results-oriented perspective, assessing the progress and quality of software products to promote the improvement of software development quality.
Different products and markets, as well as different team characteristics, require flexible adoption of various solutions. Of course, the solutions are not mutually exclusive, and I believe every software team has a tool combination that suits its characteristics.
03
How to Conduct FMEA in Embedded Software?

1. Necessity
Software FMEA is a relatively special topic. When discussing FMEA, the subjects being examined often involve systems, hardware, or production processes, while software seems less common. Although there are various systems and audits for software quality control, FMEA is often not a mandatory requirement.
However, this relatively niche method holds unique value in the automotive industry’s software development. Based on personal experience, here are some special factors that illustrate its importance in the automotive sector:
● System Integration: Software in the automotive industry must work within a complete system, so it cannot be examined in isolation. For example, when designing drivers, factors such as potential voltage fluctuations and temperature changes in the vehicle must be considered. Only by examining software design from a system perspective can a more comprehensive view be provided.
● Software-Hardware Collaboration: Software behavior needs to be closely integrated with hardware and may be affected by batch consistency. For instance, software needs to communicate with a peripheral device via SPI; while individual sample tests may pass multiple times, occasional failures in a batch can still occur, which cannot affect customer experience.
● Reliability and Maintainability: There are high overall requirements for reliability and maintainability, and issues such as function loss or system restarts can significantly impact customers. Some failure conditions related to reliability may be difficult to foresee or simulate during the R&D phase. Although maintainability is not significantly related to FMEA, it is often overlooked in regular software reviews.
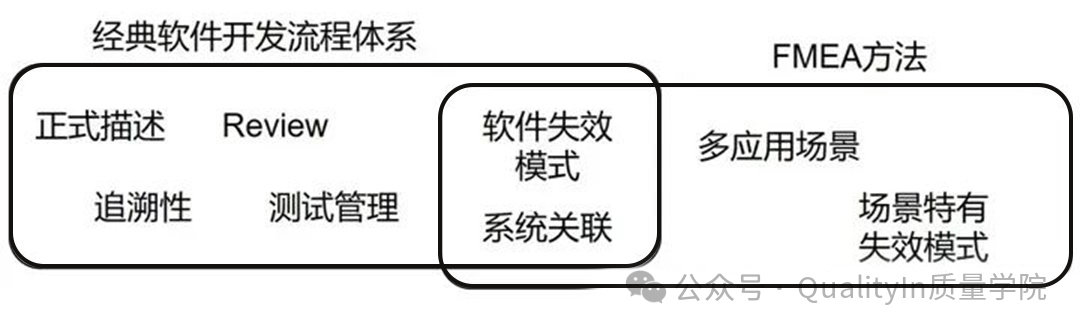
By comparing classic software quality control toolboxes, we can find that while expert experience or management supervision methods can comprehensively cover various issues, classic frameworks like ASPICE focus relatively less on the special factors mentioned above.
Software FMEA, with its inherent system perspective, focus on the interconnections between links, and ability to adjust measurement standards (such as maintainability and attention levels), has become a practical and effective tool in automotive software design. The value of this method should not be overlooked; rather, it should be emphasized and promoted as an important component of software quality control.
2. Boundaries and Methods
Of course, while software FMEA is a powerful tool, it must be wisely selected in terms of scope and focus in practical applications. Not every subsystem design requires a round of FMEA analysis, nor does every part of software design need to be fully examined.
Here are some understandings based on personal experience regarding the applicable scope and key focus of software FMEA.
Applicable Scope: Complex subsystems that combine software and hardware
● Checking coding-level errors under the FMEA framework requires significant investment with minimal output; this is the strength of tools like ASPICE;
● The FMEA framework is more suitable for conceptual/systematic/failure mode-oriented checks. The inspection target is the functionality achieved by the software product, not the software itself.
Failure modes are a significant feature of software FMEA
● It is necessary to consider the impact of failures on software: for example, while system FMEA focuses on the impact of crystal oscillator deviations, software FMEA needs to consider whether frequency changes within the deviation range can be tolerated by each module.
● It is necessary to consider software-specific failure types: for example, timing issues, resource contention, data consistency, etc. These software-specific failure types may receive special attention in software FMEA, while they may be overlooked in system FMEA.
● Special consideration for the convenience of failure localization: The time taken for software failure handling and updates should not be ignored, so “Is the failure easy to locate quickly?” is a high-value function that can save a lot of manpower and resources later on if considered in advance.
Classic software processes and different focus areas of FMEA:
The quality and reliability design of software development is a comprehensive topic, and the pursuit of this should be ensured from the design phase, rather than relying solely on testing. Various tools and methods can support the R&D process; although the software FMEA method is less mentioned, it holds special significance.
The content of this article is sourced from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact for removal.
One More Thing
On April 23rd at 8 PM, QualityIn will host a live sessionto interpret the “New Version of CP Control Plan”. After learning, you may have a new perspective and attitude towards CP!👉 There will be no replay of the live session, so please make an appointment in advance.Welcome companies to learn in groups~

Make an appointment for tonight at 8 PM (this Tuesday) for the live session
▼▼▼