Research Background
Research Content
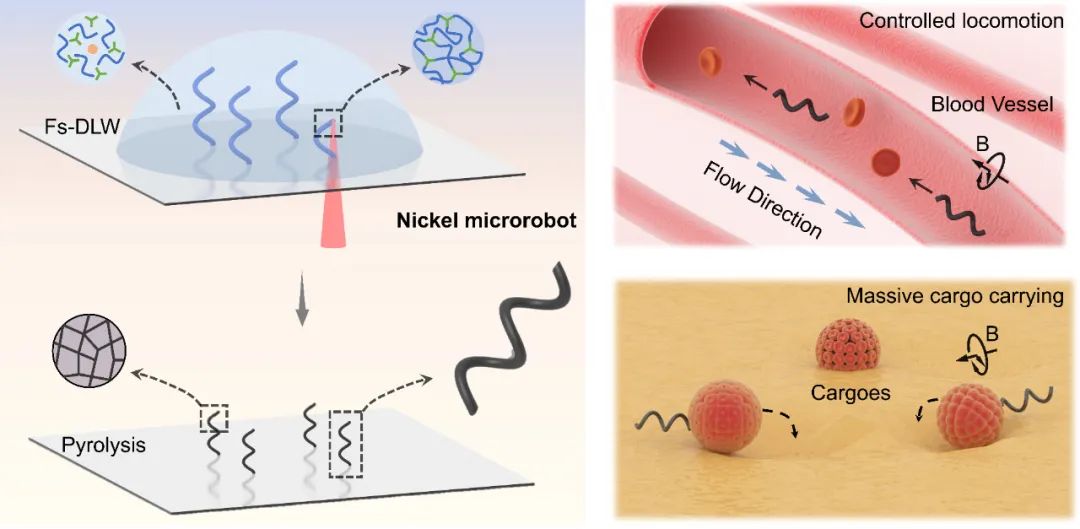
Recently, Associate Professor Jiawen Li from the University of Science and Technology of China led a research team to prepare a metal microrobot (Ni-MAR) with high magnetic content (~90 wt%) by combining femtosecond laser two-photon processing with high-temperature sintering. This microrobot exhibits strong driving torque in a magnetic field, enabling it to achieve reversible movement in fluids and targeted delivery of objects weighing 200 times its own weight.
-
Figure 1. Preparation of the metal microrobot and its reversible movement in fluid and targeted delivery of heavy objects.

Paper Information
-
High-performance magnetic metal microrobot prepared by a two-photon polymerization and sintering method
Rui Li‡, Modong Jiang ‡, Bingrui Liu, Shaojun Jiang, Chao Chen, Mengxue Liang, Lijie Qu, Chaowei Wang, Gang Zhao, Yanlei Hu, Dong Wu, Jiaru Chu and Jiawen Li*(Jiawen Li, University of Science and Technology of China)
Lab Chip, 2024,24,832-842 https://doi.org/10.1039/D3LC01084H
Author Information

First author of this paper, graduated from the University of Science and Technology of China in 2022, obtaining a PhD degree. Research direction: Micro-nano additive manufacturing of inorganic functional materials (metals/ceramics).

Co-first author of this paper, undergraduate student of the 2017 class and PhD student of the 2021 class at the University of Science and Technology of China, researching micro-nano 3D printing technology of high-entropy inorganic materials and new mechanical metamaterials.

Jiawen LiAssociate Professor
Corresponding author, research direction includes efficient processing technology with femtosecond laser, design and fabrication of micro-nano functional devices, design of new photopolymer materials, and preparation methods for 3D metamaterials.
Related Journals

rsc.li/loc
Lab Chip
| 2-Year Impact Factor* | 6.1 points |
| 5-Year Impact Factor* | 6.9 points |
| Highest JCR Quartile* | Q1 Instruments |
| CiteScore† | 11.3 points |
| Median Peer Review Time‡ | 39 days |
Lab on a Chip reports on miniaturization research at the micro and nano scales, aiming to publish original work that is highly impactful in both physical technology (micromachining, flow control, system integration, analytical separation techniques, etc.) and application potential. The journal places the highest importance on the innovation of the papers, which usually need to innovate in both of the following aspects: (i) the physics, engineering, and materials of miniaturized devices; (ii) applications in biology, chemistry, environmental science, food science, medicine, energy, etc.
-
Aaron Wheeler🇨🇦 University of Toronto
Associate Editors
|
|

