Click the blue text above to follow the "Green Learning Platform"
1.1 Recognizing Robots Again
1.2 Security Robot Scheme Design
1.3 Security Robot Production Practice
2.1 Urban Construction Robots
2.2 Safety and Fire Robots
2.3 Fall Rescue Robots
3.1 Identify Projects and Plan Robot Schemes
3.2 Practical Operation and Implementation of Robot Projects
3.3 Evaluation and Communication to Showcase Robot Achievements








|
Lesson Topic |
Lesson1 “Recognizing Robots Again” |
Unit |
Unit One |
Subject |
Information Technology |
Grade |
Grade 9 |
|
Learning Objectives |
Knowledge and Skills: 1. Understand the basic components and working principles of robots. 2. Understand common control development platforms and programming environments for educational robots in primary and secondary schools.
Process and Method: Through learning, understand the basic components and working principles of robots; through group inquiry learning, understand common control development platforms and programming environments for educational robots in primary and secondary schools.
Emotions, Attitudes, and Values: Expand students’ knowledge, improve their practical application abilities and information literacy, encourage students to use information technology to solve problems in life. Cultivate students’ computer thinking, independent inquiry, and group cooperation abilities. Enhance children’s hands-on skills. Further deepen understanding of robot working principles and basic applications of open-source hardware. Improve information literacy and innovation abilities. |
||||||
|
Key Points |
Understand the basic components and working principles of robots. |
||||||
|
Difficult Points |
Understand common control development platforms and programming environments for educational robots in primary and secondary schools. |
|
Teaching Process |
|||
|
Teaching Steps |
Teacher Activities |
Student Activities |
Design Intent |
|
Teaching Design
Teaching Design
Teaching Design
|
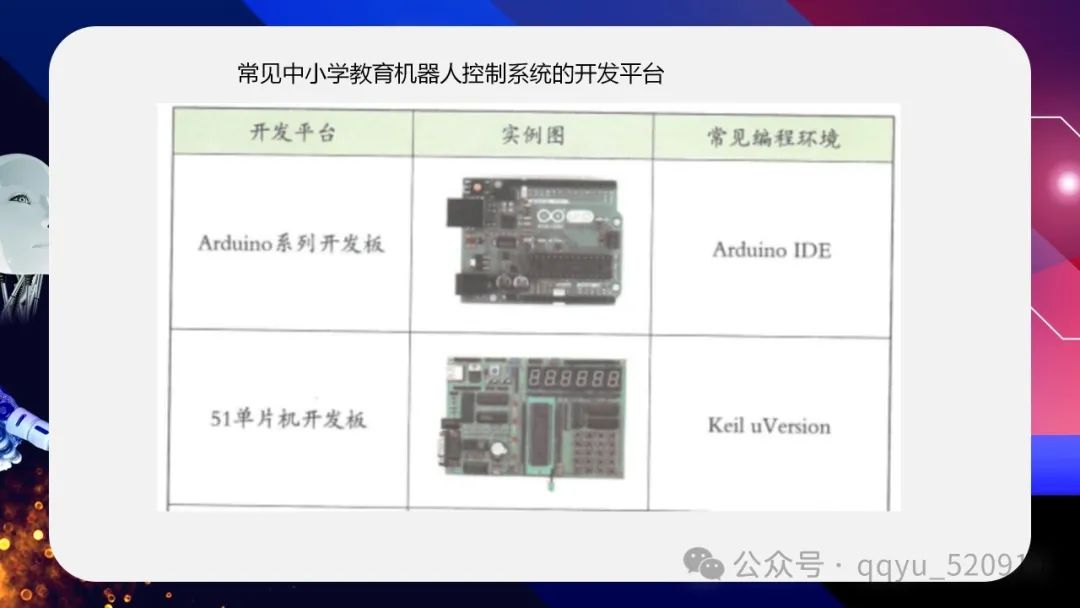
1. Unit Introduction With the continuous development of technology, robots have integrated into our work and life, becoming effective assistants for humans. To adapt to the development of the times and enhance information literacy, let’s embark on the learning journey of robots. Through this unit’s study, we will understand the basic knowledge of robots, master the Mixly programming tool and Arduino UNO development board’s basic applications, and understand the general process of designing and making educational robots. 2. New Lesson Introduction At the beginning of the new semester, the school organizes students to visit the Science and Technology Museum. The “Future City” themed hall in the museum captures everyone’s attention, showcasing robots in scenarios of urban services, management, and production life. Robots are not unfamiliar to us; they are machines that achieve designated functions through their own power and self-control abilities, consisting of control, sensing, and mechanical components. Robots receive feedback information from the sensing part through the control part, directing the mechanical part to perform corresponding actions to achieve designated functions.. 3. New Knowledge Learning (1) Control Part of Robots Every robot has a control part, generally composed of a control system and a human-machine interaction system, akin to the human brain and nervous system, controlling and coordinating the sensing system and drive system. The control system consists of control chips and peripheral circuits. The controller receives information, processes it into instructions, and drives the robot to complete designated tasks and actions.. Currently, common development platforms for educational robot control systems in primary and secondary schools include Arduino series development boards, 51 single-chip development boards, etc. The human-machine interaction system is mainly realized through control programs. Common programming languages for educational robots in primary and secondary schools include C, Java, Python, and for convenience and speed in programming, graphical programming tools can also be used, allowing programming by dragging different functional graphical modules together like building blocks. Task 1: Please name the programming tools you know and their features. (2) Sensing Part of Robots The sensing part of robots generally consists of a perception system and a “robot-environment” interaction system, mainly to perceive their own state or obtain specific external information to provide data for the control part’s calculations and judgments. The perception system is composed of sensors sensitive to signals such as images, light, sound, pressure, and smell, akin to human sensory organs like eyes, ears, nose, and skin. Depending on the information sources collected, it can be divided into internal sensor modules and external sensor modules. In addition to autonomous operation, robots also need to connect and coordinate with devices in the external environment, such as multiple robots cooperating to complete a complex task. Therefore, robots also require a “robot-environment” interaction system. With the improvement of sensor precision and intelligence, the mobility, adaptability, and intelligence level of robots have also significantly increased, greatly enriching the service fields of robots. Task 2: Through various means, learn about the working principles of a sensor. (3) Mechanical Part of Robots Most robots’ “bodies” can move, but their “legs” can be wheels, tracks, or spirals; the “arms” are composed of one or more “joints”. These devices make up the mechanical system of the robot. The devices that drive the movement of the mechanical system are called drive devices, such as motors and cylinders, whose operation is akin to the contraction and relaxation of muscles in the human arm; the mechanical system and drive system together constitute the mechanical part of the robot. In addition to the above systems, with the development of robot technology, additional human-machine interaction devices have been added, such as touch screens for displaying information or interacting through human touch; the on/off state of light-emitting diodes indicates the robot’s operational status, etc. Task 3: Through various means, learn how the robot drive device transmits force to the motion device through various structures.. 4. Class Summary What have you gained today? What difficulties did you encounter? How did you solve them? What confusions do you still have? 5. Homework Assignment Preview the next lesson “Security Robot Scheme Design”. |
Understand
Watch
Understand
Learn
Watch
Communicate; Express
Understand
Think; Express
Learn
Share and Communicate
Express Communication
Preview the next lesson |
Understand the knowledge learned in this unit
Create interesting learning scenarios, which can better stimulate students’ interest;
Understand the components of robots
Learn about the control part of robots
Develop listening habits
Develop expression abilities
Understand the sensing part of robots
Develop thinking abilities Develop expression abilities
Understand the mechanical part of robots
Develop expression abilities Develop group cooperation abilities
Develop expression abilities
Develop independent learning abilities |
|
Board Writing |
Lesson1 Recognizing Robots Again 1. Control Part of Robots 2. Sensing Part of Robots 3. Mechanical Part of Robots |
▼

Click to read the original text to download the complete set of materials
Click to read the original text to download the complete set of materials