Python Comprehensive Analysis of Composite Data Types: From Basics to Practical Applications
Core Knowledge Points Overview
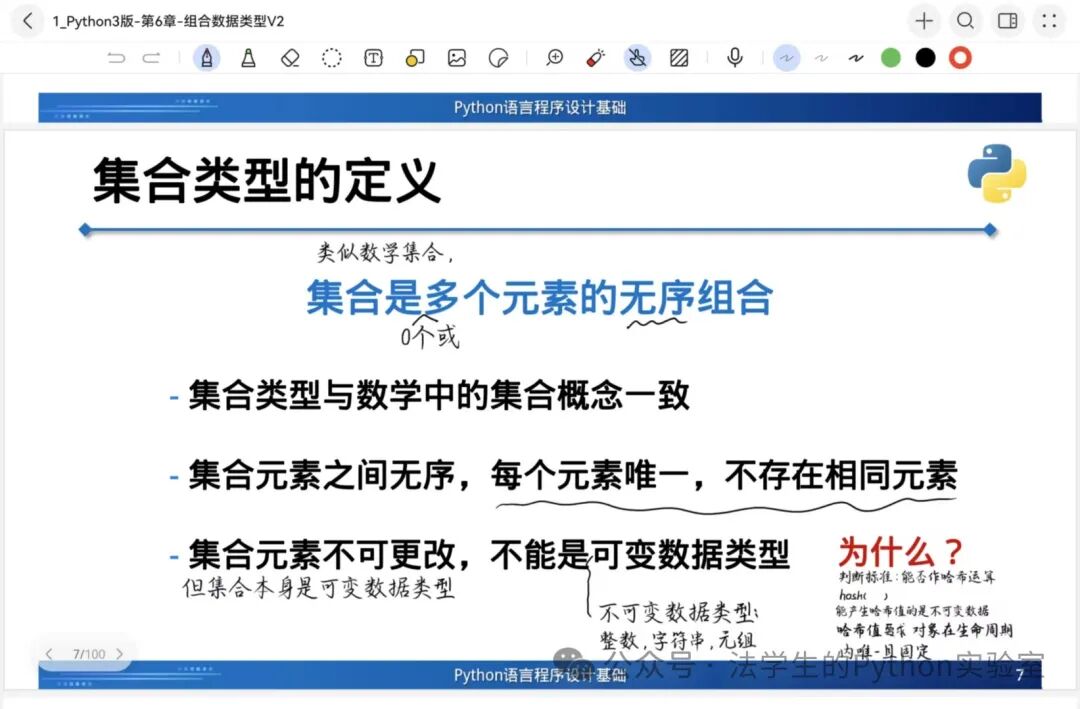
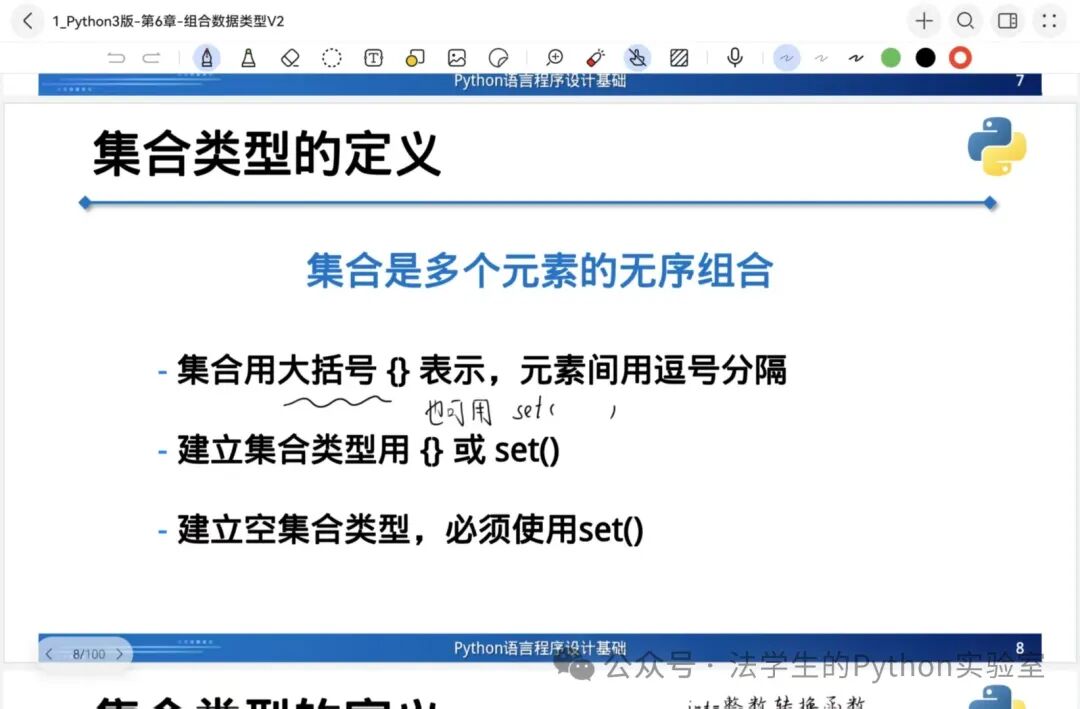
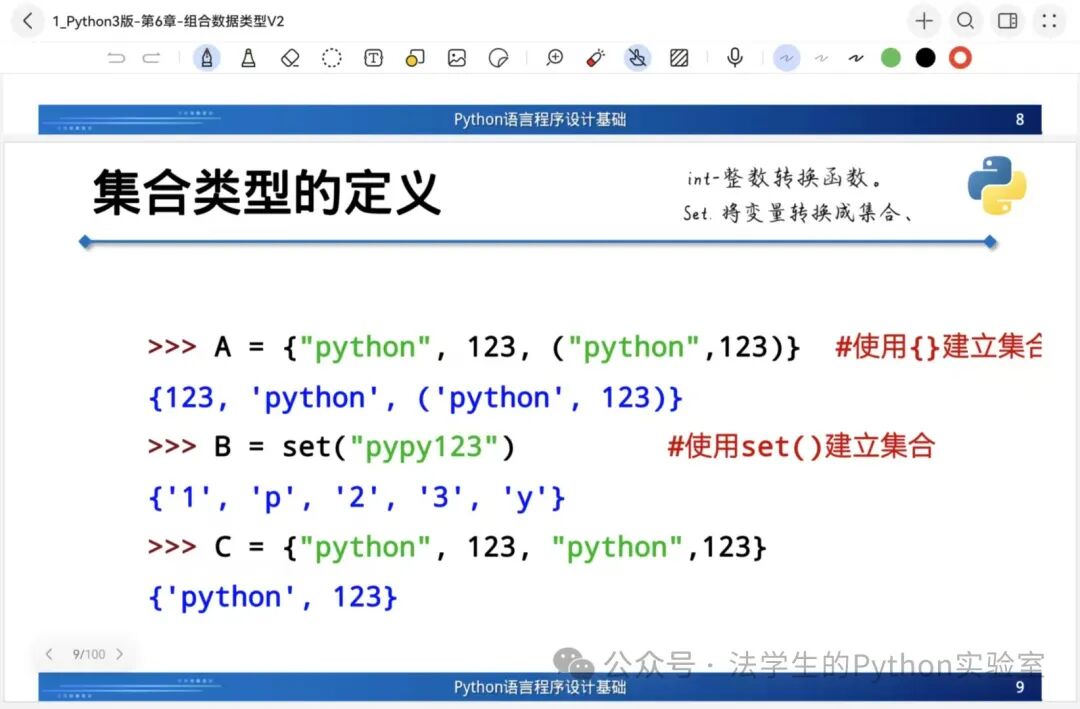
1️⃣ Set Type (Set)
Characteristics: Unordered, unique elements, immutable elements
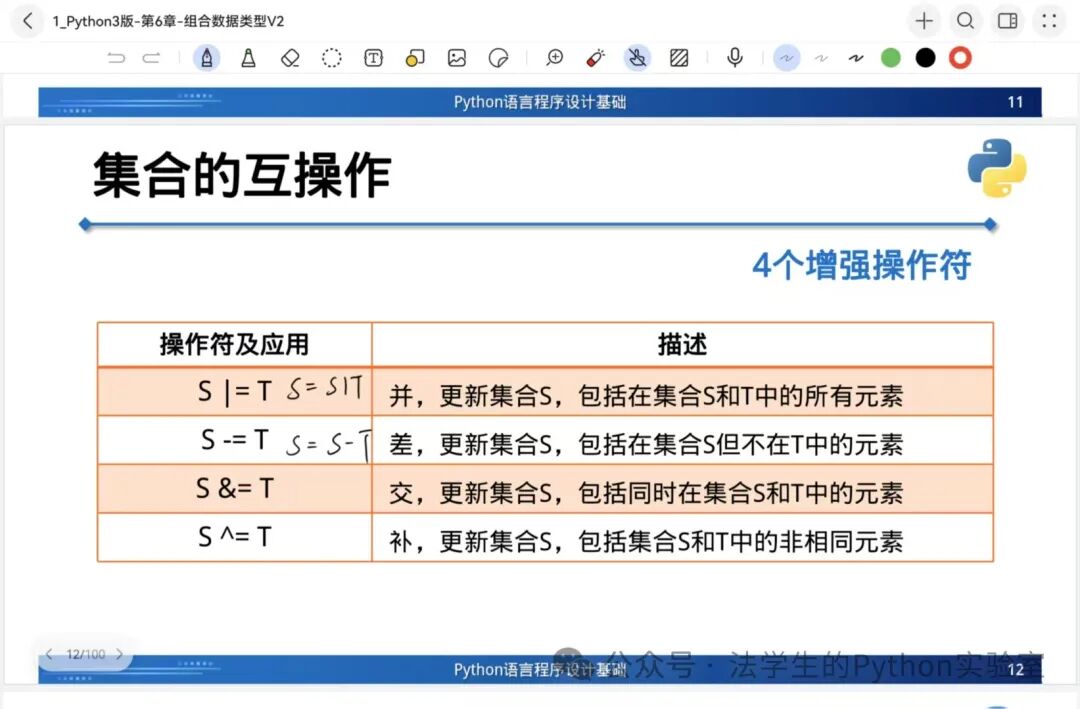
Operations: Union|, Intersection&, Difference–, Complement^
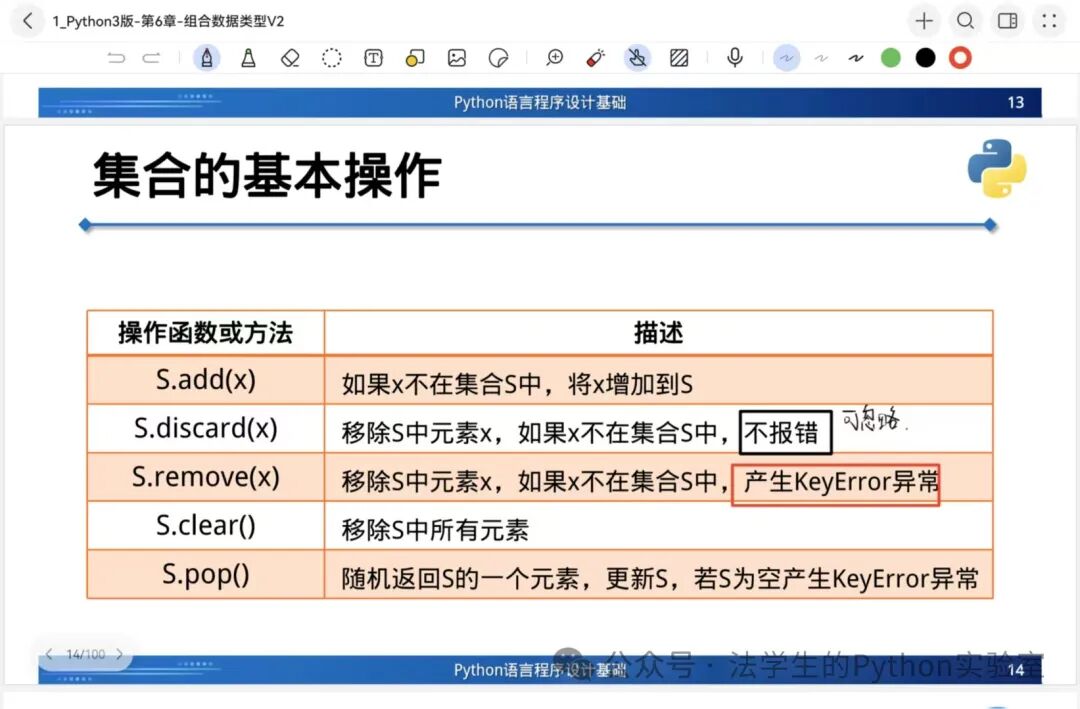
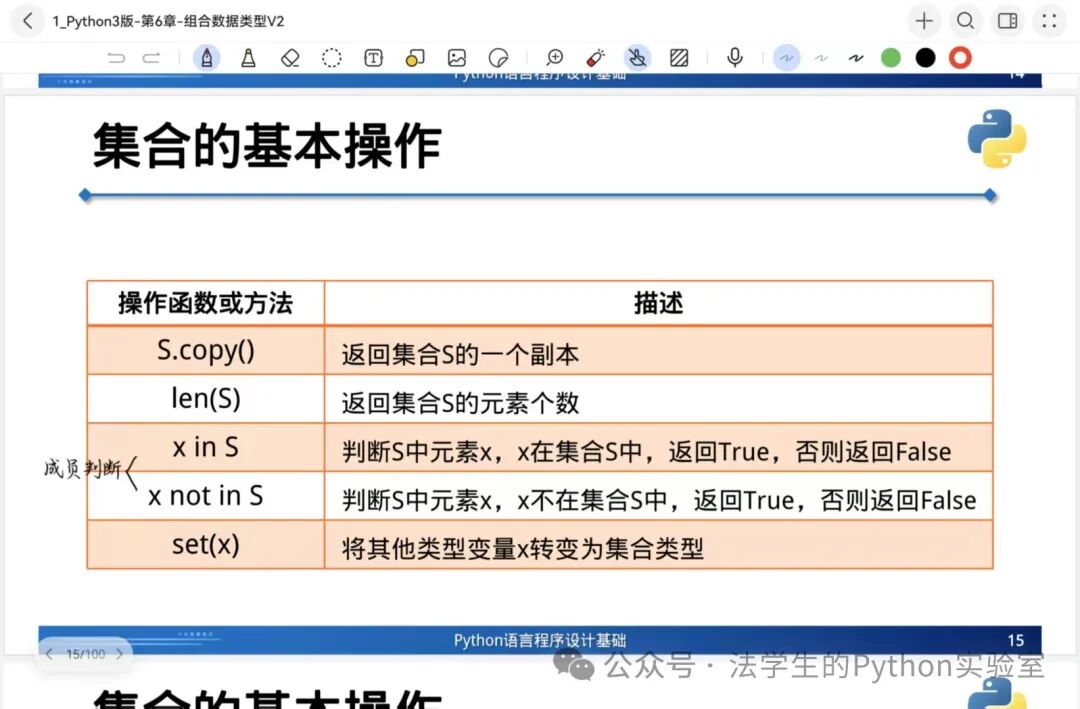
Applications: Membership testing, data deduplication
python
s={1,2,3}
s.add(4)#Add element
print(s-{2})#Output{1,3,4}
2️⃣ List Type (List)
Characteristics: Ordered, mutable elements, supports mixed types
Operations: Slicing[start:end], Add/Delete/Modify/Retrieve, Sorting
python
lst=[1,”Python”,True]
lst.append(“New Element“)
lst.sort()#Sort
3️⃣ Tuple Type (Tuple)
Characteristics: Ordered, immutable elements
Applications: Multiple return values from functions, data protection
python
t=(“Beijing“,2023)
x,y=t#Unpacking assignment
4️⃣ Dictionary Type (Dict)
Characteristics: Key-value pair mapping, keys must be unique
Operations: keys(), values(), get()
python
d={“name”:”Little Ming“,”age”:18}
print(d.get(“name”,”Unknown“))#Output“Little Ming“
Practical Case: Text Word Frequency Statistics
Character Appearance Statistics in “Romance of the Three Kingdoms”
1. Chinese Word Segmentation: Use the jieba library to segment the text
2. Word Frequency Statistics: Use a dictionary to record the number of appearances of characters
3. Result Optimization: Merge aliases (e.g., “Kongming” and “Zhuge Liang“)
python
import jieba
words=jieba.lcut(open(“threekingdoms.txt”).read())
counts={}
for word in words:
if len(word) > 1:
counts[word]=counts.get(word,0)+1
Output top 10 names
print(sorted(counts.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:10])